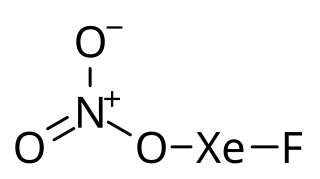The noble gases make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six naturally occurring noble gases are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).

Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized.

Xenon hexafluoroplatinate is the product of the reaction of platinum hexafluoride with xenon, in an experiment that proved the chemical reactivity of the noble gases. This experiment was performed by Neil Bartlett at the University of British Columbia, who formulated the product as "Xe+[PtF6]−", although subsequent work suggests that Bartlett's product was probably a salt mixture and did not in fact contain this specific salt.
In chemistry, noble gas compounds are chemical compounds that include an element from the noble gases, group 18 of the periodic table. Although the noble gases are generally unreactive elements, many such compounds have been observed, particularly involving the element xenon.
Xenon tetroxide is a chemical compound of xenon and oxygen with molecular formula XeO4, remarkable for being a relatively stable compound of a noble gas. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is stable below −35.9 °C; above that temperature it is very prone to exploding and decomposing into elemental xenon and oxygen (O2).
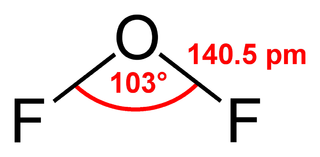
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula OF2. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a "bent" molecular geometry. It is strong oxidizer and has attracted attention in rocketry for this reason. With a boiling point of -144.75 °C, OF2 is the most volatile (isolable) triatomic compound. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.

Xenon tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with chemical formula XeF
4. It was the first discovered binary compound of a noble gas. It is produced by the chemical reaction of xenon with fluorine:
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon that have been studied experimentally, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All known are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors.
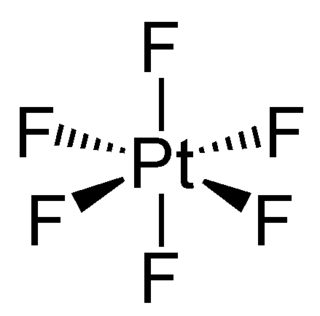
Platinum hexafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula PtF6, and is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is a dark-red volatile solid that forms a red gas. The compound is a unique example of platinum in the +6 oxidation state. With only four d-electrons, it is paramagnetic with a triplet ground state. PtF6 is a strong fluorinating agent and one of the strongest oxidants, capable of oxidising xenon and O2. PtF6 is octahedral in both the solid state and in the gaseous state. The Pt-F bond lengths are 185 picometers.

Xenon trioxide is an unstable compound of xenon in its +6 oxidation state. It is a very powerful oxidizing agent, and liberates oxygen from water slowly, accelerated by exposure to sunlight. It is dangerously explosive upon contact with organic materials. When it detonates, it releases xenon and oxygen gas.

Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.
A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m−, or QXnF6m+. Many molecules fit this formula. An important hexafluoride is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), which is a byproduct of the mining of phosphate rock. In the nuclear industry, uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is an important intermediate in the purification of this element.

Xenon dioxide, or xenon(IV) oxide, is a compound of xenon and oxygen with formula XeO2 which was synthesized in 2011. It is synthesized at 0 °C by hydrolysis of xenon tetrafluoride in aqueous sulfuric acid:

Xenon dichloride (XeCl2) is a xenon compound and the only known stable chloride of xenon. The compound can be prepared by using microwave discharges towards the mixture of xenon and chlorine, and it can be isolated from a condensate trap. One experiment tried to use xenon, chlorine and boron trichloride to produce XeCl2·BCl3, but only generated xenon dichloride.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
Xenon nitrate, also called xenon dinitrate, is an inorganic compound consisting of one xenon atom bonded to two nitrate groups. It can be made by reacting xenon difluoride with anhydrous nitric acid, but it only exists transiently before decomposing, and therefore it has not been isolated and full characterized. A related compound, xenon fluoride nitrate, has been made and is stable enough to be studied in more detail.
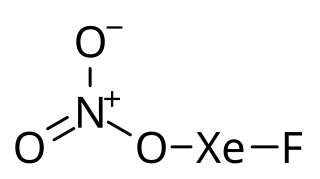
Xenon fluoride nitrate, also known as fluoroxenonium nitrate, is the chemical compound with formula FXeONO2.

Xenon tetrachloride is an unstable inorganic compound with the chemical formula XeCl4. Unlike other noble gas/halide compounds, it cannot be synthesized by simply combining the elements, by using a more-active halogenating agent, or by substitution of other halides on tetrahaloxenon compounds. Instead, a decay technique can be used, starting with K129ICl4. The iodine-129 atom of the 129
ICl–
4 covalent cluster is radioactive and undergoes beta decay to become xenon-129. The resulting XeCl4 molecule has a square planar molecular geometry analogous to xenon tetrafluoride.

Bis(pentafluorophenyl)xenon is an unstable organic compound of xenon. It consists of two fluorinated phenyl rings connected to xenon.

Radon compounds are compounds formed by the element radon (Rn). Radon is a member of the zero-valence elements that are called noble gases, and is chemically not very reactive. The 3.8-day half-life of radon-222 makes it useful in physical sciences as a natural tracer. Because radon is a gas at standard conditions, unlike its decay-chain parents, it can readily be extracted from them for research.