
Computer data storage, often called storage, is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The Ultra DMA interface was the fastest method used to transfer data through the ATA controller, usually between the computer and an ATA device. UDMA succeeded Single/Multiword DMA as the interface of choice between ATA devices and the computer. There are 8 different UDMA modes, ranging from 0 to 6 for ATA, each with its own timing.
Direct memory access (DMA) is a feature of computer systems that allows certain hardware subsystems to access main system memory, independent of the central processing unit (CPU).
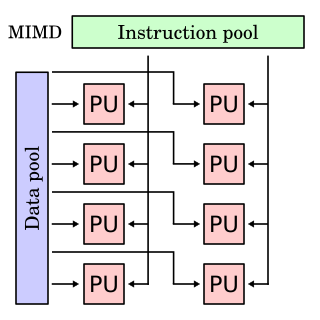
In computing, MIMD is a technique employed to achieve parallelism. Machines using MIMD have a number of processors that function asynchronously and independently. At any time, different processors may be executing different instructions on different pieces of data. MIMD architectures may be used in a number of application areas such as computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing, simulation, modeling, and as communication switches. MIMD machines can be of either shared memory or distributed memory categories. These classifications are based on how MIMD processors access memory. Shared memory machines may be of the bus-based, extended, or hierarchical type. Distributed memory machines may have hypercube or mesh interconnection schemes.

The Power Macintosh G3 is a series of personal computers designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from November 1997 to August 1999. It represented Apple's first step towards eliminating redundancy and complexity in the product line by replacing eight Power Macintosh models with three: Desktop and Mini Tower models for professional and home use, and an All-In-One model for education. The introduction of the Desktop and Mini Tower models coincided with Apple starting to sell build-to-order Macs directly from its web site in an online store, which was unusual for the time as Dell was the only major computer manufacturer doing this. Apple's move to build-to-order sales of the Power Macintosh G3 also coincided with the acquisition of Power Computing Corporation, which had been providing telephone sales of Macintosh clones for more than two years.

CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994.
Programmed input/output (PIO) is a method of transferring data between the CPU and a peripheral, such as a network adapter or an ATA storage device. Each data item transfer is initiated by an instruction in the program, involving the CPU for every transaction. In contrast, in Direct Memory Access (DMA) operations, the CPU is not involved in the data transfer.

Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented.
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. Most CPUs have different independent caches, including instruction and data caches, where the data cache is usually organized as a hierarchy of more cache levels.

Democratic Union of the Algerian Manifesto was a political party in colonial Algeria founded in 1946 by Ferhat Abbas, who was then elected deputy. The UDMA reflected the change in Abbas' point of view. He considered that after the failure of the implementation of significant reform, the assimilation of the Algerian people into France as French citizens was no longer a viable alternative. He then advocated an autonomous state within the French framework; no longer would Algeria be considered a province of France; rather it would be an autonomous state within the French federalist system. UDMA won the elections to the Constituent Assembly in June 1946, by gaining 11 of the 13 seats devoted to the colonized population of Algeria. After 1948, fraud in the elections prevented nationalist parties from any significant success in the elections. Nevertheless, the UDMA took part in the electoral campaign. After the creation of the FLN and the beginning of the War for Independence, negotiations took place to discuss the UDMA's merging with the FLN. In the end, it was decided that the UDMA, like the Algerian Communist Party, would dissolve and that its members would individually join the FLN. Ferhat Abbas and Ahmed Francis, two of the most prominent party leaders, fled to Cairo and joined the FLN leadership.

The SiS 630 and SiS 730 are a family of highly integrated chipsets for Intel and AMD respectively. At the time of release they were unique in that they not only provided VGA, Audio, LAN, IDE and USB functionality on board, but were also in a single-chip solution. At the time of release (1999) most chipsets were composed of physically separate north-bridge and south-bridge chips. Only later have single-chip solutions become popular in the mainstream, with chipsets such as the nVidia nForce4.

In computing, a physical address, is a memory address that is represented in the form of a binary number on the address bus circuitry in order to enable the data bus to access a particular storage cell of main memory, or a register of memory mapped I/O device.

In computing, an input–output memory management unit (IOMMU) is a memory management unit (MMU) that connects a direct-memory-access–capable (DMA-capable) I/O bus to the main memory. Like a traditional MMU, which translates CPU-visible virtual addresses to physical addresses, the IOMMU maps device-visible virtual addresses to physical addresses. Some units also provide memory protection from faulty or malicious devices.

A memory card reader is a device for accessing the data on a memory card such as a CompactFlash (CF), Secure Digital (SD) or MultiMediaCard (MMC). Most card readers also offer write capability, and together with the card, this can function as a pen drive.

Udma is a census town in Kasaragod district in the Indian state of Kerala.

Random-access memory is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory. In contrast, with other direct-access data storage media such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWs and the older magnetic tapes and drum memory, the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement.
In computing, input/output or I/O is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, possibly a human or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to "perform I/O" is to perform an input or output operation.

The Nikon D4 is a 16.2-megapixel professional-grade full frame (35mm) digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) announced by Nikon Corporation on 6 January 2012. It succeeds the Nikon D3S and introduces a number of improvements including a 16.2 megapixel sensor, improved auto-focus and metering sensors and the ability to shoot at an extended ISO speed of 204,800. The camera was released in February 2012 at a recommended retail price of $5999.95. It is the first camera to use the new XQD memory cards.

In computer science, shared memory is memory that may be simultaneously accessed by multiple programs with an intent to provide communication among them or avoid redundant copies. Shared memory is an efficient means of passing data between programs. Depending on context, programs may run on a single processor or on multiple separate processors.

Udma State assembly constituency is one of the 140 state legislative assembly constituencies in Kerala state in southern India. It is also one of the 7 state legislative assembly constituencies included in the Kasaragod Lok Sabha constituency.













