Weight loss is a reduction of the total body mass in an individual.
Weight loss may also refer to:
- "Weight Loss" (The Office), an episode of the American TV show The Office
- Weight Loss (novel), a novel by Upamanyu Chatterjee
Weight loss is a reduction of the total body mass in an individual.
Weight loss may also refer to:
Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated way to decrease, maintain, or increase body weight, or to prevent and treat diseases such as diabetes and obesity. As weight loss depends on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasising particular macronutrients, have been shown to be no more effective than one another. As weight regain is common, diet success is best predicted by long-term adherence. Regardless, the outcome of a diet can vary widely depending on the individual.

The Atkins diet is a low-carbohydrate fad diet devised by Robert Atkins in the 1970s, marketed with claims that carbohydrate restriction is crucial to weight loss and that the diet offered "a high calorie way to stay thin forever".

Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regulate adequate energy intake to maintain metabolic needs. It is regulated by a close interplay between the digestive tract, adipose tissue and the brain. Appetite has a relationship with every individual's behavior. Appetitive behaviour also known as approach behaviour, and consummatory behaviour, are the only processes that involve energy intake, whereas all other behaviours affect the release of energy. When stressed, appetite levels may increase and result in an increase of food intake. Decreased desire to eat is termed anorexia, while polyphagia is increased eating. Dysregulation of appetite contributes to ARFID, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, cachexia, overeating, and binge eating disorder.

Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo, which eventually forms the placenta after implantation. The presence of hCG is detected in some pregnancy tests. Some cancerous tumors produce this hormone; therefore, elevated levels measured when the patient is not pregnant may lead to a cancer diagnosis and, if high enough, paraneoplastic syndromes, however, it is unknown whether this production is a contributing cause or an effect of carcinogenesis. The pituitary analog of hCG, known as luteinizing hormone (LH), is produced in the pituitary gland of males and females of all ages.

Kirstie Louise Alley was an American actress. Her breakthrough role was as Rebecca Howe in the NBC sitcom Cheers (1987–1993), for which she received an Emmy Award and a Golden Globe in 1991. From 1997 to 2000, Alley starred as the lead in the sitcom Veronica's Closet, earning additional Emmy and Golden Globe nominations. On film, she played Mollie Jensen in Look Who's Talking (1989) and its two sequels, Look Who's Talking Too (1990) and Look Who's Talking Now (1993).

Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat, or lean mass. Weight loss can either occur unintentionally because of malnourishment or an underlying disease, or from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. "Unexplained" weight loss that is not caused by reduction in calorific intake or increase in exercise is called cachexia and may be a symptom of a serious medical condition.

WW International, Inc., formerly Weight Watchers International, Inc., is a global company headquartered in the U.S. that offers weight loss and maintenance, fitness, and mindset services such as the Weight Watchers comprehensive diet program. Founded in 1963 by Queens, New York City homemaker Jean Nidetch, WW's program has three options as of 2019: online via its mobile app and website, coaching online or by phone, or in-person meetings.
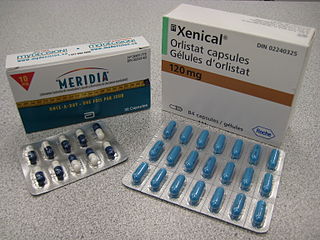
Anti-obesity medication or weight loss medications are pharmacological agents that reduce or control excess body fat. These medications alter one of the fundamental processes of the human body, weight regulation, by: reducing appetite and consequently energy intake, increasing energy expenditure, redirecting nutrients from adipose to lean tissue, or interfering with the absorption of calories.
LOS, or Los, or LoS may refer to:
Deadweight or dead weight may refer to:

Holes is a 2003 American neo-Western comedy drama film directed by Andrew Davis and written by Louis Sachar, based on his 1998 novel. The film stars Sigourney Weaver, Jon Voight, Patricia Arquette, Tim Blake Nelson, Eartha Kitt, and Shia LaBeouf.
Upamanyu Chatterjee is an author and a retired Indian civil servant. His works include the novel English, August: An Indian story, The Last Burden, The Mammaries of the Welfare State and Weight Loss. In 2008, he was awarded the Ordre des Arts et des Lettres for his contribution to literature.
Repetition may refer to:
Libra generally refers to:

Jenny Craig, Inc., often known simply as Jenny Craig, is an American weight loss, weight management, and nutrition company. At its peak, the company had more than 700 weight management centers in Australia, the United States, Canada, and New Zealand. The program combined individual weight management counseling with a menu of frozen meals and other foods which were distributed through its centers or shipped directly to clients. Founded as an independent company, the business was purchased by Nestlé in 2006 for approximately $600 million. However, the business declined, and on 4 May 2023, the company announced that it was going out of business after 40 years. It was revived as an e-commerce store by Wellful sometime after this announcement in fall 2023.

Tesofensine (NS2330) is a serotonin–noradrenaline–dopamine reuptake inhibitor from the phenyltropane family of drugs, which is being developed for the treatment of obesity. Tesofensine was originally developed by a Danish biotechnology company, NeuroSearch, who transferred the rights to Saniona in 2014.

Lorcaserin, marketed under the brand name Belviq, was a weight-loss drug developed by Arena Pharmaceuticals. It reduces appetite by activating serotonin receptor the 5-HT2C receptor in the hypothalamus, a region of the brain which is known to control appetite. It was approved in 2012, and in 2020, it was removed from the market in the United States due to an increased risk of cancer detected in users of Belviq.
"Weight Loss" is the collective name for the first and second episodes of the fifth season of the American comedy television series The Office and the show's 73rd and 74th episodes overall. Written by Lee Eisenberg and Gene Stupnitsky, and directed by Paul Feig, the episode first aired as a single 60 minute show in the United States on September 25, 2008, on NBC. "Weight Loss" guest stars Amy Ryan as Holly Flax, Dale Raoul as Ronni, and Rich Sommer as Alex.
Weight Watchers or WW may refer to:
Gelesis100, sold under the brand name Plenity, is an oral hydrogel used to treat overweight and obesity. It absorbs water and expands in the stomach and small bowel thereby increasing feelings of fullness. Possible side effects include primarily gastrointestinal symptoms, such as diarrhea, abdominal distention, infrequent bowel movements, constipation, abdominal pain, and flatulence. It is contraindicated in pregnancy, chronic malabsorption syndromes, and cholestasis. The US Food and Drug Administration approved it in 2019 as a medical device. Gelesis100 was developed by the company Gelesis.