Related Research Articles

Otorhinolaryngology ( oh-toh-RYE-noh-LAR-ən-GOL-ə-jee, abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology – head and neck surgery, or ear, nose, and throat, is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management and reconstruction of cancers and benign tumors of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck.

Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction, or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. While reconstructive surgery aims to reconstruct a part of the body or improve its functioning, cosmetic surgery aims at improving the appearance of it.

Cleft lip and cleft palate, also known as orofacial cleft, is a group of conditions that includes cleft lip, cleft palate, and both together. A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the roof of the mouth contains an opening into the nose. These disorders can result in feeding problems, speech problems, hearing problems, and frequent ear infections. Less than half the time the condition is associated with other disorders.
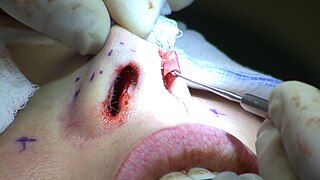
Rhinoplasty, commonly known as a nose job, is a plastic surgery procedure for altering and reconstructing the nose. There are two types of plastic surgery used – reconstructive surgery that restores the form and functions of the nose and cosmetic surgery that changes the appearance of the nose. Reconstructive surgery seeks to resolve nasal injuries caused by various traumas including blunt, and penetrating trauma and trauma caused by blast injury. Reconstructive surgery also treats birth defects, breathing problems, and failed primary rhinoplasties. Rhinoplasty may remove a bump, narrow nostril width, change the angle between the nose and the mouth, or address injuries, birth defects, or other problems that affect breathing, such as a deviated nasal septum or a sinus condition.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery.

Reconstructive surgery is surgery performed to restore normal appearance and function to body parts malformed by a disease or medical condition.

Orthognathic surgery ; also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems primarily arising from skeletal disharmonies, other orthodontic dental bite problems that cannot be easily treated with braces, as well as the broad range of facial imbalances, disharmonies, asymmetries and malproportions where correction can be considered to improve facial aesthetics and self esteem.
Craniofacial surgery is a surgical subspecialty that deals with congenital and acquired deformities of the head, skull, face, neck, jaws and associated structures. Although craniofacial treatment often involves manipulation of bone, craniofacial surgery is not tissue-specific; craniofacial surgeons deal with bone, skin, nerve, muscle, teeth, and other related anatomy.

Distraction osteogenesis (DO), also called callus distraction, callotasis and osteodistraction, is a process used in orthopedic surgery, podiatric surgery, and oral and maxillofacial surgery to repair skeletal deformities and in reconstructive surgery. The procedure involves cutting and slowly separating bone, allowing the bone healing process to fill in the gap.
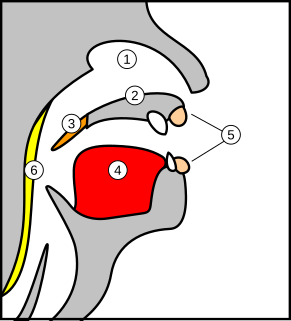
Augmentation pharyngoplasty is a kind of plastic surgery for the pharynx when the tissue at the back of the mouth is not able to close properly. It is typically used to correct speech problems in children with cleft palate. It may also be used to correct problems from a tonsillectomy or because of degenerative diseases. After the surgery, patients have an easier time pronouncing certain sounds, such as 'p' and 't', and the voice may have a less nasal sound.

A palatal obturator is a prosthesis that totally occludes an opening such as an oronasal fistula. They are similar to dental retainers, but without the front wire. Palatal obturators are typically short-term prosthetics used to close defects of the hard/soft palate that may affect speech production or cause nasal regurgitation during feeding. Following surgery, there may remain a residual orinasal opening on the palate, alveolar ridge, or vestibule of the larynx. A palatal obturator may be used to compensate for hypernasality and to aid in speech therapy targeting correction of compensatory articulation caused by the cleft palate. In simpler terms, a palatal obturator covers any fistulas in the roof of the mouth that lead to the nasal cavity, providing the wearer with a plastic/acrylic, removable roof of the mouth, which aids in speech, eating, and proper air flow.
Pharyngeal flap surgery is a procedure to correct the airflow during speech. The procedure is common among people with cleft palate and some types of dysarthria.
Velopharyngeal insufficiency is a disorder of structure that causes a failure of the velum to close against the posterior pharyngeal wall during speech in order to close off the nose during oral speech production. This is important because speech requires sound and airflow to be directed into the oral cavity (mouth) for the production of all speech sound with the exception of nasal sounds. If complete closure does not occur during speech, this can cause hypernasality and/or audible nasal emission during speech. In addition, there may be inadequate airflow to produce most consonants, making them sound weak or omitted.
Pediatric plastic surgery is plastic surgery performed on children. Its procedures are most often conducted for reconstructive or cosmetic purposes. In children, this line is often blurred, as many congenital deformities impair physical function as well as aesthetics.
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth, jaws and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin. The mouth is an important organ with many different functions. It is also prone to a variety of medical and dental disorders.
A jaw abnormality is a disorder in the formation, shape and/or size of the jaw. In general abnormalities arise within the jaw when there is a disturbance or fault in the fusion of the mandibular processes. The mandible in particular has the most differential typical growth anomalies than any other bone in the human skeleton. This is due to variants in the complex symmetrical growth pattern which formulates the mandible.

S. M. Balaji is a dental and Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon from Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. He is a dental scientist who specialises in repair of cleft palate, rhinoplasty, ear reconstruction, jaw reconstruction, facial asymmetry correction, dental implantology, maxillofacial surgery and Craniofacial surgery.He is the alumni of prestigious Annamalai University where so many efficient oral and Maxillofacial surgeon's are trained.
A facial cleft is an opening or gap in the face, or a malformation of a part of the face. Facial clefts is a collective term for all sorts of clefts. All structures like bone, soft tissue, skin etc. can be affected. Facial clefts are extremely rare congenital anomalies. There are many variations of a type of clefting and classifications are needed to describe and classify all types of clefting. Facial clefts hardly ever occur isolated; most of the time there is an overlap of adjacent facial clefts.

Hypernasal speech is a disorder that causes abnormal resonance in a human's voice due to increased airflow through the nose during speech. It is caused by an open nasal cavity resulting from an incomplete closure of the soft palate and/or velopharyngeal sphincter. In normal speech, nasality is referred to as nasalization and is a linguistic category that can apply to vowels or consonants in a specific language. The primary underlying physical variable determining the degree of nasality in normal speech is the opening and closing of a velopharyngeal passageway between the oral vocal tract and the nasal vocal tract. In the normal vocal tract anatomy, this opening is controlled by lowering and raising the velum or soft palate, to open or close, respectively, the velopharyngeal passageway.

Alveolar cleft grafting is a surgical procedure, used to repair the defect in the upper jaw that is associated with cleft lip and palate, where the bone defect is filled with bone or bone substitute, and any holes between the mouth and the nose are closed.
References
- Agrawal, Karoon and Panda, K.N. (2004). Use of vomer flap in palatoplasty: Revisited. The Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal, 43(1): 30–37.
- Friede, H. and Johanson, B. (1977). A follow-up study of cleft children treated with vomer flap as part of a three-stage soft tissue surgical procedure. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 11(1), 45–57.
- Maggiulli F, Hay N, Mars M, Worrell E, Green J, Sommerlad B (2014) Early effect of vomerine flap closure of the hard palate at the time of lip repair on the alveolar gap and other maxillary dimensions. The Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal 51(1): 43–48.
- Peterson-Falzone, Sally J., Hardin-Jones, Mary A., and Karnell, Michael P. (2001). Cleft Palate Speech. Mosby, Inc.: St. Louis, MO. 103.
- Witt, Peter. (2006). Craniofacial, cleft palate. www.emedicine.com/plastic/topic519.htm. Found on July 10, 2006.