This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
At least seven United States Navy ships have been named Alabama, after the southern state of Alabama.
The second USS Florida was a sidewheel steamer in the United States Navy.
USS St. Mary's or USS St. Marys has been the name of more than one United States Navy ship, and may refer to:

The second USS Memphis was a 7-gun screw steamer, built by William Denny and Brothers, Dumbarton, Scotland in 1861, which briefly served as a Confederate blockade runner before being captured and taken into the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Mount Vernon has been the name of five U.S. Navy ships:
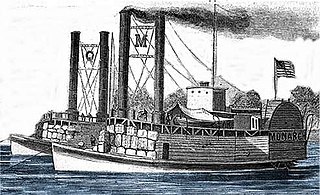
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.
USS Stettin was a 600-ton iron screw steamship, was built at Sunderland, England, in 1861 and later served as a gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Bienville was a 1,558 long tons (1,583 t) (burden) wooden side-wheel paddle steamer acquired by the Union Navy early in the American Civil War. She was armed with heavy guns and assigned to the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.
USS Whitehall (1850) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was assigned blockade duty; however, her condition was not always considered seaworthy, and she was plagued with condition problems.
USS Underwriter (1852) was a 341-ton sidewheel steamer that was purchased for military use by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Connecticut (1861) was a large steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. Her primary task was to prevent ships from penetrating the Union blockade of Southern ports.
USS Honduras (1861) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Patroon was a screw steamer acquired by the United States Navy during the American Civil War. The Union Navy used her to patrol off the coast of the Confederate States of America to enforce the Union blockade.

USS O. M. Pettit (1857) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy as a tugboat to service Union Navy ships blockading ports of the Confederate States of America.
USS Massachusetts (1860) was a large steamer acquired by the U.S. Navy prior to the American Civil War.
The second USS Tigress was a steamer chartered by the United States Navy at the beginning of the American Civil War. She was commissioned in 1861 and served in the Union Navy until lost in 1862.

Franklin Jeremiah Drake was a Rear Admiral in the United States Navy. He fought in the American Civil War and the United States expedition to Korea.
Salvador Pirates was the name given to the band of Confederate Navy sailors that attempted to seize a Panama Railroad coastal steamer on the high seas. Their intent was then to arm her and attack the Pacific Mail steamers and the American whalers in the North Pacific.

Gustavus Hall Scott was an officer in the United States Navy who served in the Second Seminole War and the American Civil War. He rose to the rank of rear admiral and late in his career was commander-in-chief of the North Atlantic Squadron.





