
Cygwin is a POSIX-compatible programming and runtime environment that runs natively on Microsoft Windows. Under Cygwin, source code designed for Unix-like operating systems may be compiled with minimal modification and executed.
Microsoft Windows, commonly referred to as Windows, is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families, all of which are developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Microsoft Windows families include Windows NT and Windows IoT; these may encompass subfamilies,. Defunct Microsoft Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone.
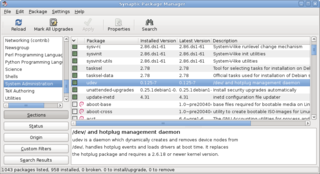
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer's operating system in a consistent manner.

Gambas is the name of an object-oriented dialect of the BASIC programming language, as well as the integrated development environment that accompanies it. Designed to run on Linux and other Unix-like computer operating systems, its name is a recursive acronym for Gambas Almost Means Basic. Gambas is also the word for prawns in the Spanish, French, and Portuguese languages, from which the project's logos are derived.
Cygwin/X is an implementation of the X Window System that runs under Microsoft Windows. It is part of the Cygwin project, and is installed using Cygwin's standard setup system. Cygwin/X is free software, licensed under the X11 License.
In computing, X-Win32 is a proprietary implementation of the X Window System for Microsoft Windows, produced by StarNet Communications. It is based on X11R7.4.
In software engineering, a compatibility layer is an interface that allows binaries for a legacy or foreign system to run on a host system. This translates system calls for the foreign system into native system calls for the host system. With some libraries for the foreign system, this will often be sufficient to run foreign binaries on the host system. A hardware compatibility layer consists of tools that allow hardware emulation.
GNU Aspell, usually called just Aspell, is a free software spell checker designed to replace Ispell. It is the standard spell checker for the GNU operating system. It also compiles for other Unix-like operating systems and Windows. The main program is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License, the documentation under the GNU Free Documentation License. Dictionaries for it are available for about 70 languages. The primary maintainer is Kevin Atkinson.
Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) is a software interface for Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that lets non-privileged users create their own file systems without editing kernel code. This is achieved by running file system code in user space while the FUSE module provides only a "bridge" to the actual kernel interfaces.

Xming is an X11 display server for Microsoft Windows operating systems, including Windows XP and later.

Transmission is a BitTorrent client which features a variety of user interfaces on top of a cross-platform back-end. Transmission is free software licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License, with parts under the MIT License.

The Apple–Intel architecture, or Mactel, is an unofficial name used for Apple Macintosh personal computers developed and manufactured by Apple Inc. that use Intel x86 processors, rather than the PowerPC and Motorola 68000 ("68k") series processors used in their predecessors or the ARM processors used in their successors. With the change in architecture, a change in firmware became necessary; Apple selected the Intel-designed Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) as its comparable component to the Open Firmware used on its PowerPC architectures, and as the firmware-based replacement for the PC BIOS from Intel. With the change in processor architecture to x86, Macs gained the ability to boot into x86-native operating systems, while Intel VT-x brought near-native virtualization with Mac OS X as the host OS.
The Windows NT startup process is the process by which Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 operating systems initialize. In Windows Vista and later, this process has changed significantly; see Windows Vista startup process for information about what has changed.

A live USB is a USB flash drive or external hard disk drive containing a full operating system that can be booted. They are the evolutionary next step after live CDs, but with the added benefit of writable storage, allowing customizations to the booted operating system. Live USBs can be used in embedded systems for system administration, data recovery, or test driving, and can persistently save settings and install software packages on the USB device.
A home server is a computing server located in a private residence providing services to other devices inside or outside the household through a home network or the Internet. Such services may include file and printer serving, media center serving, home automation control, web serving, web caching, file sharing and synchronization, video surveillance and digital video recorder, calendar and contact sharing and synchronization, account authentication, and backup services.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
This page is a comparison of remote desktop software available for various platforms.

NimbleX is a small Slackware-based Linux distribution optimized to run from a CD, USB drive or a network environment. NimbleX has been praised for how fast it boots, as well as for its small disk footprint, which is considered surprising for a distribution using KDE as desktop environment. NimbleX was also remarked for its web site that allows users to generate custom bootable images using just a web browser. It was also covered in mainstream Romanian press as the first Linux distribution put together by a Romanian.

Zorin OS is a personal computer operating system designed and promoted for users new to Linux-based computers. One of its built-in features lets users change the interface to resemble those of Microsoft Windows or macOS. Wine and PlayOnLinux can be easily installed in Zorin OS, allowing users to run compatible Windows software for ease of transition. Zorin OS's creators maintain three free-of-charge editions of the operating system, and an "Ultimate" edition for purchase.







