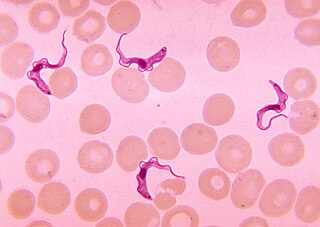
African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. It is caused by the species Trypanosoma brucei. Humans are infected by two types, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (TbG) and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (TbR). TbG causes over 98% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas.

Tsetse, sometimes spelled tzetze and also known as tik-tik flies, are large biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus Glossina, which are placed in their own family, Glossinidae. The tsetse are obligate parasites that live by feeding on the blood of vertebrate animals. Tsetse have been extensively studied because of their role in transmitting disease. They have a prominent economic impact in sub-Saharan Africa as the biological vectors of trypanosomes, which cause human sleeping sickness and animal trypanosomiasis. Tsetse are multivoltine and long-lived, typically producing about four broods per year, and up to 31 broods over their lifespans.

Hippoboscoidea is a superfamily of the Calyptratae. The flies in this superfamily are blood-feeding obligate parasites of their hosts. Four families are often placed here:

Trypanosomiasis or trypanosomosis is the name of several diseases in vertebrates caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosomes of the genus Trypanosoma. In humans this includes African trypanosomiasis and Chagas disease. A number of other diseases occur in other animals.

The sterile insect technique (SIT) is a method of biological insect control, whereby overwhelming numbers of sterile insects are released into the wild. The released insects are preferably male, as this is more cost-effective and the females may in some situations cause damage by laying eggs in the crop, or, in the case of mosquitoes, taking blood from humans. The sterile males compete with wild males to mate with the females. Females that mate with a sterile male produce no offspring, thus reducing the next generation's population. Sterile insects are not self-replicating and, therefore, cannot become established in the environment. Repeated release of sterile males over low population densities can further reduce and in cases of isolation eliminate pest populations, although cost-effective control with dense target populations is subjected to population suppression prior to the release of the sterile males.

Trypanosoma brucei is a species of parasitic kinetoplastid belonging to the genus Trypanosoma. This parasite is the cause of vector-borne diseases of vertebrate animals, including humans, carried by species of tsetse fly in sub-Saharan Africa. In humans T. brucei causes African trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness. In animals it causes animal trypanosomiasis, also called nagana in cattle and horses. T. brucei has traditionally been grouped into three subspecies: T. b. brucei, T. b. gambiense and T. b. rhodesiense. The first is a parasite of non-human vertebrates, while the latter two are known to be parasites of humans. Only rarely can the T. b. brucei infect a human.

Animal trypanosomiasis, also known as nagana and nagana pest, or sleeping sickness, is a disease of vertebrates. The disease is caused by trypanosomes of several species in the genus Trypanosoma such as Trypanosoma brucei. Trypanosoma vivax causes nagana mainly in West Africa, although it has spread to South America. The trypanosomes infect the blood of the vertebrate host, causing fever, weakness, and lethargy, which lead to weight loss and anemia; in some animals the disease is fatal unless treated. The trypanosomes are transmitted by tsetse flies.
Wigglesworthia glossinidia is a species of gram-negative bacteria which was isolated from the gut of the tsetse fly. W. glossinidia is a bacterial endosymbiont of the tsetse fly. Because of this relationship, Wigglesworthia has lost a large part of its genome and has one of the smallest known genomes of any living organism, consisting of a single chromosome of 700,000 bp and a plasmid of 5,200. Together with Buchnera aphidicola, Wigglesworthia has been the subject of genetic research into the minimal genome necessary for any living organism. Wigglesworthia also synthesizes key B-complex vitamins which the tsetse fly does not get from its diet of blood. Without the vitamins Wigglesworthia produces, the tsetse fly has greatly reduced growth and reproduction. Since the tsetse fly is the primary vector of Trypanosoma brucei, the pathogen that causes African trypanosomiasis, it has been suggested that W. glossinidia may one day be used to help control the spread of this disease.
The Tsetse was a small American nuclear bomb developed in the 1950s that was used as the primary in several US thermonuclear bombs and as a small stand-alone weapon of its own.
Paratransgenesis is a technique that attempts to eliminate a pathogen from vector populations through transgenesis of a symbiont of the vector. The goal of this technique is to control vector-borne diseases. The first step is to identify proteins that prevent the vector species from transmitting the pathogen. The genes coding for these proteins are then introduced into the symbiont, so that they can be expressed in the vector. The final step in the strategy is to introduce these transgenic symbionts into vector populations in the wild. One use of this technique is to prevent mortality for humans from insect-borne diseases. Preventive methods and current controls against vector-borne diseases depend on insecticides, even though some mosquito breeds may be resistant to them. There are other ways to fully eliminate them. “Paratransgenesis focuses on utilizing genetically modified insect symbionts to express molecules within the vector that are deleterious to pathogens they transmit.” The acidic bacteria Asaia symbionts are beneficial in the normal development of mosquito larvae; however, it is unknown what Asais symbionts do to adult mosquitoes.

Charles Francis Massy Swynnerton CMG was an English naturalist noted for his contributions to tsetse fly research.
G.D. Hale Carpenter MBE was a British entomologist and medical doctor. He worked first at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and in Uganda, on tse-tse flies and sleeping sickness. His main work in zoology was on mimicry in butterflies, an interest he developed in Uganda and Tanganyika. He succeeded E.B. Poulton as Hope Professor of Zoology at Oxford University from 1933 to 1948.
Hytrosaviridae is a family of double-stranded DNA viruses that infect insects. The name is derived from Hytrosa, sigla from the Greek Hypertrophia for 'hypertrophy' and 'sialoadenitis' for 'salivary gland inflammation.'
Sodalis is a genus of bacteria within the family Pectobacteriaceae. This genus contains several insect endosymbionts and also free-living group. It is studied due to its potential use in biological control of tsetse fly. Sodalis is important model for evolutionary biologists because of its nascent endosymbiosis with insect.
Albert Adeoye Ilemobade was one of Nigeria’s leading veterinary parasitologists who had a distinguished career in Nigeria and internationally.

La Mosca Tsé – Tsé or simply La Mosca is an Argentine rock fusion band, whose music consists of different genres like ska, cumbia, merengue, salsa and pop rock. The group was formed in 1995. Their songs reflect sporadic and eternal love while maintaining some mischief in their lyrics. While the current line-up was consolidated in March 1995, the history of the band goes back to the early 1990s with 'La Reggae & Roll Band', who did covers and some of their own songs in the town of Ramallo.
Glossina fuscipes is a riverine fly species in the genus Glossina, which are commonly known as tsetse flies. Typically found in sub-Saharan Africa but with a small Arabian range, G. fuscipes is a regional vector of African trypanosomiasis, commonly known as sleeping sickness, that causes significant rates of morbidity and mortality among humans and livestock. Consequently, the species is among several being targeted by researchers for population control as a method for controlling the disease.
Marcella Alsan is an infectious disease physician and an applied microeconomist studying health inequality. She is currently a Professor of Public Policy at the Harvard Kennedy School and was previously an Associate Professor of Medicine at Stanford University. She uses randomized evaluations and historical public health natural experiments to study how infectious disease, human capital, and economic outcomes interact. She has studied the effects of the Tuskegee Syphills Experiment on health care utilization and mortality among Black men. Alsan was awarded a MacArthur Fellowship in 2021.
Fatma Serap Aksoy is a Turkish–American medical entomologist.








