The suffix -ess appended to English words makes a female form of the word.
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to networks of spatially dispersed and dedicated sensors that monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and forward the collected data to a central location. WSNs can measure environmental conditions such as temperature, sound, pollution levels, humidity and wind.
In symmetric key cryptography, both parties must possess a secret key which they must exchange prior to using any encryption. Distribution of secret keys has been problematic until recently, because it involved face-to-face meeting, use of a trusted courier, or sending the key through an existing encryption channel. The first two are often impractical and always unsafe, while the third depends on the security of a previous key exchange.
Low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy ("LEACH") is a TDMA-based MAC protocol which is integrated with clustering and a simple routing protocol in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). The goal of LEACH is to lower the energy consumption required to create and maintain clusters in order to improve the life time of a wireless sensor network.
Key distribution is an important issue in wireless sensor network (WSN) design. WSNs are networks of small, battery-powered, memory-constraint devices named sensor nodes, which have the capability of wireless communication over a restricted area. Due to memory and power constraints, they need to be well arranged to build a fully functional network.

A sensor node, also known as a mote, is a node in a sensor network that is capable of performing some processing, gathering sensory information and communicating with other connected nodes in the network. A mote is a node but a node is not always a mote.
An Energy Neutral Design is a Design of any type that has the environment and low energy consumption practices in mind during all stages of planning and production.
Castalia is a simulator for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), Body Area Networks and generally networks of low-power embedded devices. It is based on the OMNeT++ platform and used by researchers and developers to test their distributed algorithms and/or protocols in a realistic wireless channel and radio model, with a realistic node behaviour especially relating to access of the radio. Castalia uses the lognormal shadowing model as one of the ways to model average path loss, which has been shown to explain empirical data in WSN. It also models temporal variation of path loss in an effort to capture fading phenomena in changing environments. Castalia's temporal variation modeling is designed to be fitted to measured data instead of making specific assumptions on the creation of fast fading. Other features of Castalia include: physical process modeling, sensing device bias and noise, node clock drift, and several MAC and routing protocols implemented.
A virtual sensor network (VSN) in computing and telecommunications is an emerging form of collaborative wireless sensor networks. In contrast to early wireless sensor networks that were dedicated to a specific application, VSNs enable multi-purpose, collaborative, and resource efficient WSNs. The key idea difference of VSNs is the collaboration and resource sharing. By doing so nodes achieve application objectives in a more resource efficient way. These networks may further involve dynamically varying subset of sensor nodes and/or users .
A VSN can be formed by providing logical connectivity among collaborative sensors. Nodes can be grouped into different VSNs based on the phenomenon they track or the task they perform. VSNs are expected to provide the protocol support for formation, usage, adaptation, and maintenance of subset of sensors collaborating on a specific task(s). Even the nodes that do not sense the particular event/phenomenon could be part of a VSN as far as they are willing to allow sensing nodes to communicate through them. Thus, VSNs make use of intermediate nodes, networks, or other VSNs to efficiently deliver messages across members of a VSN.

WSNS-TV is a television station in Chicago, Illinois, United States, airing programming from the Spanish-language Telemundo network. It is owned and operated by NBCUniversal's Telemundo Station Group alongside NBC outlet WMAQ-TV ; it is also sister to regional sports network NBC Sports Chicago. WSNS-TV and WMAQ-TV share studios at the NBC Tower on North Columbus Drive in the city's Streeterville neighborhood and transmitter facilities atop the Willis Tower in the Chicago Loop.
MyriaNed is a wireless sensor network (WSN) platform developed by DevLab. It uses an epidemic communication style based on standard radio broadcasting. This approach reflects the way humans interact, which is called gossiping. Messages are sent periodically and received by adjoining neighbours. Each message is repeated and duplicated towards all nodes that span the network; it spreads like a virus.
Middleware is a type of computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue".
A mobile wireless sensor network (MWSN) can simply be defined as a wireless sensor network (WSN) in which the sensor nodes are mobile. MWSNs are a smaller, emerging field of research in contrast to their well-established predecessor. MWSNs are much more versatile than static sensor networks as they can be deployed in any scenario and cope with rapid topology changes. However, many of their applications are similar, such as environment monitoring or surveillance. Commonly, the nodes consist of a radio transceiver and a microcontroller powered by a battery, as well as some kind of sensor for detecting light, heat, humidity, temperature, etc.
A sensor network query processor (SNQP), also called a sensorDB, is a user-friendly interface for programming and running applications which translates instructions from declarative programming language with high-level instructions to low-level instructions understood by the operating system. The basic idea of SNQP is the addition of a layer modeling the WSN as a distributed database searchable by a query language similar to SQL.
Low-power network (LPN) or wireless low-power network may refer to:
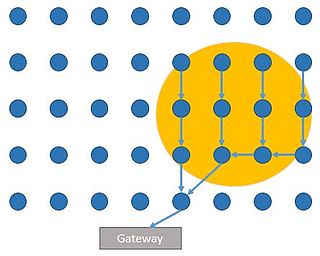
This article is about event detection for WSN.

OpenWSN is a project created at the University of California Berkeley and extended at the INRIA and at the Open University of Catalonia (UOC) which aims to build an open standard-based and open source implementation of a complete constrained network protocol stack for wireless sensor networks and Internet of Things. The root of OpenWSN is a deterministic MAC layer implementing the IEEE 802.15.4e TSCH based on the concept of Time Slotted Channel Hopping (TSCH). Above the MAC layer, the Low Power Lossy Network stack is based on IETF standards including the IETF 6TiSCH management and adaptation layer. The stack is complemented by an implementation of 6LoWPAN, RPL in non-storing mode, UDP and CoAP, enabling access to devices running the stack from the native IPv6 through open standards.
Time Slotted Channel Hopping or Time Synchronized Channel Hopping (TSCH) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks.



