USS Mizar may refer to the following ships of the United States Navy:
- USS Mizar (AF-12), was a cargo ship during World War II
- USNS Mizar (T-AGOR-11), was an oceanographic research ship and submarine rescue ship
USS Mizar may refer to the following ships of the United States Navy:
Arizona has been the name of three ships of the United States Navy and will be the name of a future submarine.
USS Cole is the name of two ships of the United States Navy;
Four ships of the United States Navy have borne the name USS Maine, named for the 23rd state:
USS Nautilus may refer to:

USS Thresher (SSN-593) was the lead boat of her class of nuclear-powered attack submarines in the United States Navy. She was the U.S. Navy's second submarine to be named after the thresher shark.
USS Liberty may refer to:
USS Franklin may refer to:
Alcor may refer to:

A reefer ship is a refrigerated cargo ship typically used to transport perishable cargo, which require temperature-controlled handling, such as fruits, meat, vegetables, dairy products, and similar items.

USNS Mizar (MA-48/T-AGOR-11/T-AK-272) was a vessel of the United States Navy. She was named after the star Mizar.
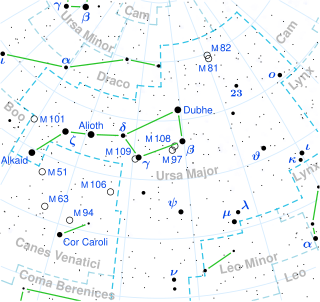
Mizar is a second-magnitude star in the handle of the Big Dipper asterism in the constellation of Ursa Major. It has the Bayer designation ζ Ursae Majoris. It forms a well-known naked eye double star with the fainter star Alcor, and is itself a quadruple star system. The whole system lies about 83 light-years away from the Sun, as measured by the Hipparcos astrometry satellite, and is part of the Ursa Major Moving Group.
USS Percival may refer to:
Mizar is a bright star in the constellation Ursa Major.

A turbo-electric transmission uses electric generators to convert the mechanical energy of a turbine into electric energy and electric motors to convert it back into mechanical energy to power the driveshafts.
USS Plover is a name the United States Navy has used more than once in naming a vessel:
USS Condor is a name used more than once by the U.S. Navy:

USS Mizar (AF-12) was the United Fruit Company fruit, mail and passenger liner Quirigua that served as a United States Navy Mizar-class stores ship in World War II.
USS Antigua may refer to more than one United States Navy ship:

USS Hunting (E-AG-398) was built as the LSM-1-class landing ship medium LSM-398 at the Charleston Navy Yard and launched in the first week of 1945. After service in the Atlantic as a landing ship the vessel was converted in 1953 to a sonar research vessel for the Naval Research Laboratory. Hunting was unique among Navy research vessels of the time in having a center well through which large towed "fish" could be transported and lowered to operating depths. The work contributed to sonar improvements and understanding ocean acoustics.

The Type R ship is a United States Maritime Administration (MARAD) designation for World War II refrigerated cargo ship, also called a reefer ship. The R type ship was used in World War II, Korean War, Vietnam War and the Cold War. Type R ships were used to transport perishable commodities which require temperature-controlled transportation, such as fruit, meat, fish, vegetables, dairy products and other foods. The US Maritime Commission ordered 41 new refrigerated ships for the US Navy. Because of the difficulty of building refrigerated ships only two were delivered in 1944, and just 26 were delivered in 1945 and the remainder in 1946–48. The 41 R type ships were built in four groups. Two of design types were modified type C1 ships and two were modified type C2 ships. The United Fruit Company operated many of the R type ships in World War II. The type R2-S-BV1 became the US Navy Alstede-class stores ship and the type R1-M-AV3 became the US Navy Adria-class stores ship.