
In computer text processing, a markup language is a system for annotating a document in a way that is syntactically distinguishable from the text. The idea and terminology evolved from the "marking up" of paper manuscripts, which is traditionally written with a red or blue pencil on authors' manuscripts. In digital media, this "blue pencil instruction text" was replaced by tags, which indicate what the parts of the document are, rather than details of how they might be shown on some display. This lets authors avoid formatting every instance of the same kind of thing redundantly. It also avoids the specification of fonts and dimensions which may not apply to many users.
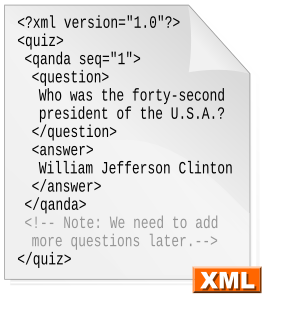
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.
The term Web service (WS) is either:
XForms is an XML format used for collecting inputs from web forms. XForms was designed to be the next generation of HTML / XHTML forms, but is generic enough that it can also be used in a standalone manner or with presentation languages other than XHTML to describe a user interface and a set of common data manipulation tasks.
Extensible Application Markup Language is a declarative XML-based language developed by Microsoft that is used for initializing structured values and objects. It is available under Microsoft's Open Specification Promise. The acronym originally stood for Extensible Avalon Markup Language, Avalon being the code-name for Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF).
XBL is an XML-based markup language for altering the behavior of XUL widgets. It has only ever been implemented in the Mozilla codebase.
MXML is an XML-based user interface markup language first introduced by Macromedia in March 2004. Application developers use MXML in combination with ActionScript to develop rich Internet applications, with products such as Apache Flex.
XRC, or XML Resource, or XML Based Resource System is a cross-platform XML-based user interface markup language used by wxWidgets. XRC allows graphical user interface elements, such as dialogs, menu bars and toolbars, to be stored as XML, which can be loaded into the application at run-time or translated into a target programming language and compiled.
A user interface markup language is a markup language that renders and describes graphical user interfaces and controls. Many of these markup languages are dialects of XML and are dependent upon a pre-existing scripting language engine, usually a JavaScript engine, for rendering of controls and extra scriptability.
User interface modeling is a development technique used by computer application programmers. Today's user interfaces (UIs) are complex software components, which play an essential role in the usability of an application. The development of UIs requires therefore, not only guidelines and best practice reports, but also a development process including the elaboration of visual models and a standardized notation for this visualization.
UIML is an XML-based user interface markup language for defining user interfaces on computers. Basically UIML tries to reduce the work needed to develop user interfaces. It allows you to describe the user interface in declarative terms and abstract it. Abstracting means that you don't exactly specify how the user interface is going to look, but rather what elements are to be shown, and how should they behave. For example, to describe a message window, you could write:
ARINC 661 is a standard which aims to normalize the definition of a Cockpit Display System (CDS), and the communication between the CDS and User Applications (UA) which manage aircraft avionics functions. The GUI definition is completely defined in binary Definition Files (DF).

The Okapi Framework is a cross-platform and open-source set of components and applications that offer extensive support for localizing and translating documentation and software.
The Extensible User Interface Protocol, or XUP, is a proposed web standard. XUP is a SOAP-based protocol for communicating events in a user interface, where the user interface is described by an XML document. The specification does not limit what format the XML document is in, or what event model is used for communicating over XUP. Examples given in the specification for possible user interface languages include XHTML, Wireless Markup Language, and XUL.
A workflow application is a software application which automates, to at least some degree, a process or processes. The processes are usually business-related but can be any process that requires a series of steps to be automated via software. Some steps of the process may require human intervention, such as an approval or the development of custom text, but functions that can be automated should be handled by the application. Advanced applications allow users to introduce new components into the operation.
eXtensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.

The Web Services Description Language is an XML-based interface description language that is used for describing the functionality offered by a web service. The acronym is also used for any specific WSDL description of a web service, which provides a machine-readable description of how the service can be called, what parameters it expects, and what data structures it returns. Therefore, its purpose is roughly similar to that of a type signature in a programming language.
The JAUS Tool Set (JTS) is a software engineering tool for the design of software services used in a distributed computing environment. JTS provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and supporting tools for the rapid design, documentation, and implementation of service interfaces that adhere to the Society of Automotive Engineers' standard AS5684A, the JAUS Service Interface Design Language (JSIDL). JTS is designed to support the modeling, analysis, implementation, and testing of the protocol for an entire distributed system.
FXML is an XML-based user interface markup language created by Oracle Corporation for defining the user interface of a JavaFX application.




