Related Research Articles

Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.

The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue, and an inner layer made of serous membrane. It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements.
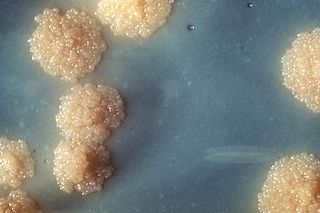
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, M. tuberculosis has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, M. tuberculosis can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen, or fluorescent stains such as auramine are used instead to identify M. tuberculosis with a microscope. The physiology of M. tuberculosis is highly aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the tuberculin skin test, acid-fast stain, culture, and polymerase chain reaction.

Constrictive pericarditis is a medical condition characterized by a thickened, fibrotic pericardium, limiting the heart's ability to function normally. In many cases, the condition continues to be difficult to diagnose and therefore benefits from a good understanding of the underlying cause.
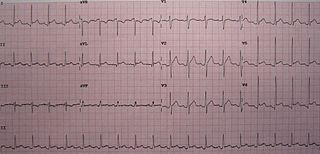
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe when sitting up and more severe when lying down or breathing deeply. Other symptoms of pericarditis can include fever, weakness, palpitations, and shortness of breath. The onset of symptoms can occasionally be gradual rather than sudden.
Dressler syndrome is a secondary form of pericarditis that occurs in the setting of injury to the heart or the pericardium. It consists of fever, pleuritic pain, pericarditis and/or a pericardial effusion.

Editions of the word board game Scrabble in different languages have differing letter distributions of the tiles, because the frequency of each letter of the alphabet is different for every language. As a general rule, the rarer the letter, the more points it is worth.

A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane. The two layers of the serous membrane enclose the pericardial cavity between them. This pericardial space contains a small amount of pericardial fluid. The fluid is normally 15-50 mL in volume. The pericardium, specifically the pericardial fluid provides lubrication, maintains the anatomic position of the heart in the chest, and also serves as a barrier to protect the heart from infection and inflammation in adjacent tissues and organs.
Points in basketball are used to keep track of the score in a game. Points can be accumulated by making field goals or free throws. If a player makes a field goal from within the three-point line, the player scores two points. If the player makes a field goal from beyond the three-point line, the player scores three points. The team that has recorded the most points at the end of a game is declared that game's winner.

Acute pericarditis is a type of pericarditis usually lasting less than 6 weeks. It is the most common condition affecting the pericardium.

James Edward Harden Jr. is an American professional basketball player for the Philadelphia 76ers of the National Basketball Association (NBA). Harden is regarded as one of the greatest scorers and shooting guards in NBA history.
Obstructive shock is one of the four types of shock, caused by a physical obstruction in the flow of blood. Obstruction can occur at the level of the great vessels or the heart itself. Causes include pulmonary embolism, cardiac tamponade, and tension pneumothorax. These are all life-threatening. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, weakness, or altered mental status. Low blood pressure and tachycardia are often seen in shock. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause.

ST elevation refers to a finding on an electrocardiogram wherein the trace in the ST segment is abnormally high above the baseline.
Tuberculous pericarditis is a form of pericarditis.

Uremic pericarditis is a form of pericarditis. It causes fibrinous pericarditis. The main cause of the disease is poorly understood.

Frédéric Chopin's disease and the reason for his premature death at age 39 were frequently debated for over 150 years. Although he was diagnosed with and treated for tuberculosis throughout his lifetime, a number of alternative diagnoses have been suggested since his death in 1849. A comprehensive review of the possible causes of Chopin's illness was published in 2011. A visual examination of Chopin's heart, for which permission was finally given in 2017, indicated the likely cause of death as pericarditis, caused by tuberculosis. This has been disputed by pathologists who say that a visual examination alone cannot confirm such a disease.

Damian Lamonte Ollie Lillard Sr. is an American professional basketball player for the Portland Trail Blazers of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He played college basketball for the Weber State Wildcats and earned third-team All-American honors in 2012. After being selected by Portland with the sixth overall pick in the 2012 NBA draft, Lillard was unanimously voted the NBA Rookie of the Year. Nicknamed Dame Time for his history of making big shots in the clutch, he has received six NBA All-Star and All-NBA Team selections, the only player in Trail Blazers franchise history to do so. In October 2021, Lillard was honored as one of the league's greatest players of all time by being named to the NBA 75th Anniversary Team. He also won a gold medal on the 2020 U.S. Olympic team in Tokyo.
Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic medical condition due to a mutation in the gene proteoglycan 4 (PRG4) – a mucin-type glycoprotein that acts as a lubricant for the cartilage surfaces. This gene is also known as lubricin.
References
- Reuter H, Burgess L, van Vuuren W, Doubell A (2006). "Diagnosing tuberculous pericarditis". Q J Med. 99 (12): 827–39. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcl123 . PMID 17121764.