The net present value (NPV) or net present worth (NPW) applies to a series of cash flows occurring at different times. The present value of a cash flow depends on the interval of time between now and the cash flow. It also depends on the discount rate. NPV accounts for the time value of money. It provides a method for evaluating and comparing capital projects or financial products with cash flows spread over time, as in loans, investments, payouts from insurance contracts plus many other applications.
In international economics, the balance of payments of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services.
In economics, hot money is the flow of funds from one country to another in order to earn a short-term profit on interest rate differences and/or anticipated exchange rate shifts. These speculative capital flows are called "hot money" because they can move very quickly in and out of markets, potentially leading to market instability.

Financial accounting is the field of accounting concerned with the summary, analysis and reporting of financial transactions related to a business. This involves the preparation of financial statements available for public use. Stockholders, suppliers, banks, employees, government agencies, business owners, and other stakeholders are examples of people interested in receiving such information for decision making purposes.

In financial accounting, a cash flow statement, also known as statement of cash flows, is a financial statement that shows how changes in balance sheet accounts and income affect cash and cash equivalents, and breaks the analysis down to operating, investing and financing activities. Essentially, the cash flow statement is concerned with the flow of cash in and out of the business. As an analytical tool, the statement of cash flows is useful in determining the short-term viability of a company, particularly its ability to pay bills. International Accounting Standard 7 is the International Accounting Standard that deals with cash flow statements.
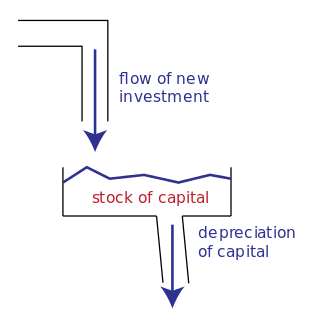
Economics, business, accounting, and related fields often distinguish between quantities that are stocks and those that are flows. These differ in their units of measurement. A stock is measured at one specific time, and represents a quantity existing at that point in time, which may have accumulated in the past. A flow variable is measured over an interval of time. Therefore, a flow would be measured per unit of time. Flow is roughly analogous to rate or speed in this sense.

In bookkeeping, an account refers to assets, liabilities, income, expenses, and equity, as represented by individual ledger pages, to which changes in value are chronologically recorded with debit and credit entries. These entries, referred to as postings, become part of a book of final entry or ledger. Examples of common financial accounts are sales, accountsreceivable, mortgages, loans, PP&E, common stock, sales, services, wages and payroll.

National accounts or national account systems (NAS) are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that rely on double-entry accounting. By design, such accounting makes the totals on both sides of an account equal even though they each measure different characteristics, for example production and the income from it. As a method, the subject is termed national accounting or, more generally, social accounting. Stated otherwise, national accounts as systems may be distinguished from the economic data associated with those systems. While sharing many common principles with business accounting, national accounts are based on economic concepts. One conceptual construct for representing flows of all economic transactions that take place in an economy is a social accounting matrix with accounts in each respective row-column entry.
In macroeconomics and international finance, the capital account records the net flow of investment transaction into an economy. It is one of the two primary components of the balance of payments, the other being the current account. Whereas the current account reflects a nation's net income, the capital account reflects net change in ownership of national assets.

The Mundell–Fleming model, also known as the IS-LM-BoP model, is an economic model first set forth (independently) by Robert Mundell and Marcus Fleming. The model is an extension of the IS–LM model. Whereas the traditional IS-LM model deals with economy under autarky, the Mundell–Fleming model describes a small open economy.

Capital budgeting, and investment appraisal, in corporate finance, is the planning process used to determine whether an organization's long term investments such as new machinery, replacement of machinery, new plants, new products, and research development projects are worth the funding of cash through the firm's capitalization structures. It is the process of allocating resources for major capital, or investment, expenditures. An underlying goal, consistent with the overall approach in corporate finance, is to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders.
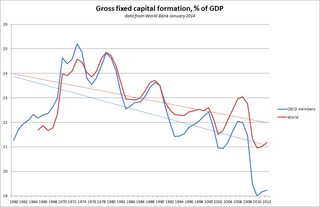
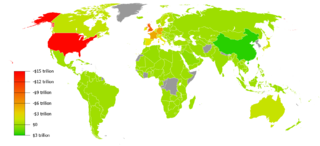
Capital formation is a concept used in macroeconomics, national accounts and financial economics. Occasionally it is also used in corporate accounts. It can be defined in three ways:
Capital began to flow in and out of Japan following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, but policy restricted loans from overseas. In the aftermath of World War II, Japan was a debtor nation until the mid-1960s. Subsequently, capital controls were progressively removed, in part as a result of agreements with the United States. This process led to rapid expansion of capital flows during the 1970s and especially the 1980s, when Japan became a creditor nation and the largest net investor in the world. This credit position resulted both from foreign direct investment by Japanese corporations, and portfolio investment. In particular, the rapid increase of Japan's direct investments overseas, much exceeding foreign investment in Japan, led to some tension with the US at the end of the 1980s.
Capital controls are residency-based measures such as transaction taxes, other limits, or outright prohibitions that a nation's government can use to regulate flows from capital markets into and out of the country's capital account. These measures may be economy-wide, sector-specific, or industry specific. They may apply to all flows, or may differentiate by type or duration of the flow.
Payback period in capital budgeting refers to the time required to recoup the funds expended in an investment, or to reach the break-even point.
Asset and liability management is the practice of managing financial risks that arise due to mismatches between the assets and liabilities as part of an investment strategy in financial accounting.
A sudden stop in capital flows is defined as a sudden slowdown in private capital inflows into emerging market economies, and a corresponding sharp reversal from large current account deficits into smaller deficits or small surpluses. Sudden stops are usually followed by a sharp decrease in output, private spending and credit to the private sector, and real exchange rate depreciation. The term “sudden stop” was inspired by a banker’s comment on a paper by Rüdiger Dornbusch and Alejandro Werner about Mexico, that “it is not speed that kills, it is the sudden stop”.

In business accounting, the statement of change in financial position is a financial statement that outlines the sources and uses of funds and explains any changes in cash or working capital.
Prudential capital controls are typical ways of prudential regulation that takes the form of capital controls and regulates a country’s capital account inflows. Prudential capital controls aim to mitigate systemic risk, reduce business cycle volatility, increase macroeconomic stability, and enhance social welfare.

The annual United Kingdom National Accounts records and describes economic activity in the United Kingdom and as such is used by government, banks, academics and industries to formulate the economic and social policies and monitor the economic progress of the United Kingdom. It also allows international comparisons to be made. The Blue Book is published by the UK Office for National Statistics alongside the United Kingdom Balance of Payments – The Pink Book.






