External links
- Manufacturer's site, global
- "Non-Metallic Transducer Mounting Brackets," US Naval Research Laboratory
Vectra is a brand of liquid crystal polymer (LCP) manufactured by Ticona (a subsidiary of Celanese).
Physical properties of Vectra were tested in the report "Non-Metallic Transducer Mounting Brackets" by the US Naval Research Laboratory in 1992, and the resulting test data is publicly available from the external link below.
CAS: 81843-52-9 (Vectra A 910).

Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels.
A hydrophone is a microphone designed for underwater use, for recording or listening to underwater sound. Most hydrophones contains a piezoelectric transducer that generates an electric potential when subjected to a pressure change, such as a sound wave.

A railgun or rail gun, sometimes referred to as a rail cannon, is a linear motor device, typically designed as a weapon, that uses electromagnetic force to launch high-velocity projectiles. The projectile normally does not contain explosives, instead relying on the projectile's high kinetic energy to inflict damage. The railgun uses a pair of parallel rail-shaped conductors, along which a sliding projectile called an armature is accelerated by the electromagnetic effects of a current that flows down one rail, into the armature and then back along the other rail. It is based on principles similar to those of the homopolar motor.

The Naval Undersea Warfare Center (NUWC) is the United States Navy's full-spectrum research, development, test and evaluation, engineering and fleet support center for submarines, autonomous underwater systems, and offensive and defensive weapons systems associated with undersea warfare. It is one of the corporate laboratories of the Naval Sea Systems Command. NUWC is headquartered in Newport, Rhode Island and has two major subordinate activities: Division Newport and Division Keyport in Keyport, Washington. NUWC also controls the Fox Island facility and Gould Island. It employs more than 4,400 civilian and military personnel, with budgets over $1 billion.

The United States Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren Division (NSWCDD), named for Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren, is located in King George County, Virginia, in close proximity to the largest fleet concentration area in the Navy. NSWCDD is part of the Naval Surface Warfare Centers under the Naval Sea Systems Command (NAVSEA). NSWCDD was initially established 16 October 1918 as a remote extension of Maryland's Indian Head Proving Ground used for testing naval guns. The Dahlgren site was named the Lower Station, Dahlgren Naval Proving Ground when it first opened. The location on the Potomac River was specifically chosen for the development of a long ballistic test range on the Potomac River, required for the testing of modern, high-powered munitions.
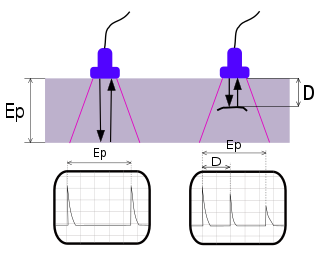
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse waves with centre frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz and occasionally up to 50 MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion and erosion. Ultrasonic testing is extensively used to detect flaws in welds.

A multibeam echosounder (MBES) is a type of sonar that is used to map the seabed. It emits acoustic waves in a fan shape beneath its transceiver. The time it takes for the sound waves to reflect off the seabed and return to the receiver is used to calculate the water depth. Unlike other sonars and echo sounders, MBES uses beamforming to extract directional information from the returning soundwaves, producing a swathe of depth soundings from a single ping.

USNS Titan (T-AGOS-15) was a Stalwart-class modified tactical auxiliary general ocean surveillance ship in service in the United States Navy from 1989 to 1993. From 1996 to 2014, she was in commission in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) fleet as the oceanographic research ship NOAAS Ka'imimoana.

The Naval Submarine Medical Research Laboratory (NSMRL) is located on the New London Submarine Base in Groton, Connecticut. It is a subordinate command of the Naval Medical Research Command.

Project Artemis was a United States Navy acoustics research and development experiment from the late 1950s into the mid 1960s to test a potential low-frequency active sonar system for ocean surveillance. The at sea testing began in 1960 after research and development in the late 1950s. The project's test requirement was to prove detection of a submerged submarine at 500 nmi. The experiment, covering a number of years, involved a large active element and a massive receiver array.
An electromagnetic acoustic transducer (EMAT) is a transducer for non-contact acoustic wave generation and reception in conducting materials. Its effect is based on electromagnetic mechanisms, which do not need direct coupling with the surface of the material. Due to this couplant-free feature, EMATs are particularly useful in harsh, i.e., hot, cold, clean, or dry environments. EMATs are suitable to generate all kinds of waves in metallic and/or magnetostrictive materials. Depending on the design and orientation of coils and magnets, shear horizontal (SH) bulk wave mode, surface wave, plate waves such as SH and Lamb waves, and all sorts of other bulk and guided-wave modes can be excited. After decades of research and development, EMAT has found its applications in many industries such as primary metal manufacturing and processing, automotive, railroad, pipeline, boiler and pressure vessel industries, in which they are typically used for nondestructive testing (NDT) of metallic structures.
Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL) is a laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) which comes under Ministry of Defence. Located in Chandigarh, the laboratory has become one of the major DRDO labs in the field of armament studies. TBRL is organized under the Armaments Directorate of DRDO. The present director of TBRL is Shri. Prateek Kishore.

USS Hunting (E-AG-398) was built as the LSM-1-class landing ship medium LSM-398 at the Charleston Navy Yard and launched in the first week of 1945. After service in the Atlantic as a landing ship the vessel was converted in 1953 to a sonar research vessel for the Naval Research Laboratory. Hunting was unique among Navy research vessels of the time in having a center well through which large towed "fish" could be transported and lowered to operating depths. The work contributed to sonar improvements and understanding ocean acoustics.
Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL) is an Indian defence laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Located at Ambernath, in Thane district, Maharashtra. It develops materials and alloys for Naval use, and is a single-window agency for all materials requirement of the Indian Navy. NMRL is organized under the Naval Research & Development Directorate of DRDO. The present director of NMRL is Shri Prashant T Rojatkar.
An underwater acoustic positioning system is a system for the tracking and navigation of underwater vehicles or divers by means of acoustic distance and/or direction measurements, and subsequent position triangulation. Underwater acoustic positioning systems are commonly used in a wide variety of underwater work, including oil and gas exploration, ocean sciences, salvage operations, marine archaeology, law enforcement and military activities.
Small arms ammunition pressure testing is used to establish standards for maximum average peak pressures of chamberings, as well as determining the safety of particular loads for the purposes of new load development. In metallic cartridges, peak pressure can vary based on propellant used, primers used, charge weight, projectile type, projectile seating depth, neck tension, chamber throat/lead parameters. In shotshells, the primary factors are charge weight, projectile weight, wad type, hull construction, and crimp quality.
The Pennsylvania State University Applied Research Laboratory, is a specialized research unit dedicated to interdisciplinary scientific research at the Penn State University Park campus. The ARL is a DoD designated U.S. Navy University Affiliated Research Center. It is the university's largest research unit with over 1,000 faculty and staff. The Laboratory ranks 2nd in DoD and 10th in NASA funding to universities.

Doppler ultrasonography is medical ultrasonography that employs the Doppler effect to perform imaging of the movement of tissues and body fluids, and their relative velocity to the probe. By calculating the frequency shift of a particular sample volume, for example, flow in an artery or a jet of blood flow over a heart valve, its speed and direction can be determined and visualized.
The Naval Research Laboratory Flyrt, or Flying Radar Target, was a small electric-powered unmanned aerial vehicle developed by the United States Naval Research Laboratory to serve as an expendable radar decoy for the defense of United States Navy ships. Tested in the fall of 1993, it was considered successful but was not ordered into production.

Submarine signals had a specific, even proprietary, meaning in the early 20th century. It applied to a navigation aid system developed, patented and produced by the Submarine Signal Company of Boston. The company produced submarine acoustic signals, first bells and receivers then transducers, as aids to navigation. The signals were fixed, associated with lights and other fixed aids, or installed aboard ships enabling warning of fixed hazards or signaling between ships. ATLAS-Werke, at the time Norddeutsche Maschinen und Armaturenfabrik, of Germany also manufactured the equipment under license largely for the European market.