See also
| | This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Wilno. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Wilno is the Polish name of the city of Vilnius, Lithuania.
Wilno may also refer to:
| | This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Wilno. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

The Second Polish Republic, commonly known as Interwar Poland, refers to the country of Poland in the period between the two World Wars (1918–1939). Officially known as the Republic of Poland, the Polish state was re-established in 1918, in the aftermath of World War I. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II.

Paneriai is a neighborhood of Vilnius, situated about 10 kilometres away from the city center. It is the largest elderate in the Vilnius city municipality. It is located on low forested hills, on the Vilnius-Warsaw road. Paneriai was the site of the Ponary massacre, a mass killing of as many as 100,000 people from Vilnius and nearby towns and villages during World War II.
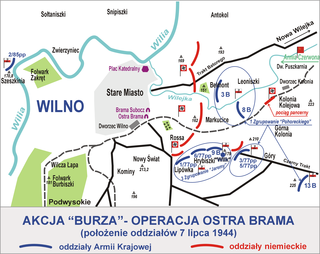
Operation Ostra Brama was an attempt by the Polish Home Army to take over Vilnius from Nazi Germany's evacuating troops ahead of the approaching Soviet Vilnius Offensive. A part of a Polish national uprising, Operation Tempest, the action began on 7 July 1944 and lasted until 14 July 1944.

The Wilno Voivodeship was one of 16 Voivodeships in the Second Polish Republic, with the capital in Wilno. It was created in 1926 and populated predominantly by Poles with notable minorities of Belarusians, Jews and Lithuanians.

Varėna is a city in Dzūkija, Lithuania.

Wilno is a township in municipality of Madawaska Valley, Renfrew County, Ontario, Canada.

Zygmunt Szendzielarz was the commander of the Polish 5th Wilno Brigade of the Home Army, nom de guerre "Łupaszka". He was executed in the notorious Mokotów Prison as one of anti-communist so-called Cursed soldiers following the Soviet takeover of Poland at the end of World War II.

Lucjan Żeligowski was a Polish general, politician, military commander and veteran of World War I, the Polish-Soviet War and World War II. He is mostly remembered for his role in Żeligowski's Mutiny and as head of a short-lived Republic of Central Lithuania.
Polish 1st Legions Infantry Division was a tactical unit of the Polish Army between the World Wars. Formed on February 20, 1919, partially of veterans of the I Brigade of the Polish Legions, the unit saw extensive action during the Polish-Bolshevik War and World War II. Regarded by the soldiers of the Wehrmacht as the Iron Division, it distinguished itself in the Invasion of Poland.
Śmigły Wilno was a Polish association football team. Founded in 1933 in Wilno, Second Polish Republic. Śmigły's full name was Wojskowy Klub Sportowy "Śmigły" Wilno. The club enjoyed full support of Wilno's military garrison of the Polish Army, located in present-day Šiaurės miestelis of Žirmūnai; in fact – it was created by a group of officers, passionate fans of soccer.
Battle of Vilnius may refer to:
The 1st Lithuanian–Belarusian Division was a volunteer unit of the Polish Army formed around December 1918 and January 1919 during the Polish–Soviet War. It was created out of several dozen smaller units of self-defence forces composed of local volunteers in what is now Lithuania and Belarus, amidst a growing series of territorial disputes between the Second Polish Republic, the Russian SFSR, and several other local provisional governments. The Division took part in several key battles of the war.

Sapieha Palace is a High Baroque palace in Sapiegos str., Antakalnis district of Vilnius, Lithuania. It is the only surviving of several palaces formerly belonging to the Sapieha family in the city.

Jan Brunon Bułhak (1876–1950) was a pioneer of photography in Poland and present-day Belarus and Lithuania, and one of the best-known Polish photographers of the early 20th century. A theoretician and philosopher of photography, he was among the most prominent exponents of pictorialism. He is best known for his landscapes and photographs of various places, especially the city of Vilnius. He was the founder of the Wilno Photoclub and Polish Photoclub, the predecessors of the modern Union of Polish Art Photographers (ZPAF), of which he was an honorary headperson. He is also known as an ethnographer and folklorist.

The Battle of Wilno was fought by the Polish Army against the Soviet invasion of Poland in 1939, which accompanied the German Invasion of Poland in accordance with Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. On 18–19 September, Soviet forces took over the city of Wilno. Polish forces, concentrated in the west, were relatively weak in the east. The Polish commanders, unsure whether to actively oppose the Soviet entry into Poland, did not use the full defensive capabilities of the town and nearby fortifications, although the outcome of the battle would not have been likely any different, given the overwhelming Soviet numerical superiority.

Żeligowski's Mutiny was a Polish false flag operation led by General Lucjan Żeligowski in October 1920, which resulted in the creation of the Republic of Central Lithuania. Polish Chief of State Józef Piłsudski surreptitiously ordered Żeligowski to carry out the operation, and revealed the truth several years later. The area was formally annexed by Poland in 1922 and internationally recognized as Polish territory in 1923. Nevertheless, Lithuania continued to claim the Vilnius region.
Latający Wilnianin was the popular name of a passenger train which in the interbellum period linked Warsaw with Wilno. Another name for that train was Gwiazda Północy.
President of Poland's Football Cup was an annual football competition, taking place in the Second Polish Republic in the years 1936–1939. It was sponsored by President Ignacy Moscicki, and unlike today's Polish Cup, it did not feature clubs. Instead, it was a competition of the local districts of the PZPN.
Mieczysław Witold Gutkowski was a Polish lawyer, a world-renowned economist who specialized in public finance, and one of the first scholars of economic analysis of law in Poland. He was a professor at the Stefan Batory University in Wilno. He was murdered by German SS units and Lithuanian collaborators in the Ponary massacre.

Wilno is an unincorporated community located in Royal Township, Lincoln County, Minnesota, United States.