This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
Iris or IRIS may refer to:

A lathe is a machine that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry about that axis.

A shaper is a type of machine tool that uses linear relative motion between the workpiece and a single-point cutting tool to machine a linear toolpath. Its cut is analogous to that of a lathe, except that it is (archetypally) linear instead of helical.

A machinist is a person who machines using hand tools and machine tools to create or modify a part that is made of metal, plastics, or wood.
Plate may refer to a range of generally thin and flat objects upon where food or other items—including additional plates—can be placed.
A falcon is a bird of prey.

A tool bit is a non-rotary cutting tool used in metal lathes, shapers, and planers. Such cutters are also often referred to by the set-phrase name of single-point cutting tool, as distinguished from other cutting tools such as a saw or water jet cutter. The cutting edge is ground to suit a particular machining operation and may be resharpened or reshaped as needed. The ground tool bit is held rigidly by a tool holder while it is cutting.

A machine taper is a system for securing cutting tools or toolholders in the spindle of a machine tool or power tool. A male member of conical form fits into the female socket, which has a matching taper of equal angle.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.

A metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of applications, and a broad range of materials. In machining jargon, where the larger context is already understood, they are usually simply called lathes, or else referred to by more-specific subtype names. These rigid machine tools remove material from a rotating workpiece via the movements of various cutting tools, such as tool bits and drill bits.

The turret lathe is a form of metalworking lathe that is used for repetitive production of duplicate parts, which by the nature of their cutting process are usually interchangeable. It evolved from earlier lathes with the addition of the turret, which is an indexable toolholder that allows multiple cutting operations to be performed, each with a different cutting tool, in easy, rapid succession, with no need for the operator to perform set-up tasks in between, such as installing or uninstalling tools, nor to control the toolpath. The latter is due to the toolpath's being controlled by the machine, either in jig-like fashion, via the mechanical limits placed on it by the turret's slide and stops, or via electronically-directed servomechanisms for computer numerical control lathes.

James Hartness was an American inventor; a mechanical engineer; an entrepreneur who mentored other inventors to develop their machine tool products and create a thriving industrial center in southeastern Vermont; an amateur astronomer who fostered the construction of telescopes by amateurs in his town; an early aviator who built one of Vermont's first airports; and the 58th Governor of Vermont from 1921 to 1923.
I is the ninth letter of the Latin alphabet.
Kennametal is a supplier of tooling and industrial materials founded in 1938 by Philip M. McKenna in the Latrobe, Pennsylvania area.
Arms or ARMS may refer to:
Indexing in reference to motion is moving into a new position or location quickly and easily but also precisely. When indexing a machine part, its new location is known to within a few hundredths of a millimeter, or often even to within a few thousandths of a millimeter, despite the fact that no elaborate measuring or layout was needed to establish that location. In reference to multi-edge cutting inserts, indexing is the process of exposing a new cutting edge for use. Indexing is a necessary kind of motion in many areas of mechanical engineering and machining. A object that indexes, or can be indexed, is said to be indexable.
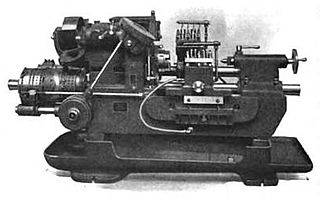
An automatic lathe is a lathe whose actions are controlled automatically. Although all electronically controlled (CNC) lathes are automatic, they are usually not called by that name, as explained under "General nomenclature". The first kinds of automatic lathes were mechanically automated ones, from the 1870s until the advent of NC and CNC in the 1950s and 1960s. CNC has not yet entirely displaced mechanically automated machines. The latter type of machine tool is no longer being newly built, but many existing examples remain in service.
A bar puller is a tool for automatically drawing in material on a CNC lathe. The machined part is cut off and new material has to be fed into the machine.
An Automatic tool changer or ATC is used in computerized numerical control (CNC) machine tools to improve the production and tool carrying capacity of the machine. ATC changes the tool very quickly, reducing the non-productive time. Generally, it is used to improve the capacity of the machine to work with a number of tools. It is also used to change worn out or broken tools. It is one more step towards complete automation.











