Other
- Spirit XPL, a Gibson Spirit guitar model
- XPL (band), a Greek rap group
- XPL, an abbreviation for cross-polarized light
XPL may refer to:
While Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) has been in use since 1991, HTML 4.0 from December 1997 was the first standardized version where international characters were given reasonably complete treatment. When an HTML document includes special characters outside the range of seven-bit ASCII, two goals are worth considering: the information's integrity, and universal browser display.

Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.

Wireless Markup Language (WML), based on XML, is a now-obsolete markup language intended for devices that implement the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) specification, such as mobile phones. It provides navigational support, data input, hyperlinks, text and image presentation, and forms, much like HTML. It preceded the use of other markup languages now used with WAP, such as HTML itself, and XHTML.
In computer science, Backus–Naur form or Backus normal form (BNF) is a metasyntax notation for context-free grammars, often used to describe the syntax of languages used in computing, such as computer programming languages, document formats, instruction sets and communication protocols. They are applied wherever exact descriptions of languages are needed: for instance, in official language specifications, in manuals, and in textbooks on programming language theory.
The Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards is a nonprofit consortium that works on the development, convergence, and adoption of open standards for cybersecurity, blockchain, Internet of things (IoT), emergency management, cloud computing, legal data exchange, energy, content technologies, and other areas.
In software, an XML pipeline is formed when XML processes, especially XML transformations and XML validations, are connected.
The Web Services Business Process Execution Language (WS-BPEL), commonly known as BPEL, is an OASIS standard executable language for specifying actions within business processes with web services. Processes in BPEL export and import information by using web service interfaces exclusively.
The name Atom applies to a pair of related Web standards. The Atom Syndication Format is an XML language used for web feeds, while the Atom Publishing Protocol is a simple HTTP-based protocol for creating and updating web resources.
Apache Cocoon, usually abbreviated as Cocoon, is a web application framework built around the concepts of Pipeline, separation of concerns, and component-based web development. The framework focuses on XML and XSLT publishing and is built using the Java programming language. Cocoon's use of XML is intended to improve compatibility of publishing formats, such as HTML and PDF. The content management systems Apache Lenya and Daisy have been created on top of the framework. Cocoon is also commonly used as a data warehousing ETL tool or as middleware for transporting data between systems.
GML may refer to:

JSON is an open standard file format and data interchange format that uses human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of attribute–value pairs and arrays. It is a common data format with diverse uses in electronic data interchange, including that of web applications with servers.
The Sitemaps protocol allows a webmaster to inform search engines about URLs on a website that are available for crawling. A Sitemap is an XML file that lists the URLs for a site. It allows webmasters to include additional information about each URL: when it was last updated, how often it changes, and how important it is in relation to other URLs of the site. This allows search engines to crawl the site more efficiently and to find URLs that may be isolated from the rest of the site's content. The Sitemaps protocol is a URL inclusion protocol and complements robots.txt, a URL exclusion protocol.
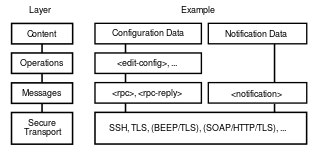
The Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) is a network management protocol developed and standardized by the IETF. It was developed in the NETCONF working group and published in December 2006 as RFC 4741 and later revised in June 2011 and published as RFC 6241. The NETCONF protocol specification is an Internet Standards Track document.
The Open Packaging Conventions (OPC) is a container-file technology initially created by Microsoft to store a combination of XML and non-XML files that together form a single entity such as an Open XML Paper Specification (OpenXPS) document. OPC-based file formats combine the advantages of leaving the independent file entities embedded in the document intact and resulting in much smaller files compared to normal use of XML.
xPL is an open protocol intended to permit the control and monitoring of home automation devices. The primary design goal of xPL is to provide a rich set of features and functionality, whilst maintaining an elegant, uncomplicated message structure. The protocol includes complete discovery and auto-configuration capabilities which support a fully "plug-n-play" architecture - essential to ensure a good end-user experience.
XQuery is a query and functional programming language that queries and transforms collections of structured and unstructured data, usually in the form of XML, text and with vendor-specific extensions for other data formats. The language is developed by the XML Query working group of the W3C. The work is closely coordinated with the development of XSLT by the XSL Working Group; the two groups share responsibility for XPath, which is a subset of XQuery.
In computing, Open Data Protocol (OData) is an open protocol that allows the creation and consumption of queryable and interoperable REST APIs in a simple and standard way. Microsoft initiated OData in 2007. Versions 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0 are released under the Microsoft Open Specification Promise. Version 4.0 was standardized at OASIS, with a release in March 2014. In April 2015 OASIS submitted OData v4 and OData JSON Format v4 to ISO/IEC JTC 1 for approval as an international standard. In December 2016, ISO/IEC published OData 4.0 Core as ISO/IEC 20802-1:2016 and the OData JSON Format as ISO/IEC 20802-2:2016.
XEP may refer to: