The Water of Leith, is a small river in the South Island of New Zealand.

The McGillicuddy Highland Army is the fighting wing of New Zealand's Clan McGillicuddy and does battle with enemies of the Clan in accordance with the rules of the pastime of pacifist warfare. Battles have taken place at wide range of locations and events around the country. During the period 1984–1999 it shared many members in common with the Clan's political wing, the better-known McGillicuddy Serious Party.

The Port Chalmers Branch was the first railway line built in Otago, New Zealand, and linked the region's major city of Dunedin with the port in Port Chalmers. The line is still operational today.
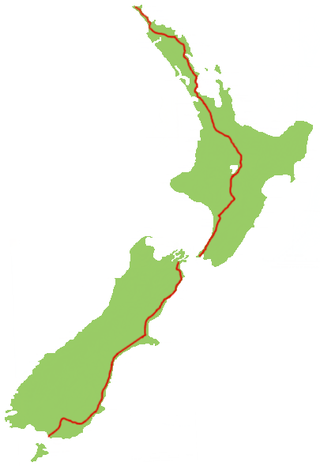
State Highway 1 is the longest and most significant road in the New Zealand road network, running the length of both main islands. It appears on road maps as SH 1 and on road signs as a white number 1 on a red shield, but it has the official designations SH 1N in the North Island, SH 1S in the South Island.
The Otago Province was a province of New Zealand until the abolition of provincial government in 1876. The capital of the province was Dunedin. Southland Province split from Otago in 1861, but became part of the province again in 1870.
Waitati, from the Māori Waitete, is a small seaside settlement in Otago, New Zealand, within the city limits of Dunedin. It is located close to the tidal mudflats of Blueskin Bay, 19 kilometres north of the Dunedin city centre. The small Waitati River flows through the bay to the sea.
The Kilmog, occasionally called Kilmog Hill and known in Māori as Kirimoko, is a hilly area approximately 20 kilometres north of Dunedin, New Zealand, on State Highway 1, to the north of Blueskin Bay and south of Karitane. Technically more a series of hills than a single hill, it lies between the south branch of the Waikouaiti River and the Pacific Ocean, and reaches its highest point at the 431 m (1436 ft) Hammond Hill, close to the farming community of Merton. A second peak, Porteous Hill, lies at the southern end of the Kilmog, rising to 395 m (1317 ft).

Warrington, known in Māori as Ōkāhau, is a small settlement on the coast of Otago, in the South Island of New Zealand. It is situated close to the northern shore of Blueskin Bay, an area of mudflats north of Dunedin, and is administered as part of Dunedin City. Warrington is 3 km (1.9 mi) from State Highway 1 linked by Coast Road. The Main South Line railway passes through the township and a tourist train, the Seasider passes through the settlement once or twice a week between Dunedin and Palmerston.

Blueskin Bay is an estuary in coastal Otago, about 25 km north of Dunedin, New Zealand. The name also unofficially describes the rural district which includes the northern slopes of Mount Cargill, the southern slopes of the Kilmog, and the townships of Doctors Point, Waitati, Evansdale, Warrington, and Seacliff.
Seacliff is a small village located north of Dunedin in the Otago region of New Zealand's South Island. The village lies roughly halfway between the estuary of Blueskin Bay and the mouth of the Waikouaiti River at Karitane, on the eastern slopes of Kilmog hill. Coast Road, an old route north from Dunedin, and the South Island Main Trunk Railway pass through the village.
Evansdale is a locality on State Highway 1, 25 km north of Dunedin, at the north west of Blueskin Bay. It also has lent its name to a cheese producer, and a census-gathering district, which has a population of 1,482 in the 2013 New Zealand census, an increase of 198 people since the 2006 census.

Orokonui Ecosanctuary, called Te Korowai o Mihiwaka in Māori, is an ecological island wildlife reserve developed by the Otago Natural History Trust in the Orokonui Valley between Waitati and Pūrākaunui, New Zealand, 20 kilometres (12 mi) to the north of central Dunedin.

St Barnabas' Church is a heritage listed Anglican church, located at 266 Coast Road, Warrington, Otago, New Zealand. The small wooden church was built in 1872.

The Southern Scenic Route is a tourist highway in New Zealand linking Queenstown, Fiordland, Te Anau and the iconic Milford Road to Dunedin via, Riverton, Invercargill and The Catlins. An Australian travel magazine labelled it "one of the world's great undiscovered drives" in 2008.

The Seasider is a tourist train in the South Island of New Zealand, operated by the Dunedin Railways along the Main South Line between the historic Dunedin Railway Station and Waitati once or twice a month. Since the demise of the Southerner in February 2002 it has been the only regular passenger train on this stretch of line.

Dunedin Public Libraries is a network of six libraries and two bookbuses in Dunedin, New Zealand, owned and operated by the Dunedin City Council. The Libraries' collection includes over 700,000 items, and around 30,000 books and audiovisual items plus 15,000 magazines are added each year. Members can borrow or return items from any library or bookbus in the network.

Leith Saddle is a saddle between the sources of the Water of Leith and the Waitati River, approximately halfway between Dunedin's northern suburb of Pine Hill and the outlying settlement of Waitati. The saddle is a strategic point where the Dunedin-Waitati Highway, part of State Highway 1 traverses a fragile alpine forest. Proposed road works to straighten a dangerous corner here conflict with conservation values. Water supply pipelines, and popular tramping and cycling routes also converge at the saddle.

Dunedin–Waitati Highway, formerly called Dunedin Northern Motorway, is a two-to-four-lane limited-access road which provides the main route north from the city of Dunedin, New Zealand. Opened on 14 December 1957, it superseded the narrow and winding routes via Port Chalmers and Mount Cargill. The road is occasionally briefly closed by snowfall in winter.

James George Leckie was a New Zealand track and field athlete who won a bronze medal at the 1938 British Empire Games.
Alexander L. Garvie, was a British-born pioneer land surveyor in the South Island of New Zealand. Of particular note, the Garvie Mountains in Southland are named for him, and Garvie named The Remarkables, near Queenstown.