
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi and Kamchatka Peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and the Yukon in Canada.

The dire wolf is an extinct canine. The dire wolf lived in the Americas during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene epochs. The species was named in 1858, four years after the first specimen had been found. Two subspecies are recognized: Aenocyon dirus guildayi and Aenocyon dirus dirus. The largest collection of its fossils has been obtained from the Rancho La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles.

Ekoostik hookah is a jam band from Columbus, Ohio. Formed in 1991, the band has made multiple national tours in the US, as well as performing in overseas locales like Amsterdam and Jamaica, although they may more commonly be found playing local Columbus, Ohio venues like Newport Music Hall and Lifestyle Communities Pavilion. They are fixtures in many fine venues across the midwest. The band has shared the stage with many of today's top touring "jam bands", as well as stars such as Willie Nelson, Arlo Guthrie, Bob Weir, and Bruce Hornsby.

During the Last Glacial Maximum, the mammoth steppe, also known as steppe-tundra, was once the Earth's most extensive biome. It stretched east-to-west, from the Iberian Peninsula in the west of Europe, across Eurasia to North America, through Beringia and Canada; from north-to-south, the steppe reached from the arctic islands southward to China. The mammoth steppe was cold and dry, and relatively featureless, though topography and geography varied considerably throughout. Some areas featured rivers which, through erosion, naturally created gorges, gulleys, or small glens. The continual glacial recession and advancement over millennia contributed more to the formation of larger valleys and different geographical features. Overall, however, the steppe is known to be flat and expansive grassland. The vegetation was dominated by palatable, high-productivity grasses, herbs and willow shrubs.

The Africanis is a dog landrace found across southern Africa.
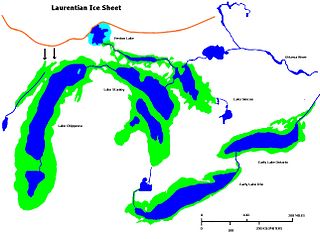
Early Lake Erie was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago. The early Erie fed waters to Glacial Lake Iroquois.

Haplogroup M is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. An enormous haplogroup spanning all the continents, the macro-haplogroup M, like its sibling the macro-haplogroup N, is a descendant of the haplogroup L3.

Haplogroup N is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) clade. A macrohaplogroup, its descendant lineages are distributed across many continents. Like its sibling macrohaplogroup M, macrohaplogroup N is a descendant of the haplogroup L3.

In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup A is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup Z is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.

The domestication of the dog was the process which created the domestic dog. This included the dog's genetic divergence from the wolf, its domestication, and the emergence of the first dogs. Genetic studies suggest that all ancient and modern dogs share a common ancestry and descended from an ancient, now-extinct wolf population – or closely related wolf populations – which was distinct from the modern wolf lineage. The dog's similarity to the grey wolf is the result of substantial dog-into-wolf gene flow, with the modern grey wolf being the dog's nearest living relative. An extinct Late Pleistocene wolf may have been the ancestor of the dog.
Haplogroup I-M438, also known as I2, is a human DNA Y-chromosome haplogroup, a subclade of haplogroup I-M170. Haplogroup I-M438 originated some time around 26,000–31,000 BCE. It originated in Europe and developed into several main subgroups: I2-M438*, I2a-L460, I2b-L415 and I2c-L596. The haplogroup can be found all over Europe and reaches its maximum frequency in the Dinaric Alps (Balkans) via founder effect, related to the migrations of the Early Slavs to the Balkan peninsula.

Yellow Bird Project is a company that collaborates with indie bands to raise money for charity, primarily through the sale of T-shirts. They approach indie bands, asking them to choose a charity and submit an original design. Each design is then printed onto T-shirts and sold exclusively through the YBP website to raise money for the charity of the artist's choosing. Some of the bands which they have collaborated with include Andrew Bird, Bloc Party, Bon Iver, Broken Social Scene, Devendra Banhart, and The National. Over the years, the company has diversified to include book publishing, album releases and film projects. In 2016, UK based charity Trekstock took over the management of the project, enabling all funds to be raised for one cause - young adults living with cancer.
African village dogs are dogs found in Africa that are directly descended from an ancestral pool of indigenous dogs. African village dogs became the close companion of people in Africa, beginning in North Africa and spreading south.
YBP 1194 is a G-type main-sequence star, class G5V, in the open cluster M67 in the constellation Cancer. It is the best solar twin found to date, having the near exact temperature and mass as the Sun. YBP 1194 has a higher metallicity than the Sun and is 0.5 billion years younger at an age of 4.2 billion years old, but due to the distance, the error bar is high at ±1.6 billion years. On December 19, 2013, it was announced to have an extrasolar planet with a period of 6.9 days and a high eccentricity of 0.24 with a mass of 0.34 MJ. It is about 2,772 light-years from the Sun. It is packed in a small cluster, Messier 67, with a radius of 10 ly, with over 500 other stars. For comparison, the Sun has 17 stars at a distance of 10 ly and about 134 stars at a distance of 20 ly.

The Beringian wolf is an extinct population of wolf that lived during the Ice Age. It inhabited what is now modern-day Alaska, Yukon, and northern British Columbia. Some of these wolves survived well into the Holocene. The Beringian wolf is an ecomorph of the gray wolf and has been comprehensively studied using a range of scientific techniques, yielding new information on their prey species and feeding behaviors. It has been determined that these wolves are morphologically distinct from modern North American wolves and genetically basal to most modern and extinct wolves. The Beringian wolf has not been assigned a subspecies classification and its relationship with the extinct European cave wolf is not clear.

Lake Chippewa was a prehistoric proglacial lake. The basin is now Lake Michigan. It formed about 10,600 years before present (YBP). The lake occupied the depression left by the Michigan Lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet.

The evolution of the wolf occurred over a geologic time scale of at least 300 thousand years. The grey wolf Canis lupus is a highly adaptable species that is able to exist in a range of environments and which possesses a wide distribution across the Holarctic. Studies of modern grey wolves have identified distinct sub-populations that live in close proximity to each other. This variation in sub-populations is closely linked to differences in habitat – precipitation, temperature, vegetation, and prey specialization – which affect cranio-dental plasticity.

Canis mosbachensis, sometimes known as the Mosbach wolf, is an extinct small wolf that once inhabited Eurasia from the Middle Pleistocene era to the Late Pleistocene. It is widely accepted as the ancestor of Canis lupus, the grey wolf.












