In the United States, Social Security is the commonly used term for the federal Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) program and is administered by the Social Security Administration. The original Social Security Act was signed into law by Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1935, and the current version of the Act, as amended, encompasses several social welfare and social insurance programs.

The Federal Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund and Federal Disability Insurance Trust Fund are trust funds that provide for payment of Social Security benefits administered by the United States Social Security Administration.
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment or unemployment compensation, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a compulsory governmental insurance system, not taxes on individual citizens. Depending on the jurisdiction and the status of the person, those sums may be small, covering only basic needs, or may compensate the lost time proportionally to the previous earned salary.
The Fair Deal was an ambitious set of proposals put forward by U.S. President Harry S. Truman to Congress in his January 1949 State of the Union address. More generally the term characterizes the entire domestic agenda of the Truman administration, from 1945 to 1953. It offered new proposals to continue New Deal liberalism, but with the Conservative Coalition controlling Congress, only a few of its major initiatives became law and then only if they had considerable GOP support. As Richard Neustadt concludes, the most important proposals were aid to education, universal health insurance, the Fair Employment Practices Commission, and repeal of the Taft–Hartley Act. They were all debated at length, then voted down. Nevertheless, enough smaller and less controversial items passed that liberals could claim some success.

Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees, and are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their staff. Payroll taxes generally fall into two categories: deductions from an employee's wages, and taxes paid by the employer based on the employee's wages.
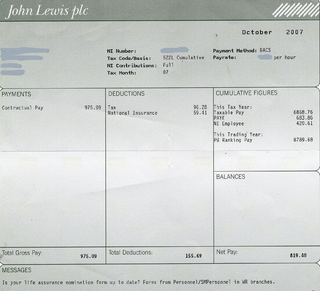
A company's payroll is the list of employees of that company that are entitled to receive pay and the amounts that each should receive. Along with the amounts that each employee should receive for time worked or tasks performed, payroll can also refer to a company's records of payments that were previously made to employees, including salaries and wages, bonuses, and withheld taxes, or the company's department that calculates and pays out these amounts. One way that payroll can be handled is in-house. This means that a company handles all aspects of the payroll process on its own, including timesheets, calculating wages, producing pay checks, sending the ACH, or Automated Clearing House, for any direct deposits, and remitting any tax payments necessary. Payroll can also be outsourced to a full-service payroll processing company. When a company chooses to outsource their payroll, timesheets, wage calculations, creating pay checks, direct deposits, and tax payments can be handled all, or in part, by the payroll company.

The Federal Insurance Contributions Act is a United States federal payroll contribution directed towards both employees and employers to fund Social Security and Medicare—federal programs that provide benefits for retirees, people with disabilities, and children of deceased workers.
Universal life insurance is a type of cash value life insurance, sold primarily in the United States. Under the terms of the policy, the excess of premium payments above the current cost of insurance is credited to the cash value of the policy, which is credited each month with interest. The policy is debited each month by a cost of insurance (COI) charge as well as any other policy charges and fees drawn from the cash value, even if no premium payment is made that month. Interest credited to the account is determined by the insurer but has a contractual minimum rate. When an earnings rate is pegged to a financial index such as a stock, bond or other interest rate index, the policy is an "Indexed universal life" contract. Such policies offer the advantage of guaranteed level premiums throughout the insured's lifetime at a substantially lower premium cost than an equivalent whole life policy at first. The cost of insurance always increases, as is found on the cost index table. That not only allows for easy comparison of costs between carriers but also works well in irrevocable life insurance trusts (ILITs) since cash is of no consequence.

The U.S. Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) is an independent agency in the executive branch of the United States government created in 1935 to administer a social insurance program providing retirement benefits to the country's railroad workers.
The Federal Unemployment Tax Act is a United States federal law that imposes a federal employer tax used to help fund state workforce agencies. Employers report this tax by filing an annual Form 940 with the Internal Revenue Service. In some cases, the employer is required to pay the tax in installments during the tax year.
A VA loan is a mortgage loan in the United States guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). The program is for American veterans, military members currently serving in the U.S. military, reservists and select surviving spouses and can be used to purchase single-family homes, condominiums, multi-unit properties, manufactured homes and new construction. The VA does not originate loans, but sets the rules for who may qualify, issues minimum guidelines and requirements under which mortgages may be offered and financially guarantees loans that qualify under the program.
Stock appreciation rights (SAR) is a method for companies to give their management or employees a bonus if the company performs well financially. Such a method is called a 'plan'. SARs resemble employee stock options in that the holder/employee benefits from an increase in stock price. They differ from options in that the holder/employee does not have to purchase anything to receive the proceeds. They are not required to pay the (options') exercise price, but just receive the amount of the increase in cash or stock.

The Oklahoma Employment Security Commission (OESC) is an independent agency of the state of Oklahoma responsible for providing employment services to the citizens of Oklahoma. The Commission is part of a national network of employment service agencies and is funded by money from the United States Department of Labor. The Commission is also responsible for administering the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 on behalf of the state.
Internal Revenue Service (IRS) tax forms are forms used for taxpayers and tax-exempt organizations to report financial information to the Internal Revenue Service of the United States. They are used to report income, calculate taxes to be paid to the federal government, and disclose other information as required by the Internal Revenue Code (IRC). There are over 800 various forms and schedules. Other tax forms in the United States are filed with state and local governments.
The Benefit Financing Model (BFM), also known as Unemployment Insurance Benefit Financing Model (UIBFM), is an actuarial forecasting model designed to help analysts project the condition of Unemployment Trust Fund (UTF) a number of years into the future, and quickly assess the financial impact of various economic scenarios and possible law changes. This model was constructed to be highly comprehensive yet flexible enough to adapt to individual state needs. It is considered a useful tool in unemployment insurance (UI) benefit financing and trust fund forecasting.

A limited form of the Social Security program began as a measure to implement "social insurance" during the Great Depression of the 1930s, when poverty rates among senior citizens exceeded 50 percent.
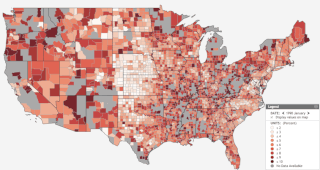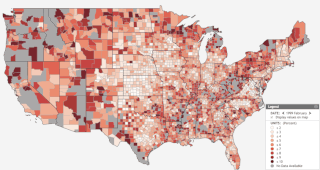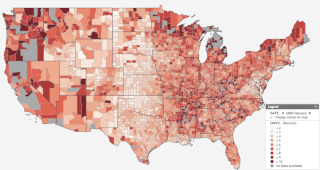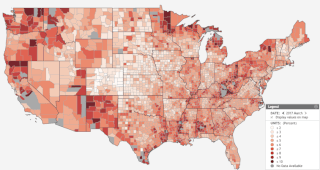
Unemployment benefits in the United States refer to social insurance programs administered by state governments which replace a portion of wages for individuals during unemployment. The first unemployment insurance program in the U.S. was created in Wisconsin in 1932, and federal-state programs were created nationwide by the Social Security Act of 1935. The constitutionality of the program was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1937.

The Families First Coronavirus Response Act is an Act of Congress meant to respond to the economic impacts of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The act will provide funding for free coronavirus testing, 14-day paid leave for American workers affected by the pandemic, and increased funding for food stamps.

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, also known as the CARES Act, is a $2.2 trillion economic stimulus bill passed by the 116th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump on March 27, 2020 in response to the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The spending primarily includes $300 billion in one-time cash payments to individual Americans, $260 billion in increased unemployment benefits, the creation of the Paycheck Protection Program that provides forgivable loans to small businesses with an initial $350 billion in funding, $500 billion in aid for large corporations, and $339.8 billion to state and local governments.
The Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) is a $669-billion business loan program established by the 2020 US Federal government Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act to help certain businesses, self-employed workers, sole proprietors, certain nonprofit organizations, and tribal businesses continue paying their workers.