
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly, instead using a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden, such as preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made up of a large number of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the color of the backlight, and a character negative LCD will have a black background with the letters being of the same color as the backlight. Optical filters are added to white on blue LCDs to give them their characteristic appearance.
Gamma correction, or often simply gamma, is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma; ionized gas that responds to electric fields.

Liquid-crystal-display televisions are television sets that use liquid-crystal displays to produce images. They are, by far, the most widely produced and sold television display type. LCD TVs are thin and light, but have some disadvantages compared to other display types such as high power consumption, poorer contrast ratio, and inferior color gamut.
The contrast ratio is a property of a display system, defined as the ratio of the luminance of the brightest color (white) to that of the darkest color (black) that the system is capable of producing. A high contrast ratio is a desired aspect of any display. It has similarities with dynamic range.

A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). As LCDs do not produce light by themselves—unlike, for example, cathode ray tube (CRT) displays—they need illumination to produce a visible image. Backlights illuminate the LCD from the side or back of the display panel, unlike frontlights, which are placed in front of the LCD. Backlights are used in small displays to increase readability in low light conditions such as in wristwatches, and are used in smart phones, computer displays and LCD televisions to produce light in a manner similar to a CRT display. A review of some early backlighting schemes for LCDs is given in a report Engineering and Technology History by Peter J. Wild.

Fill flash is a photographic technique used to brighten deep shadow areas, typically outdoors on sunny days, though the technique is useful any time the background is significantly brighter than the subject of the photograph, particularly in backlit subjects. To use fill flash, the aperture and shutter speed are adjusted to correctly expose the background, and the flash is fired to lighten the foreground.

High-dynamic-range rendering, also known as high-dynamic-range lighting, is the rendering of computer graphics scenes by using lighting calculations done in high dynamic range (HDR). This allows preservation of details that may be lost due to limiting contrast ratios. Video games and computer-generated movies and special effects benefit from this as it creates more realistic scenes than with the more simplistic lighting models used.

Tone mapping is a technique used in image processing and computer graphics to map one set of colors to another to approximate the appearance of high-dynamic-range images in a medium that has a more limited dynamic range. Print-outs, CRT or LCD monitors, and projectors all have a limited dynamic range that is inadequate to reproduce the full range of light intensities present in natural scenes. Tone mapping addresses the problem of strong contrast reduction from the scene radiance to the displayable range while preserving the image details and color appearance important to appreciate the original scene content.

An image histogram is a type of histogram that acts as a graphical representation of the tonal distribution in a digital image. It plots the number of pixels for each tonal value. By looking at the histogram for a specific image a viewer will be able to judge the entire tonal distribution at a glance.

A transflective liquid-crystal display is a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that reflects and transmits light. Under bright illumination the display acts mainly as a reflective display with the contrast being constant with illuminance. Only in dim and dark ambient situations is an auxiliary transmissive backlight needed.

A parallax barrier is a device placed in front of an image source, such as a liquid crystal display, to allow it to show a stereoscopic or multiscopic image without the need for the viewer to wear 3D glasses. Placed in front of the normal LCD, it consists of an opaque layer with a series of precisely spaced slits, allowing each eye to see a different set of pixels, so creating a sense of depth through parallax in an effect similar to what lenticular printing produces for printed products and lenticular lenses for other displays. A disadvantage of the method in its simplest form is that the viewer must be positioned in a well-defined spot to experience the 3D effect. However, recent versions of this technology have addressed this issue by using face-tracking to adjust the relative positions of the pixels and barrier slits according to the location of the user's eyes, allowing the user to experience the 3D from a wide range of positions. Another disadvantage is that the horizontal pixel count viewable by each eye is halved, reducing the overall horizontal resolution of the image.
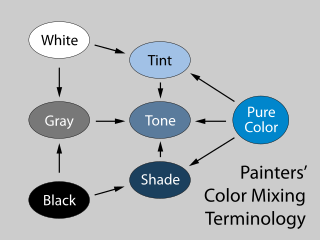
In color theory, a tint is a mixture of a color with white, which reduces darkness, while a shade is a mixture with black, which increases darkness. Both processes affect the resulting color mixture's relative lightness. A tone is produced either by mixing a color with grey, or by both tinting and shading. Mixing a color with any neutral color reduces the chroma, or colorfulness, while the hue remains unchanged.

An image processor, also called media processor, is a specialized digital signal processor (DSP) used for image processing in digital cameras, or other devices. Image processors often employ parallel computing even with SIMD or MIMD technologies to increase speed and efficiency. The digital image processing engine can perform a range of tasks. To increase the system integration on embedded devices, often it is a system on a chip with multi-core processor architecture.
Image quality can refer to the level of accuracy in which different imaging systems capture, process, store, compress, transmit and display the signals that form an image. Another definition refers to image quality as "the weighted combination of all of the visually significant attributes of an image". The difference between the two definitions is that one focus on the characteristics of signal processing in different imaging systems and the latter on the perceptual assessments that make an image pleasant for human viewers.
Contrast in visual perception is the difference in appearance of two or more parts of a field seen simultaneously or successively.

A LED-backlit LCD is a flat panel display which uses LED backlighting instead of the cold cathode fluorescent (CCFL) backlighting. LED-backlit displays use the same TFT LCD technologies as CCFL-backlit displays, but offer reduced energy consumption, better contrast and brightness, greater color range, more rapid response to changes in scene, and photorefractive effects.
A scotophor is a material showing reversible darkening and bleaching when subjected to certain types of radiation. The name means dark bearer, in contrast to phosphor, which means light bearer. Scotophors show tenebrescence and darken when subjected to an intense radiation such as sunlight. Minerals showing such behavior include hackmanite sodalite, spodumene and tugtupite. Some pure alkali halides also show such behavior.
The Blue Only Mode is special display mode on display units, in this mode, only the blue pixels, or the blue cathode ray tube is used to generate the image. Especially in the broadcast area displays have this mode, because hue and saturation can be adjusted quickly and accurately. On professional monitors, a separate button on the front of the display can activate the blue only mode.

darktable is a free and open-source photography workflow application and raw developer. Rather than being a raster graphics editor like Adobe Photoshop or GIMP, it comprises a subset of image editing operations specifically aimed at non-destructive raw photo post-production. It is primarily focused on improving a photographer's workflow by facilitating the handling of large numbers of images. It is freely available in versions tailored for most major Linux distributions, macOS, Solaris and Windows and is released under the GNU General Public License 3 or later.













