Ubiquinone reductase may refer to:
- NADH dehydrogenase, an enzyme
- NADH:ubiquinone reductase (non-electrogenic), an enzyme
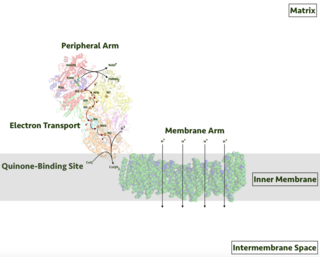
NADH dehydrogenase (EC 1.6.99.3, cytochrome c reductase, type 1 dehydrogenase, beta-NADH dehydrogenase dinucleotide, diaphorase, dihydrocodehydrogenase I dehydrogenase, dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase, diphosphopyridine diaphorase, DPNH diaphorase, NADH diaphorase, NADH hydrogenase, NADH oxidoreductase, NADH-menadione oxidoreductase, reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide diaphorase) is an enzyme with systematic name NADH:acceptor oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
NADH:ubiquinone reductase (non-electrogenic) (EC 1.6.5.9, NDH-2, ubiquinone reductase, coenzyme Q reductase, dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-ubiquinone reductase, NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase, NADH-coenzyme Q reductase, NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase, NADH-CoQ reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
| This set index page lists enzyme articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |