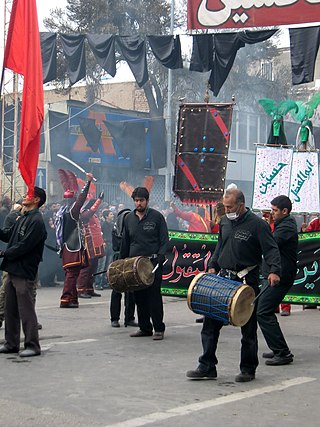The bass drum is a large drum that produces a note of low definite or indefinite pitch. The instrument is typically cylindrical, with the drum's diameter much greater than the drum's depth, with a struck head at both ends of the cylinder. The heads may be made of calfskin or plastic and there is normally a means of adjusting the tension either by threaded taps or by strings. Bass drums are built in a variety of sizes, but size does not dictate the volume produced by the drum. The pitch and the sound can vary much with different sizes, but the size is also chosen based on convenience and aesthetics. Bass drums are percussion instruments and vary in size and are used in several musical genres. Three major types of bass drums can be distinguished.

Dhol can refer to any one of a number of similar types of double-headed drum widely used, with regional variations, throughout the Indian subcontinent. Its range of distribution in Indian subcontinent primarily includes northern areas such as the Jammu, Himachal, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Kashmir, Sindh, Assam Valley, Uttarakhand, West Bengal, Odisha, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Konkan, Goa, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Bihar, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh. A related instrument is the dholak or dholki. Dhols are amongst other events used in Indian wedding ceremony processions such as Baraat or Varyatra.
The music of Sri Lanka has its roots in five primary influences: ancient folk rituals, Hindu religious traditions, Buddhist religious traditions, the legacy of European colonisation, and the commercial and historical influence of nearby Indian culture—specifically, Kollywood cinema and Bollywood cinema.

Santali, also known as Santal or Santhali, is the most widely-spoken language of the Munda subfamily of the Austroasiatic languages, related to Ho and Mundari, spoken mainly in the Indian states of Assam, Bihar, Jharkhand, Mizoram, Odisha, Tripura and West Bengal by Santals. It is a recognised regional language of India as per the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution. It is spoken by around 7.6 million people in India, Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal, making it the third most-spoken Austroasiatic language after Vietnamese and Khmer.

The Santal are an Austroasiatic-speaking Munda ethnic group of the Indian subcontinent. Santals are the largest tribe in the Jharkhand and West Bengal in terms of population and are also found in the states of Odisha, Bihar, Assam and Tripura. They are the largest ethnic minority in northern Bangladesh's Rajshahi Division and Rangpur Division. They have a sizeable population in Nepal. The Santals speak Santali, the most widely spoken Munda languages of Austroasiatic language family.
The tribes of Jharkhand consist of 32 scheduled tribes inhabiting the Jharkhand state in India. In 1872, only 18 tribes were counted among the scheduled tribes from which Banjara, Bhatudi, Chik Baraik, and Mahli were marked as semi-Hindu aboriginal and Kora as proletariat Hindu. In the 1931 census, including the above four semi-Hindu aboriginal and Kora, a proletariat Hindu, the number was raised to 26 from 18. They were Birajia, Godait, Karmali and Paharia, but Kisan was excluded from the list. In the 1941 census, Baga, Bedia and Lohra were included again taking Kisan in the annexure and the number came to 30 which prevailed till June 2003. Kanwar and Kol were added on 8 June 2003 in the annexure and the number of Schedule Tribes came to 32.

A kendang or gendang is a two-headed drum used by people from the Indonesian Archipelago. The kendang is one of the primary instruments used in the gamelan ensembles of Javanese, Sundanese, and Balinese music. It is also used in various Kulintang ensembles in Indonesia, Brunei, Malaysia, Singapore, and the Philippines. It is constructed in a variety of ways by different ethnic groups. It is related to the Indian double-headed mridangam drum.

A damaru is a small two-headed drum, used in Hinduism and Tibetan Buddhism. In Hinduism, the damaru is known as the instrument of the deity Lord Shiva, associated with Tantric traditions. It is said to be created by Lord Shiva to produce spiritual sounds by which the whole universe has been created and regulated. In Tibetan Buddhism, the damaru is used as an instrument in meditation practices.

The Santal people love music and dance. Like other ethnic groups of the Indian subcontinent, their culture has been influenced by mainstream Indian culture and by Western culture, but traditional music and dance still remain. Santal music differs from Hindustani classical music in significant ways. Onkar Prasad has done the most recent work on the music of the Santal but others preceded his work, notably W. G. Archer who collected and analyzed hundreds of Santal songs in the mid-twentieth century. The Santal traditionally accompany many of their dances with two drums: the Tamak' and the Tumdak'. The flute was considered the most important Santal traditional instrument and still evokes feelings of nostalgia for many Santal.

The tamak' is a stick-struck double-headed drum of the Santal people of the Indian subcontinent.
Ethnic minorities of Bangladesh or loosely termed indigenous people of Bangladesh are ethnic minorities in Chittagong Hill Tracts (southeastern), Sylhet Division (northeastern), Rajshahi Division (west), and Mymensingh Division (north-central) areas of the country. They are assumed as indigenous and the tribal races, total population of ethnic minorities in Bangladesh was estimated to be over 2 million in 2010. They are diverse ethnic communities including Tibeto-Burman, Austric and Dravidian people.

The urumi is a double-headed hourglass drum from the state of Tamil Nadu, South India. Two skin heads are attached to a single hollow, often intricately carved wooden shell. The preferred wood is jackwood, although other woods like rosewood may be used. Both left and right heads are usually made from cow hide that is stretched around a thin metal ring. The outer circumference of each head is perforated with approximately seven to eight holes. The two heads are held in tension by a continuous rope that is woven around the drum in a V-shape pattern. Additional small coils of string or metal are tied around each pair of ropes near the left head. These coils can be slide horizontally along the length of the drum, increasing or decreasing the tension between the heads as necessary. For example, during the monsoon season the drum heads will slacken so much that the instrument becomes unplayable. Using these coils drummers can easily rectify such problems.

Parai also known as Thappattai or Thappu is a traditional percussion instrument from South India. It is a traditional instrument used to make announcements and played during festivals, folk dances, weddings and functions. The instrument in played predominantly by Tamil people in Tamil Nadu and other regions with significant Tamil diaspora such as Sri Lanka. There are many variants of the instrument, but generally consists of a drum made of wood, open on one side and closed with a stretched animal hide on the other side along with two wooden sticks used for beating the drum.
The Loh Tarang is a melodic percussion instrument. It consists of a set of iron circular plates, of different sizes, held in a frame. Each plate is pitched to a note and they are struck with sticks on each hand. 'Tarang' literally means waves. Plates sound depends on the different size of plate and hand movement. Theory is based like Jal-Tarang.

Baha parab or Baa parab is a spring festival of Ho, Santhal,Munda and other tribes in India. "Baha" or "Baa" means flower. At Baha parab or Baa parab men, women and children are attired in traditional clothes, Offering Flowers to God Marang Buru and Jaher Ayo, and Madal tamak(drums) are beat and tribal woman and man dancing.

Timotheas Hembrom was an ordained Minister of the Church of North India and an Old Testament Scholar who taught at the Bishop's College, Kolkata, affiliated to the nation's first University, the Senate of Serampore College (University). As a Biblical scholar, Hembrom was a member of the scholarly Society for Biblical Studies in India, with members from the Protestant, Orthodox, Catholic and Charismatic Church societies. He researched on Santali creation traditions and his work was first published in 1996 was simultaneously reviewed in the Indian Journal of Theology and the Journal of Hindu-Christian Studies.

The Lungi Panchi Dance is a traditional dancing style of the Santal people of West Bengal. This dance is performed by both men and women and is accompanied by traditional music.
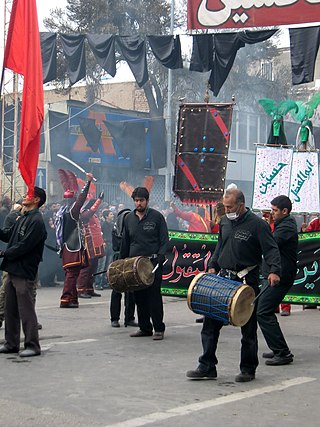
The Dammam is a large double-headed cylinder drum or frame drum played by Shias in Iraq and Iran in religious ceremonies. The dammām is usually struck with the left hand and a curved stick in the right hand, especially during passion plays in the mourning month of Muharram or to wake up the devotees early in the morning of Ramadan.