
An electrical insulator is a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely; very little electric current will flow through it under the influence of an electric field. This contrasts with other materials, semiconductors and conductors, which conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors.

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the branch of electrical engineering concerned with the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or even physical damage in operational equipment. Also, it is the ability of an equipment or system to function satisfactorily in its electromagnetic environment without introducing intolerable electromagnetic disturbances to anything in that environment. The goal of EMC is the correct operation of different equipment in a common electromagnetic environment.

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the earth.
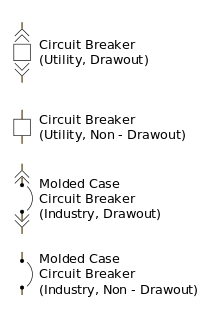
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow after a fault is detected. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset to resume normal operation.

A power cord, line cord, or mains cable is an electrical cable that temporarily connects an appliance to the mains electricity supply via a wall socket or extension cord. The terms are generally used for cables using a power plug to connect to a single-phase alternating current power source at the local line voltage—(generally 100 to 240 volts, depending on the location). The terms power cable, mains lead, flex or kettle lead are also used. A lamp cord is a light-weight, ungrounded, single-insulated two-wire cord used for small loads such as a table or floor lamp.

An Earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations with high Earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous voltage is detected. Once widely used, more recent installations instead use residual current circuit breakers which instead detect leakage current directly.

In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, and it must be replaced or rewired, depending on type.

In electric power distribution, a busbar is a metallic strip or bar, typically housed inside switchgear, panel boards, and busway enclosures for local high current power distribution. They are also used to connect high voltage equipment at electrical switchyards, and low voltage equipment in battery banks. They are generally uninsulated, and have sufficient stiffness to be supported in air by insulated pillars. These features allow sufficient cooling of the conductors, and the ability to tap in at various points without creating a new joint.
As the neutral point of an electrical supply system is often connected to earth ground, ground and neutral are closely related. Under certain conditions, a conductor used to connect to a system neutral is also used for grounding (earthing) of equipment and structures. Current carried on a grounding conductor can result in objectionable or dangerous voltages appearing on equipment enclosures, so the installation of grounding conductors and neutral conductors is carefully defined in electrical regulations. Where a neutral conductor is used also to connect equipment enclosures to earth, care must be taken that the neutral conductor never rises to a high voltage with respect to local ground.

Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom is commonly understood to be an electrical installation for operation by end users within domestic, commercial, industrial, and other buildings, and also in special installations and locations, such as marinas or caravan parks. It does not normally cover the transmission of electrical power to them.

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial, military and scientific applications.
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a ceramic or glass core but other constructions are also used. The RTD wire is a pure material, typically platinum, nickel, or copper. The material has an accurate resistance/temperature relationship which is used to provide an indication of temperature. As RTD elements are fragile, they are often housed in protective probes.

In an electric power system, switchgear is the combination of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be done and to clear faults downstream. This type of equipment is directly linked to the reliability of the electricity supply.
In an electrical installation, an earthing system or grounding system connects specific parts of that installation with the Earth's conductive surface for safety and functional purposes. The point of reference is the Earth's conductive surface. The choice of earthing system can affect the safety and electromagnetic compatibility of the installation. Regulations for earthing systems vary considerably among countries, though most follow the recommendations of the International Electrotechnical Commission. Regulations may identify special cases for earthing in mines, in patient care areas, or in hazardous areas of industrial plants.

A test light, test lamp, voltage tester, or mains tester is a piece of electronic test equipment used to determine the presence of electricity in a piece of equipment under test. A test light is simpler and less costly than a measuring instrument such as a multimeter, and often suffices for checking for the presence of voltage on a conductor. Properly designed test lights include features to protect the user from accidental electric shock. Non-contact test lights can detect voltage on insulated conductors.

Stray voltage is the occurrence of electrical potential between two objects that ideally should not have any voltage difference between them. Small voltages often exist between two grounded objects in separate locations, due to normal current flow in the power system. Large voltages can appear on the enclosures of electrical equipment due to a fault in the electrical power system, such as a failure of insulation.

In electrical engineering, live-line working, also known as hotline maintenance, is the maintenance of electrical equipment, often operating at high voltage, while the equipment is energised. Although this is more hazardous for personnel than working on electrical equipment with the power off, live-line maintenance techniques are used in the electric power distribution industry to avoid the disruption and high economic costs of having to turn off power to customers to perform essential periodic maintenance on transmission lines and other equipment.

Copper has been used in electrical wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s. The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor.

















