
Anubis, also known as Inpu, Inpw, Jnpw, or Anpu in Ancient Egyptian is the god of death, mummification, embalming, the afterlife, cemeteries, tombs, and the Underworld, in ancient Egyptian religion, usually depicted as a canine or a man with a canine head.

Pharaoh is the common title now used for the monarchs of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BCE, although the term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until Merneptah, c. 1210 BCE, during the Nineteenth dynasty, "king" being the term used most frequently until the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings used to have up to three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee, and the Two Ladies or Nebty name. The Golden Horus as well as the nomen and prenomen titles were added later.

The Egyptian language or Ancient Egyptian is an extinct Afro-Asiatic language that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest written languages, first being recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4000 years. Its classical form is known as Middle Egyptian, the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt which remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era it had diversified into the Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic remains in use as the liturgical language of the Coptic Church.

Thebes, known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile about 800 kilometers (500 mi) south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Thebes was the main city of the fourth Upper Egyptian nome and was the capital of Egypt for long periods during the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom eras. It was close to Nubia and the Eastern Desert, with its valuable mineral resources and trade routes. It was a cult center and the most venerated city during many periods of ancient Egyptian history. The site of Thebes includes areas on both the eastern bank of the Nile, where the temples of Karnak and Luxor stand and where the city was situated; and the western bank, where a necropolis of large private and royal cemeteries and funerary complexes can be found. In 1979, the ruins of ancient Thebes were classified by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.

Hathor was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god Ra, both of whom were connected with kingship, and thus she was the symbolic mother of their earthly representatives, the pharaohs. She was one of several goddesses who acted as the Eye of Ra, Ra's feminine counterpart, and in this form she had a vengeful aspect that protected him from his enemies. Her beneficent side represented music, dance, joy, love, sexuality, and maternal care, and she acted as the consort of several male deities and the mother of their sons. These two aspects of the goddess exemplified the Egyptian conception of femininity. Hathor crossed boundaries between worlds, helping deceased souls in the transition to the afterlife.

Saqqara, also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English, is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some 30 km (19 mi) south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around 7 by 1.5 km.
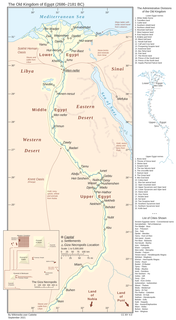
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley.

Luxor is a modern city in Upper (southern) Egypt which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of Thebes.

Mansoura is a city in Egypt, with a population of 960,423. It is the capital of the Dakahlia Governorate.

For administrative purposes, Egypt is divided into twenty-seven governorates. Egyptian governorates are the top tier of the country's jurisdiction hierarchy. A governorate is administered by a governor, who is appointed by the President of Egypt and serves at the president's discretion. Most governorates have a population density of less than one thousand per km2, while the three largest have a population density of less than three per km2.

Hurghada is a city in the Red Sea Governorate of Egypt. It is one of the country's main tourist centres located on the Red Sea coast.

The Giza pyramid complex, also called the Giza necropolis, is the site on the Giza Plateau in Greater Cairo, Egypt that includes the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure, along with their associated pyramid complexes and the Great Sphinx of Giza. All were built during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, between 2600 and 2500 BC. The site also includes several cemeteries and the remains of a workers' village.
Abusir is the name given to an Egyptian archaeological locality – specifically, an extensive necropolis of the Old Kingdom period, together with later additions – in the vicinity of the modern capital Cairo. The name is also that of a neighbouring village in the Nile Valley, whence the site takes its name. Abusir is located several kilometres north of Saqqara and, like it, served as one of the main elite cemeteries for the ancient Egyptian capital city of Memphis. Several other villages in northern and southern Egypt are named Abusir or Busiri. Abusir is one relatively small segment of the extensive "pyramid field" that extends from north of Giza to below Saqqara. The locality of Abusir took its turn as the focus of the prestigious western burial rites operating out of the then-capital of Memphis during the Old Kingdom 5th Dynasty. As an elite cemetery, neighbouring Giza had by then "filled up" with the massive pyramids and other monuments of the 4th Dynasty, leading the 5th Dynasty pharaohs to seek sites elsewhere for their own funerary monuments.

Kurna are various spelling for a group of three closely related villages located on the West Bank of the River Nile opposite the modern city of Luxor in Egypt near the Theban Hills.

Minya Governorate is one of the governorates of Upper Egypt. Its capital city, Minya, is located on the left bank of the Nile River.

Shibin El Qanater, previously known as Shaybin al-Qasr and Scenae Veteranorum is a region (markaz) in Egypt situated in the center of the Qalyubia Governorate. Its population was 423,783 at the 2006 Census and comprises 36 villages.
Amun was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. With the 11th Dynasty, Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu.
Saqultah is a small Upper Egyptian city near Akhmim. It is located on the east bank of the Nile, in the Sohag Governorate. The former name of the town is Saqiyat Qultah "saqiyas of Kollouthos ".

The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmosid Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose.

Balat, is a small town in the New Valley Governorate, Egypt. Its population was estimated at 3,700 people in 2006.
















