Related Research Articles

The United Nations General Assembly is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its 79th session, its powers, composition, functions, and procedures are set out in Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter.

The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm in June 1972. Its mandate is to provide leadership, deliver science and develop solutions on a wide range of issues, including climate change, the management of marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and green economic development. The organization also develops international environmental agreements; publishes and promotes environmental science and helps national governments achieve environmental targets.

The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that assists countries in economic and industrial development. It is headquartered at the UN Office in Vienna, Austria, with a permanent presence in over 60 countries. As of April 2019, UNIDO comprises 170 member states, which together set the organization's policies, programs, and principles through the biannual General Conference.
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.
Issues relating to the State of Israel and aspects of the Arab–Israeli conflict, and more recently the Iran–Israel conflict, occupy repeated annual debate times, resolutions and resources at the United Nations. Since its founding in 1948, the United Nations Security Council, has adopted 79 resolutions directly related to the Arab–Israeli conflict as of January 2010.

War can heavily damage the environment, and warring countries often place operational requirements ahead of environmental concerns for the duration of the war. Some international law is designed to limit this environmental harm.
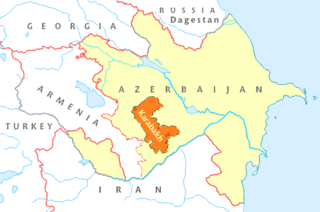
United Nations Security Council resolution 874, adopted unanimously on 14 October 1993, reaffirmed sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Azerbaijani Republic and of all other States in the region, called for the preservation of the ceasefire, cessation of hostilities and withdrawal of forces from recently occupied districts of the Republic of Azerbaijan, and reaffirmed resolutions 822 (1993) and 853 (1993). The Council expressed its concern at "...the conflict in and around the Nagorny Karabakh region of the Azerbaijani Republic, and of the tensions between the Republic of Armenia and the Azerbaijani Republic...", and called upon the parties to observe the ceasefire agreed with by the government of Russia and OSCE Minsk Group.
The Stockholm Declaration of 1972, or the Declaration of the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, is the first United Nations declaration on the global environment. It consists of 26 principles and led to the creation of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), which laid the foundation for future global environmental governance. The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm, Sweden, from June 5–16 in 1972. The 1972 United Nations Conference on the Human Environment signifies the first international effort to place environmental issues at the forefront of global concerns. The Conference sought to recognize the finite nature of Earth's resources and human impacts on the environment. It represented the beginning of a global dialogue on the link between economic growth, the pollution of the environment, and the well-being of humanity. The resulting Stockholm Declaration urged its partnering nations to reduce air, land, and water degradation by integrating science and technology in their development plans. It also called nations to create regulations on wildlife protection, environmental conservation, and population control. While the reception of the ideas in the Declaration generally stayed positive, it received wide criticisms on its practical implementation, especially from developing nations.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution 62/243, titled "The Situation in the Occupied Territories of Azerbaijan", is a resolution of the United Nations General Assembly about the situation in Nagorno-Karabakh, which was adopted on March 14, 2008 at the 62nd session of the General Assembly. It became the seventh United Nations document concerning Nagorno-Karabakh and the third and last United Nations General Assembly document on it.
Organisation of the Islamic Conference Resolution 10/11, titled "The aggression of the Republic of Armenia against the Republic of Azerbaijan", is an Organisation of the Islamic Conference Resolution on Nagorno-Karabakh conflict adopted by its member states on March 13–14, 2008 during the OIC summit in Dakar, Senegal. The resolution, titled "Aggression by the Republic of Armenia against the Republic of Azerbaijan," aims to express concern over Armenia's aggression against Azerbaijan and to provide comprehensive support for the territorial integrity of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The Dakar conference is considered a "successful step" towards supporting Azerbaijan's just cause. It was during this session that the new Charter of the Islamic Cooperation Organization was adopted, and in the section on the purposes and objectives of this international organization, it was stipulated that the member states support the right of states under occupation to restore their territorial integrity.
Organisation of the Islamic Conference of Foreign Ministers Resolution 10/37, titled "The aggression of the Republic of Armenia against the Republic of Azerbaijan", is a set of three Organisation of the Islamic Conference resolutions on Nagorno-Karabakh conflict adopted at the 37th annual session of Foreign Ministers of OIC member states on May 18–20, 2010 held in Dushanbe, Tajikistan. The session was attended by 80 delegations from member states, observer states and international organizations.
Council of Europe Parliamentary Assembly (PACE) Resolution 1416 (2005), titled “The conflict over the Nagorno-Karabakh region dealt with by the OSCE Minsk Conference”, is a resolution of PACE about the situation on occupied territories currently in the possession of Azerbaijan by Armenian military forces, adopted by PACE on January 25, 2005.
Soil governance refers to the policies, strategies, and the processes of decision-making employed by nation states and local governments regarding the use of soil. Globally, governance of the soil has been limited to an agricultural perspective due to increased food insecurity from the most populated regions on earth. The Global Soil Partnership, GSP, was initiated by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and its members with the hope to improve governance of the limited soil resources of the planet in order to guarantee healthy and productive soils for a food-secure world, as well as support other essential ecosystem services.

In the United Nations, the Post-2015 Development Agenda was a set of talks and discussions that led to the creation of the 2016 Sustainable Development Goals. This replaced the 2015 Millennium Development Goals.
Malaysia became the 82nd member of the United Nations on 17 September 1957. Malaysia has held a rotational non-permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council for four terms, and has participated in over 30 United Nations peacekeeping missions since October 1960.
Azerbaijan has been a member in the United Nations since March 2, 1992, after the UN General Assembly admitted Azerbaijan at its 46th session. The Permanent Mission of the Republic of Azerbaijan was opened in New York City in May 1992. On October 29, 1991, soon after gaining independence from the Soviet Union, Azerbaijan applied to the UN General Assembly for joining the organization. Azerbaijan was elected as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council for the term of 2012–2013.
In 1991, Azerbaijan joined the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and started to build relations with the organization. As a result, the ambassador of Azerbaijan to Saudi Arabia was given a mandate of permanent representative of Azerbaijan to the General Secretariat of the OIC in May 1994.
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 48/144 of 20 December 1993 is a resolution in which the General Assembly expressed its concern at the ongoing degradation of the humanitarian situation in Azerbaijan because of the displacement of considerable number of citizens due to Nagorno Karabakh conflict and supporting "emergency international assistance to refugees and displaced persons in Azerbaijan". The resolution is titled “48/114. Emergency international assistance to refugees and displaced persons in Azerbaijan”. It became the fifth United Nations document concerning Nagorno-Karabakh and the first United Nations General Assembly document on humanitarian aid to those affected by this conflict. This resolution was the first international document affirming the number of refugees and displaced persons in Azerbaijan exceeded one million. The document does not make any specific reference to previous UN resolutions on the ongoing conflict, but "its relevant resolutions regarding humanitarian assistance to refugees and displaced persons". The resolution was adopted by consensus without voting.

The Republic of Kazakhstan became a member of the United Nations on March 2, 1992. Kazakhstan was elected to serve on the UN Security Council for the 2017–2018 term. UN Secretary-General António Guterres in remarks to the UNSC recognized Kazakhstan's work to rid the world of weapons of mass destruction and global non-proliferation efforts.

The International Day of Clean Air for blue skies is designated by the United Nations General Assembly on 7 September to strengthen international cooperation in improving air quality and reducing air pollution. The designation was made through the Assembly resolution 74/212, and adopted at that session's 52nd plenary meeting on 19 December 2019.
References
- ↑ "United Nations Official Document". www.un.org. Retrieved 2017-12-25.
- ↑ "GENERAL ASSEMBLY DECIDES TO CONTINUE CONSIDERATION OF SECRETARY-GENERAL'S REPORT ON PREVENTING ARMED CONFLICT, AT UPCOMING SESSIONS | Meetings Coverage and Press Releases". www.un.org. Retrieved 2017-12-25.
- ↑ "United Nations Official Document". www.un.org. Retrieved 2017-12-25.
- ↑ "United Nations Official Document". www.un.org. Retrieved 2017-12-25.