Latin is an Italic language, originally spoken in ancient Rome and its empire.

Hindustani, also known as Hindi-Urdu and historically known as Hindavi, Dehlavi and Rekhta, is the lingua franca of Northern India and Pakistan. It is an Indo-Aryan language, deriving its base primarily from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi, a Western Hindi language. The colloquial language became an expression of Indian national unity during the Indian Independence movement but after the Partition of British India in 1947, it was split into two different standardised registers, Modern Standard Hindi and Modern Standard Urdu. Hindustani continues to be spoken as the common language of the people of the northern Indian subcontinent, which is reflected in the Hindustani vocabulary of Bollywood films and songs.

Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of writing from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription, for representing the spoken word, and combinations of both. Transcription methods can be subdivided into phonemic transcription, which records the phonemes or units of semantic meaning in speech, and more strict phonetic transcription, which records speech sounds with precision.
Pakistan is home to many dozens of languages spoken as first languages. Five languages have more than 10 million speakers each in Pakistan – Punjabi, Pashto, Sindhi, Saraiki and Urdu. Almost all of Pakistan's languages belong to the Indo-Iranian group of the Indo-European language family.

Balti is a Tibetic language spoken in the Baltistan region of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan, the Nubra Valley of Leh district and in the Kargil district of Ladakh, India. It is quite different from Standard Tibetan. Many sounds of Old Tibetan that were lost in Standard Tibetan are retained in the Balti language. It also has a simple pitch accent system only in multi-syllabic words while Standard Tibetan has a complex and distinct pitch system that includes tone contour.
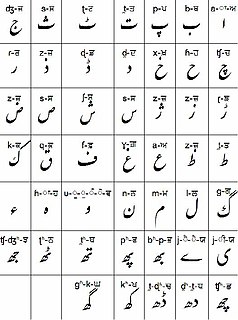
Shahmukhi is a Perso-Arabic alphabet used by Muslims in Punjab to write the Punjabi language. It is generally written in the Nastaʿlīq calligraphic hand, which is also used for Urdu. Perso-Arabic is one of two scripts used for Punjabi, the other being Gurmukhi.
UR, Ur or ur may refer to:
3 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
It is thought that the Arabic alphabet is a derivative of the Nabataean variation of the region, which descended from the Phoenician alphabet, which, among others, gave rise to the Hebrew alphabet and the Greek alphabet.
E is the fifth letter of the Latin alphabet.
An alphabet is a standard set of letters used to write one or more languages.

The Arabic script is a writing system used for writing Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa, such as Persian, Kurdish, Azerbaijani, Sindhi, Balochi, Pashto, Lurish, Urdu and Mandinka. Until the 16th century, it was also used to write some texts in Spanish. Additionally, prior to the language reform in 1928, it was the writing system of Turkish. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by the number of countries using it and the third by the number of users, after Latin and Chinese characters.

The Urdu alphabet is the right-to-left alphabet used for the Urdu language. It is a modification of the Persian alphabet, which is itself a derivative of the Arabic alphabet. The Urdu alphabet has up to 40 letters. With 39 basic letters and no distinct letter cases, the Urdu alphabet is typically written in the calligraphic Nastaʿlīq script, whereas Arabic is more commonly in the Naskh style.
Hindustani has been written in several different scripts. Most Hindi texts are written in the Devanagari script, which is derived from the Brāhmī script of Ancient India. Most Urdu texts are written in the Urdu alphabet, which comes from the Persian alphabet. Hindustani has been written in both scripts. In recent years the Latin script has been used in these languages for technological or internationalization reasons.
Urdu Informatics relates to the research and contributions in bringing the utilities and usage of Urdu to the modern information and communication technologies in education and business. National Language Authority in Pakistan has been at the forefront in introducing Urdu Informatics as a tool for the standardisation of Urdu language. Major steps in this respect include the development of Urdu keyboard and launching of software to automate translations between Urdu and English languages.

Bharati braille, or Bharatiya Braille, is a largely unified braille script for writing the languages of India. When India gained independence, eleven braille scripts were in use, in different parts of the country and for different languages. By 1951 a single national standard had been settled on, Bharati braille, which has since been adopted by Sri Lanka, Nepal, and Bangladesh. There are slight differences in the orthographies for Nepali in India and Nepal, and for Tamil in India and Sri Lanka. There are significant differences in Bengali Braille between India and Bangladesh, with several letters differing. Pakistan has not adopted Bharati braille, so the Urdu Braille of Pakistan is an entirely different alphabet than the Urdu Braille of India, with their commonalities largely due to their common inheritance from English or International Braille. Sinhala Braille largely conforms to other Bharati, but differs significantly toward the end of the alphabet, and is covered in its own article.
According to Unesco (2013), there are different braille alphabets for Urdu in India and in Pakistan. The Indian alphabet is based on national Bharati Braille, while the Pakistani alphabet is based on Persian Braille.
Bangla is the endonym of Bengal, a geographical and ethno-linguistic region in South Asia or of the Bengali language, an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It may also refer to:






