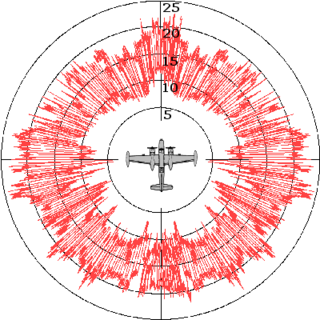
Radar cross-section (RCS), denoted σ, also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected.

An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased-array antenna, which is a computer-controlled antenna array in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antenna. In the AESA, each antenna element is connected to a small solid-state transmit/receive module (TRM) under the control of a computer, which performs the functions of a transmitter and/or receiver for the antenna. This contrasts with a passive electronically scanned array (PESA), in which all the antenna elements are connected to a single transmitter and/or receiver through phase shifters under the control of the computer. AESA's main use is in radar, and these are known as active phased-array radar (APAR).

A counter-battery radar or weapon tracking radar is a radar system that detects artillery projectiles fired by one or more guns, howitzers, mortars or rocket launchers and, from their trajectories, locates the position on the ground of the weapon that fired it. Such radars are a subclass of the wider class of target acquisition radars.

Over-the-horizon radar (OTH), sometimes called beyond the horizon radar (BTH), is a type of radar system with the ability to detect targets at very long ranges, typically hundreds to thousands of kilometres, beyond the radar horizon, which is the distance limit for ordinary radar. Several OTH radar systems were deployed starting in the 1950s and 1960s as part of early-warning radar systems, but airborne early warning systems have generally replaced these. OTH radars have recently been making a comeback, as the need for accurate long-range tracking has become less important since the ending of the Cold War, and less-expensive ground-based radars are once again being considered for roles such as maritime reconnaissance and drug enforcement.
Passive radar is a class of radar systems that detect and track objects by processing reflections from non-cooperative sources of illumination in the environment, such as commercial broadcast and communications signals. It is a specific case of bistatic radar – passive bistatic radar (PBR) – which is a broad type also including the exploitation of cooperative and non-cooperative radar transmitters.

The Type 364 radar was developed by the Yangzhou Marine Electronic Instruments Research Institute (扬州船用电子仪器研究所) / No. 723 Research Institute. It is typically enclosed in a dome on new PLA-N's frigates and destroyers.
The Type 347G "Rice Bowl" I-band fire-control radar is found on Chinese Navy ships, in conjunction with the Type 76A dual-37mm automatic AAA gun. Typically, the system includes 2 Type 347G fire-control radar with optical director, and 4 Type 76A guns. They're used on the Luda, Luhu, Luhai, Jiangwei class surface warships, as well as the Houjian, Houxin, and Haiging class patrol boats.
The JY-9 Radar is a mobile S band low altitude search radar intended for use in air defense, gap filling, airport surveillance, and coastal defense. It is designed for effective detection of targets at low altitude in both ECM and natural clutter environments. The general designer of the JY-9 is academician of Chinese Academy of Sciences Mr. Wu Manqing, the head of 38th Research Institute, who is also the general designer of the JY-8 Radar and of the radar systems for the KJ-2000 and KJ-200 early warning aircraft.

The Saab Giraffe Radar is a family of land and naval two- or three-dimensional G/H-band passive electronically scanned array radar-based surveillance and air defense command and control systems. It is tailored for operations with medium- and Short Range Air Defense (SHORAD) missile or gun systems, or for use as gap-fillers in a larger air defense system.

The AN/FPS-17 was a ground-based fixed-beam radar system that was installed at three locations worldwide, including Pirinçlik Air Base in south-eastern Turkey, Laredo, Texas and Shemya Island, Alaska.
The PS-05/A is a pulse-doppler radar currently used by the JAS 39 Gripen fighter aircraft. It weighs 156 kg and was developed by Ericsson in collaboration with GEC-Marconi, sharing some technology with the latter's Blue Vixen radar for the Sea Harrier.
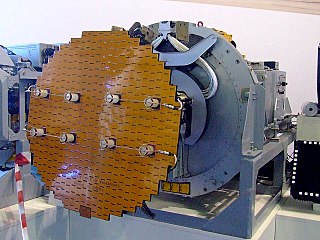
The Zhuk are a family of Russian all-weather multimode airborne radars developed by NIIR Phazotron for multi-role combat aircraft such as the MiG-29. The PESA versions were also known as Sokol.
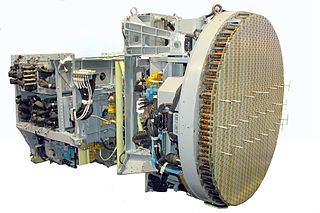
The Bars (Leopard) is a family of Russian all-weather multimode airborne radars developed by the Tikhomirov Scientific Research Institute of Instrument Design for multi-role combat aircraft such as the Su-27, Su-30 and the MiG-29.

The Russian BRLS-8B "Zaslon" (Barrier) is an all-weather multimode airborne radar developed between 1975 and 1980 by the Tikhomirov Scientific Research Institute of Instrument Design as part of the weapons control system of the MiG-31 supersonic interceptor. The NATO reporting name for the radar is Flash Dance with the designations "SBI-16", "RP-31", "N007" and "S-800" also being associated with the radar.

The KLJ-7, also referred to as the Type 1478, is an X band airborne fire-control radar (FCR) developed by Nanjing Research Institute of Electronic Technology (NRIET), also known as the China Electronics Technology Company's (CETC's) No. 14 Research Institute. In December 2010, Pakistan Air Force's Air Chief Marshal Rao Qamar Suleman announced that KLJ-7 radar will be built at Pakistan Aeronautical Complex (PAC), in Kamra, north of Islamabad.

The P-18 or 1RL131Terek is a 2D VHF radar developed and operated by the former Soviet Union.
German Luftwaffe and Kriegsmarine Radar Equipment during World War II, relied on an increasingly diverse array of communications, IFF and RDF equipment for its function. Most of this equipment received the generic prefix FuG, meaning "radio equipment". During the war, Germany renumbered their radars. From using the year of introduction as their number, they moved to a different numbering scheme.

The AN/TPY-2 Surveillance Transportable Radar, also called the Forward Based X-Band Transportable (FBX-T) is a long-range, very high-altitude active digital antenna array X band surveillance radar designed to add a tier to existing missile and air defence systems. It has a range of up to 3,000 km, depending on target/mode. Made by Raytheon, it is the primary radar for the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) missile system, but also cues the AN/MPQ-53 radar of the MIM-104 Patriot system. Patriot PAC-3 is a lower-altitude missile and air defense system than THAAD.
ESR-32B is an Egyptian bi-dimensional L band for air and sea surveillance and early-warning radar. It was unveiled in EDEX 2018 by Benha Electronic Industries Company.













