
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves leased telecommunication circuits.

Niklaus Emil Wirth is a Swiss computer scientist. He has designed several programming languages, including Pascal, and pioneered several classic topics in software engineering. In 1984 he won the Turing Award, generally recognized as the highest distinction in computer science, for developing a sequence of innovative computer languages.

Oberon is a general-purpose programming language first published in 1987 by Niklaus Wirth and the latest member of the Wirthian family of ALGOL-like languages. Oberon was the result of a concentrated effort to increase the power of Modula-2, the direct successor of Pascal, and simultaneously to reduce its complexity. Its principal new feature is the concept of type extension of record types: It permits the construction of new data types on the basis of existing ones and to relate them, deviating from the dogma of strictly static data typing. Type extension is Wirth's way of inheritance reflecting the viewpoint of the parent site. Oberon was developed as part of the implementation of the Oberon operating system at ETH Zurich in Switzerland. The name is from the moon of Uranus, Oberon.
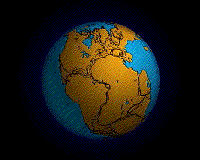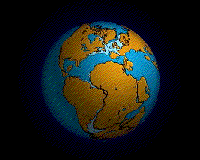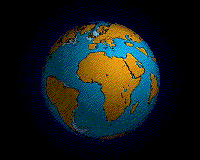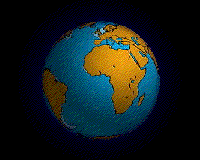
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some earth scientists use a different definition: "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times, although a minimum of about 75% of the continental crust then in existence has been proposed as a limit to separate supercontinents from other groupings.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used for the transfer of computer files between a client and server on a computer network.

ETH Zurich is a public research university in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. Founded by the Swiss Federal Government in 1854 with the stated mission to educate engineers and scientists, the school focuses exclusively on science, technology, engineering and mathematics. Like its sister institution EPFL, it is part of the Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology Domain, part of the Swiss Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research.

The Oberon System is a modular, single-user, single-process, multitasking operating system written in the programming language of the same name. It was originally developed in the late 1980s at ETH Zürich. The Oberon System has an unconventional visual text user interface instead of a conventional CLI or GUI. This "TUI" was very innovative in its time and influenced the design of the Acme text editor for the Plan 9 from Bell Labs operating system.

Oberon-2 is an extension of the original Oberon programming language that adds limited reflection and object-oriented programming facilities, open arrays as pointer base types, read-only field export and reintroduces the FOR loop from Modula-2.

Data corruption refers to errors in computer data that occur during writing, reading, storage, transmission, or processing, which introduce unintended changes to the original data. Computer, transmission, and storage systems use a number of measures to provide end-to-end data integrity, or lack of errors.

The Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) is a multi-disciplinary research institute for natural and engineering sciences in Switzerland. It is located in the Canton of Aargau in the municipalities Villigen and Würenlingen on either side of the River Aare, and covers an area over 35 hectares in size. Like ETH Zurich and EPFL, PSI belongs to the Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology Domain of the Swiss Confederation. The PSI employs around 2100 people. It conducts basic basic and applied research in the fields of matter and materials, human health, and energy and the environment. About 37 % of PSI’s research activities focus on material sciences, 24 % on life sciences, 19 % on general energy, 11 % on nuclear energy and safety, and 9 % on particle physics.

FileZilla is a free software, cross-platform FTP application, consisting of FileZilla Client and FileZilla Server. Client binaries are available for Windows, Linux, and macOS, server binaries are available for Windows only. Both server and client support FTP and FTPS, while the client can in addition connect to SFTP servers.

Barbara Liskov is an American computer scientist who is an Institute Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Ford Professor of Engineering in its School of Engineering's electrical engineering and computer science department. She was one of the first women to be granted a doctorate in computer science in the United States and is a Turing Award winner who developed the Liskov substitution principle.
Corrado Böhm was a Professor Emeritus at the University of Rome "La Sapienza" and a computer scientist known especially for his contributions to the theory of structured programming, constructive mathematics, combinatory logic, lambda calculus, and the semantics and implementation of functional programming languages.

The Dobson spectrophotometer, also known as Dobsonmeter, Dobson spectrometer, or just Dobson is one of the earliest instruments used to measure atmospheric ozone.
Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN) is a project of the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP) and the Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment (GEWEX) and as such is aimed detecting important changes in the Earth's radiation field at the Earth's surface which may be related to climate changes. The central archive of the BSRN is the World Radiation Monitoring Center (WRMC) which was initiated by Atsumu Ohmura in 1992 and operated at ETH until 2007. Since 2008 the WRMC is operated by the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI), Germany.

PANGAEA - Data Publisher for Earth & Environmental Science is a digital data library and a data publisher for earth system science. Data can be georeferenced in time and space.

The Federal Department of Home Affairs is a department of the federal administration of Switzerland and serves as the Swiss ministry of the interior. As of 2012, it is headed by Federal Councillor Alain Berset.

ETH Library is the largest public scientific and technical library in Switzerland. It serves as a central university library for ETH Zurich and a national centre for scientific and technical information. Besides providing information for members of ETH Zurich, it also offers resources for the interested public and companies from research and development. Its main focuses are electronic information services for university members and the development of innovative services.
Tanja Stadler is a German mathematician and professor of Computational Evolution at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology. She is known for her work in the field of phylogenetics.

The 'ERMETH was one of the first computers in Europe and was developed and built by Eduard Stiefel and his Institute for Applied Mathematics at the ETH Zurich between 1948 and 1956. It was then in use until 1963.














