
Sun Microsystems, Inc. was an American company that sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services and created the Java programming language, the Solaris operating system, ZFS, the Network File System (NFS), and SPARC. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualized computing. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California, on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center.

Silicon Graphics, Inc. was an American high-performance computing manufacturer, producing computer hardware and software. Founded in Mountain View, California in November 1981 by Jim Clark, its initial market was 3D graphics computer workstations, but its products, strategies and market positions developed significantly over time.

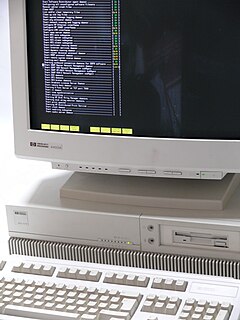
HP-UX is Hewlett Packard Enterprise's proprietary implementation of the Unix operating system, based on Unix System V and first released in 1984. Recent versions support the HP 9000 series of computer systems, based on the PA-RISC instruction set architecture, and HP Integrity systems, based on Intel's Itanium architecture.

Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. It superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993. In 2010, after the Sun acquisition by Oracle, it was renamed Oracle Solaris.
DNIX was a Unix-like real-time operating system from the Swedish company Dataindustrier AB (DIAB). A version called ABCenix was also developed for the ABC 1600 computer from Luxor.

A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term workstation has also been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT and IBM which opened the door for the 3D graphics animation revolution of the late 1990s.
Unix System V is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. System V Release 4 (SVR4) was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as Unix System Unification, which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV.

HP 9000 is a line of workstation and server computer systems produced by the Hewlett-Packard Company (HP). The native operating system for almost all HP 9000 systems is HP-UX, which is based on UNIX System V. The HP 9000 brand was introduced in 1984 to encompass several existing technical workstation models previously launched in the early 1980s.
The VP2000 was the second series of vector supercomputers from Fujitsu. Announced in December 1988, they replaced Fujitsu's earlier FACOM VP Model E Series. The VP2000 was succeeded in 1995 by the VPP300, a massively parallel supercomputer with up to 256 vector processors.
SPARC64 is a microprocessor developed by HAL Computer Systems and fabricated by Fujitsu. It implements the SPARC V9 instruction set architecture (ISA), the first microprocessor to do so. SPARC64 was HAL's first microprocessor and was the first in the SPARC64 brand. It operates at 101 and 118 MHz. The SPARC64 was used exclusively by Fujitsu in their systems; the first systems, the Fujitsu HALstation Model 330 and Model 350 workstations, were formally announced in September 1995 and were introduced in October 1995, two years late. It was succeeded by the SPARC64 II in 1996.

Fujitsu Siemens Computers GmbH was a Japanese and German vendor of information technology. The company was founded in 1999 as a 50/50 joint venture between Fujitsu Limited of Japan and Siemens of Germany. On April 1, 2009, the company became Fujitsu Technology Solutions as a result of Fujitsu buying out Siemens' share of the company.
A logical partition (LPAR) is a subset of a computer's hardware resources, virtualized as a separate computer. In effect, a physical machine can be partitioned into multiple logical partitions, each hosting a separate instance of an operating system.
Sun-4 is a series of Unix workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in 1987. The original Sun-4 series were VMEbus-based systems similar to the earlier Sun-3 series, but employing microprocessors based on Sun's own SPARC V7 RISC architecture in place of the 68k family processors of previous Sun models.

The Sony NEWS is a series of Unix workstations sold during the late 1980s and 1990s. The first NEWS machine was the NWS-800, which originally appeared in Japan in January 1987 and was conceived as a desktop replacement for the VAX series of minicomputers.
The SPARC Enterprise series is a range of UNIX server computers based on the SPARC V9 architecture. It was co-developed by Sun Microsystems and Fujitsu, and introduced in 2007. They were marketed and sold by Sun Microsystems, Fujitsu, and Fujitsu Siemens Computers under the common brand of "SPARC Enterprise", superseding Sun's Sun Fire and Fujitsu's PRIMEPOWER server product lines.
UTS is a discontinued implementation of the UNIX operating system for IBM mainframe computers. Amdahl created the first versions of UTS, and released it in May 1981, with UTS Global acquiring rights to the product in 2002. UTS Global has since gone out of business.
The SPARC64 V (Zeus) is a SPARC V9 microprocessor designed by Fujitsu. The SPARC64 V was the basis for a series of successive processors designed for servers, and later, supercomputers.

Fujitsu Technology Solutions is a European information technology vendor with a presence in markets in Europe, the Middle East, Africa, as well as India. A subsidiary of Fujitsu Limited headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, FTS was founded in 2009 after Fujitsu bought out Siemens' 50% share of Fujitsu Siemens Computers.
PFU Limited is a Japanese information technology company. The company was formed by the merger of Panafacom and USAC Electronic Industrial in 1987.










