A walking boot may refer to:
A walking boot may refer to:
Nordic most commonly refers to:

A boot is a type of footwear. Most boots mainly cover the foot and the ankle, while some also cover some part of the lower calf. Some boots extend up the leg, sometimes as far as the knee or even the hip. Most boots have a heel that is clearly distinguishable from the rest of the sole, even if the two are made of one piece. Traditionally made of leather or rubber, modern boots are made from a variety of materials.
The Perishers was a long-running British comic strip about a group of neighbourhood children and a dog. It was printed in the Daily Mirror as a daily strip and first appeared on 19 October 1959. For most of its life it was written by Maurice Dodd, and was drawn by Dennis Collins until his retirement in 1983, after which it was drawn by Dodd and later by Bill Mevin. When Dodd died, the strip continued with several weeks' backlog of unpublished strips and some reprints until 10 June 2006. The strip then returned to the Daily Mirror, again as reprints, on 22 February 2010, replacing Pooch Café.
NTLDR is the boot loader for all releases of Windows NT operating system from 1993 with the release of Windows NT 3.1 up until Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. From Windows Vista onwards it was replaced by the BOOTMGR bootloader. NTLDR is typically run from the primary storage device, but it can also run from portable storage devices such as a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or floppy disk. NTLDR can also load a non NT-based operating system given the appropriate boot sector in a file.
Boot camp may refer to:

A bootloader, also spelled as boot loader or called bootstrap loader, is a computer program that is responsible for booting a computer. If it also provides an interactive menu with multiple boot choices then it's often called a boot manager.

A riding boot is a boot made to be used for horse riding. The classic boot comes high enough up the leg to prevent the leathers of the saddle from pinching the leg of the rider, has a sturdy toe to protect the rider's foot when on the ground and has a distinct heel to prevent the foot from sliding through the stirrup. The sole is smooth or lightly textured to avoid being caught on the tread of the stirrup in the event of a fall.
Walking Dead or The Walking Dead may refer to: dead people walking

Hiking (walking) boots are footwear specifically designed for protecting the feet and ankles during outdoor walking activities such as hiking. They are one of the most important items of hiking gear since their quality and durability can determine a hiker's ability to walk long distances without injury. Hiking boots are constructed to provide comfort for walking considerable distances over rough terrain. Boots that protect the hiker's feet and heel are recommended. Hiking boots give ankle support and are fairly stiff. A less popular alternative is to use light trainers with thin soles. Footwear should be neither too loose nor too tight, to help prevent blisters and sore feet. Hiking socks that wick sweat from the feet, provide warmth, and cushion the feet are recommended and a thin, inner sock may also help. Most hiking boots are also designed for other outdoor activities such as backpacking, climbing, mountaineering, and hunting.

Galoshes, also known by many other names, are a type of overshoe or rubber boot that is put on over shoes to keep them from getting muddy or wet during inclement weather.

The ballet boot is a contemporary style of fetish footwear that merges the look of the pointe shoe with a high heel. The idea is to restrict the wearer's feet almost en pointe, like those of a ballerina, with the aid of long, slender heels. When upright, the feet are held nearly vertical by the shoe, thus putting nearly all of the body's weight on the tips of the toes. However, a properly tight fit will hold the shoe to the wearer's instep and heel, thereby reducing the weight on the wearer's toes.

Waders denotes a waterproof boot or overalls extending from the foot to the thigh, the chest or even the neck. They are traditionally made from vulcanised rubber, but available in more modern PVC, neoprene and Gore-Tex variants. Waders are generally distinguished from counterpart waterproof boots by shaft height; the hip boot extending to the thigh and the Wellington boot to the knee. For the sake of emphasis, therefore, waders are sometimes defined by the extent of their coverage as thigh waders, chest waders or full-body waders. As a drysuit variant, full-body waders come with leaktight cuffs or gloves fitted to the sleeves and with a leaktight collar or hood fitted to the neck, enabling the wearer to remain dry when standing or walking in deeper water. Waders are available with boots attached or can have attached stocking feet, to wear inside boots, or inside swimfins in the case of float tube fishing.
Cam or CAM may refer to:
U-boat is a German military submarine of World War I and II.

The Leadville Historic District is in the mining town of Leadville, Colorado. The National Historic Landmark District includes 67 mines in the mining district east of the city up to the 12,000 foot level, and a defined portion of the village area. It was designated in 1961. Then, when the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) program was started in 1966, Leadville's National Historic District was included in its first day's listings, along with all other existing National Historic Landmarks. The NRHP district was later expanded, adding a number of structures along the Harrison Avenue corridor, and making them eligible for historic preservation grants and tax subsidies, too.

"As She's Walking Away" is a song by American country music group Zac Brown Band. Written by lead singer Zac Brown, along with Wyatt Durrette, it features guest vocals from veteran country singer Alan Jackson. The song is the sixth single release by the band, and the first from the album You Get What You Give. It won the Grammy Award for Best Country Collaboration with Vocals at the 53rd Grammy Awards, and is the second Grammy for both the band and Jackson overall.

Cowboy boots are a specific style of riding boot, historically worn by cowboys. They have a high heel that is traditionally made of stacked leather, rounded to pointed toe, high shaft, and, traditionally, no lacing. Cowboy boots are normally made from cowhide leather, which may be decoratively hand-tooled, but are also sometimes made from "exotic" skins like alligator, snake, ostrich, lizard, eel, elephant, stingray, elk, buffalo, and so on.
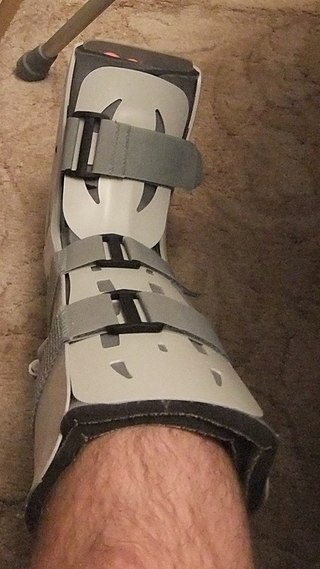
A variety of orthopedic boots are used for the treatment of injuries of the foot or ankle. Along with orthopedic casts, leg braces, splints and orthotics, they can immobilize and shift weight bearing to help treat injuries to the foot area.

ReBoot: The Guardian Code is a Canadian teen drama science fiction live-action/CGI-animated television series produced by Mainframe Studios. Originally announced in 2013, the first ten episodes debuted on Netflix worldwide on March 30, 2018. YTV aired all twenty episodes from June 4 to July 5, 2018.
Walking shoe may refer to: