USS Tonawanda is a name used more than once by the United States Navy:

The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most capable navy in the world and it has been estimated that in terms of tonnage of its active battle fleet alone, it is larger than the next 13 navies combined, which includes 11 U.S. allies or partner nations. with the highest combined battle fleet tonnage and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, and two new carriers under construction. With 319,421 personnel on active duty and 99,616 in the Ready Reserve, the Navy is the third largest of the service branches. It has 282 deployable combat vessels and more than 3,700 operational aircraft as of March 2018, making it the second-largest air force in the world, after the United States Air Force.
- USS Tonawanda (1864), a monitor operating during the American Civil War.
- USS Tonawanda (AN-89), a World War II net laying ship.

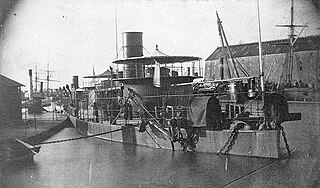
USS Tonawanda was a double-turreted coastal monitor built by the Philadelphia Navy Yard, launched on 6 May 1864; and commissioned on 12 October 1865, Commander William Ronckendorff in command.

The American Civil War was a war fought in the United States from 1861 to 1865, between the North and the South. The Civil War is the most studied and written about episode in U.S. history. Primarily as a result of the long-standing controversy over the enslavement of black people, war broke out in April 1861 when secessionist forces attacked Fort Sumter in South Carolina shortly after Abraham Lincoln had been inaugurated as the President of the United States. The loyalists of the Union in the North proclaimed support for the Constitution. They faced secessionists of the Confederate States in the South, who advocated for states' rights to uphold slavery.
USS Tonawanda (YN-115/AN-89) was a Cohoes-class net laying ship which was assigned to protect U.S. Navy ships and harbors during World War II by deploying and maintaining anti-submarine nets. Her World War II career was short due to the war coming to an end, but, post-war, she was reactivated in 1952 and served the Navy until 1959 when she was put into reserve and eventually transferred to Haiti as Jean-Jacques Dessalines.