
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. For the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all of the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude. The treaty entered into force in 1961 and currently has 54 parties. The treaty sets aside Antarctica as a scientific preserve, establishes freedom of scientific investigation, and bans military activity on the continent. The treaty was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat headquarters has been located in Buenos Aires, Argentina.

The United Nations member states are the 193 sovereign states that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the UN General Assembly. The UN is the world's largest intergovernmental organization.

The Charter of the United Nations is the foundational treaty of the United Nations, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the Secretariat, the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Trusteeship Council.

The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966, and in force from 23 March 1976 in accordance with Article 49 of the covenant. Article 49 allowed that the covenant would enter into force three months after the date of the deposit of the thirty-fifth instrument of ratification or accession. The covenant commits its parties to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. As of September 2019, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification.

The United Nations Secretariat is one of the six major organs of the United Nations, with the others being (a) the General Assembly; (b) the Security Council; (c) the Economic and Social Council; (d) the defunct Trusteeship Council; and (e) the International Court of Justice. The Secretariat is the United Nations' executive arm. The Secretariat has an important role in setting the agenda for the deliberative and decision-making bodies of the UN, and the implementation of the decision of these bodies. The Secretary-General, who is appointed by the General Assembly, is the head of the secretariat.
A crime against peace, in international law, is "planning, preparation, initiation, or waging of wars of aggression, or a war in violation of international treaties, agreements or assurances, or participation in a common plan or conspiracy for the accomplishment of any of the foregoing". This definition of crimes against peace was first incorporated into the Nuremberg Principles and later included in the United Nations Charter. This definition would play a part in defining aggression as a crime against peace. It can also refer to the core international crimes set out in Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, which adopted crimes negotiated previously in the Draft code of crimes against the peace and security of mankind.

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is an international agreement regulating treaties between states. Known as the "treaty on treaties", it establishes comprehensive rules, procedures, and guidelines for how treaties are defined, drafted, amended, interpreted, and generally operated. An international treaty is a written agreement between international law subjects reflecting their consent to the creation, alteration, or termination of their rights and obligations. The VCLT is considered a codification of customary international law and state practice concerning treaties.
A secret treaty is a treaty in which the contracting state parties have agreed to conceal the treaty's existence or substance from other states and the public. Such a commitment to keep the agreement secret may be contained in the instrument itself or in a separate agreement.
A war of aggression, sometimes also war of conquest, is a military conflict waged without the justification of self-defense, usually for territorial gain and subjugation.
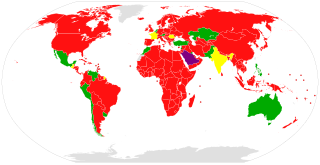
The Agreement Governing the Activities of States on the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies, better known as the Moon Treaty or Moon Agreement, is a multilateral treaty that turns jurisdiction of all celestial bodies over to the participant countries. Thus, all activities would conform to international law, including the United Nations Charter.
The International law bearing on issues of Arab–Israeli conflict, which became a major arena of regional and international tension since the birth of Israel in 1948, resulting in several disputes between a number of Arab countries and Israel.

A United Nations resolution is a formal text adopted by a United Nations (UN) body. Although any UN body can issue resolutions, in practice most resolutions are issued by the Security Council or the General Assembly.

The United Nations Office of Legal Affairs is a United Nations office currently administered by Under-Secretary-General for Legal Affairs and Legal Counsel of the United Nations Miguel de Serpa Soares.
The Energy Charter Treaty (ECT) is an international agreement that establishes a multilateral framework for cross-border cooperation in the energy industry. The treaty covers all aspects of commercial energy activities including trade, transit, investments and energy efficiency. The treaty contains dispute resolution procedures both for States Parties to the Treaty and as between States and the investors of other States, who have made investments in the territory of the former.
A crime of aggression is a specific type of crime where a person plans, initiates, or executes an act of aggression using state military force that violates the Charter of the United Nations. The act is judged as a violation based on its character, gravity, and scale.
A treaty series is an officially published collection of treaties and other international agreements.
Chapter XVI of the United Nations Charter contains miscellaneous provisions prohibiting secret treaties, establishing the UN Charter as supreme over any other treaties, and providing for privileges and immunities of UN officials and representatives.

Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter contains the Charter's provisions dealing with the UN General Assembly, specifically its composition, functions, powers, voting, and procedures.

The Manila Accord was signed on 31 July 1963 by the Federation of Malaya, the Republic of Indonesia and the Republic of the Philippines, after a meeting from 7 to 11 June 1963 in Manila.

The Inter-American Convention on the Prevention, Punishment, and Eradication of Violence against Women, better known as the Belém do Pará Convention, is an international human rights instrument adopted by the Inter-American Commission of Women (CIM) of the Organization of American States at a conference held in Belém do Pará, Brazil on 9 June 1994. It is the first legally binding international treaty that criminalises all forms of violence against women, especially sexual violence. On 26 October 2004, the Follow-Up Mechanism (MESECVI) agency was established to ensure the State parties' compliance with the Convention.










