Other uses
- Vintage motocross
- VMX (TalkTalk), an on-demand music television service
- VMX (Voice Message Exchange), a voicemail company
- VMX (streaming service), also known as Vivamax, an online streaming service in the Philippines
VMX may refer to:
MIPS is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures (ISA) developed by MIPS Computer Systems, now MIPS Technologies, based in the United States.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It uses a link state routing (LSR) algorithm and falls into the group of interior gateway protocols (IGPs), operating within a single autonomous system (AS).
AltiVec is a single-precision floating point and integer SIMD instruction set designed and owned by Apple, IBM, and Freescale Semiconductor — the AIM alliance. It is implemented on versions of the PowerPC processor architecture, including Motorola's G4, IBM's G5 and POWER6 processors, and P.A. Semi's PWRficient PA6T. AltiVec is a trademark owned solely by Freescale, so the system is also referred to as Velocity Engine by Apple and VMX by IBM and P.A. Semi.
ARM is a family of RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for computer processors. Arm Holdings develops the ISAs and licenses them to other companies, who build the physical devices that use the instruction set. It also designs and licenses cores that implement these ISAs.

Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol is an open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML, it enables the near-real-time exchange of structured data between two or more network entities. Designed to be extensible, the protocol offers a multitude of applications beyond traditional IM in the broader realm of message-oriented middleware, including signalling for VoIP, video, file transfer, gaming and other uses.
MX, Mx, mX, or mx may refer to:

x86-64 is a 64-bit version of the x86 instruction set, first announced in 1999. It introduced two new modes of operation, 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new 4-level paging mode.
In the 80386 microprocessor and later, virtual 8086 mode allows the execution of real mode applications that are incapable of running directly in protected mode while the processor is running a protected mode operating system. It is a hardware virtualization technique that allowed multiple 8086 processors to be emulated by the 386 chip. It emerged from the painful experiences with the 80286 protected mode, which by itself was not suitable to run concurrent real-mode applications well. John Crawford developed the Virtual Mode bit at the register set, paving the way to this environment.
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
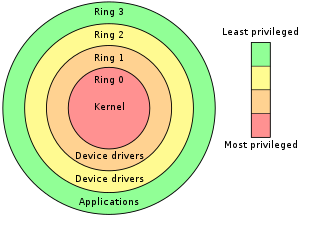
In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are mechanisms to protect data and functionality from faults and malicious behavior.
Software development for the Cell microprocessor involves a mixture of conventional development practices for the PowerPC-compatible PPU core, and novel software development challenges with regard to the functionally reduced SPU coprocessors.
VMware Workstation Player, formerly VMware Player, is a discontinued virtualization software package for x64 computers running Microsoft Windows or Linux, supplied free of charge by VMware, Inc. VMware Player could run existing virtual appliances and create its own virtual machines. It used the same virtualization core as VMware Workstation, a similar program with more features, which became available free of charge for personal, but not commercial, use in 2024. VMware Player was available for personal non-commercial use, or for distribution or other use by written agreement. VMware, Inc. did not formally support Player, but there was an active community website for discussing and resolving issues, and a knowledge base.
Microsoft Application Virtualization is an application virtualization and application streaming solution from Microsoft. It was originally developed by Softricity, a company based in Boston, Massachusetts, acquired by Microsoft on July 17, 2006. App-V represents Microsoft's entry to the application virtualization market, alongside their other virtualization technologies such as Hyper-V, Microsoft User Environment Virtualization (UE-V), Remote Desktop Services, and System Center Virtual Machine Manager.

Junos OS is a FreeBSD-based network operating system used in Juniper Networks routing, switching and security devices.

The Juniper MX Series is a family of ethernet routers and switches designed and manufactured by Juniper Networks. In 2006, Juniper released the first of the MX-series, the MX960, MX240, and MX480. The second generation routers, called MX "3D", were first released in 2009 and featured a new Trio chipset and IPv6 support. In 2013, the MX routers were improved to increase their bandwidth, and a virtualized MX 3D router, the vMX 3D, was released in 2014. Utilizing the Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET), third party software can be integrated into the routers.
Java bytecode is the instruction set of the Java virtual machine (JVM), the language to which Java and other JVM-compatible source code is compiled. Each instruction is represented by a single byte, hence the name bytecode, making it a compact form of data.

AArch64 or ARM64 is the 64-bit Execution state of the ARM architecture family. It was first introduced with the Armv8-A architecture, and has had many extension updates.

Power ISA is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) currently developed by the OpenPOWER Foundation, led by IBM. It was originally developed by IBM and the now-defunct Power.org industry group. Power ISA is an evolution of the PowerPC ISA, created by the mergers of the core PowerPC ISA and the optional Book E for embedded applications. The merger of these two components in 2006 was led by Power.org founders IBM and Freescale Semiconductor.