See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Yiman. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Yiman may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Yiman. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
The terms aborigine and aboriginal are used in reference to peoples that inhabited a given region before colonisation by a foreign power. The terms are used particularly in association with former British colonies of 19th and 20th centuries; in the U.S. the terms native and Native American are preferred.

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania extending from New Guinea island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea, and eastward to Tonga.

Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands.
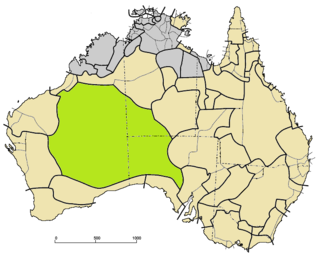
The Western Desert language, or Wati, is a dialect cluster of Australian Aboriginal languages in the Pama–Nyungan family.
Yimenosaurus is an extinct genus of plateosaurid sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived in China in the Early Jurassic. The genus was first named in 1990 by Ziqi Bai, Jie Yang and Guohui Wang, along with its type and only species, Yimenosaurus youngi. The species name honours renowned Chinese paleontologist Yang Zhongjian, the father of Chinese paleontology, known as C.C. Young in English. Known material includes the holotype, an almost complete skull and mandible, as well as incomplete cervical and dorsal vertebrae, a mostly complete sacrum, an ilium, ischia, partial ribs and complete femur, and a paratype, a well-preserved postcrania with a fragmentary skull.
Iman, Imann, Imaan, Eman, Emaan, or Imman may refer to:
Pitta Pitta is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language. It was spoken around Boulia, Queensland.
Diyari or Dieri is an Australian Aboriginal language spoken by the Diyari people in the far north of South Australia, to the east of Lake Eyre. It was studied by German Lutheran missionaries who translated Christian works into the language in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, so that it developed an extensive written form. Only a few fluent speakers of Diyari remained by the early 21st century, but a dictionary and grammar of the language was produced by linguist Peter K. Austin, and there is a project under way to teach it in schools.
Australians are people associated with the country of Australia, usually holding Australian citizenship. Australia is a multicultural society and has the world's ninth-largest immigrant population, with immigrants accounting for 29 percent of the population as of 2017.
Indigenous Australians are people who are descended from groups that lived in Australia and surrounding islands before British colonisation. They include the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples of Australia. The term Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people is preferred by many; First Nations of Australia, First Peoples of Australia and First Australians are also increasingly common terms.
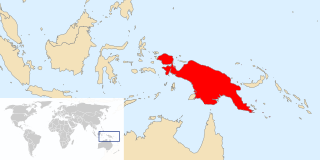
New Guinea is a large island separated by the shallow Torres Strait from the rest of the Australian continent. It is the world's second-largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), and the largest island wholly or partly within the Southern Hemisphere and Oceania.

Zhao Yiman was a female Chinese resistance fighter against the Imperial Japanese Army in Northeast China, which was under the occupation of the Japanese puppet state Manchukuo. She was captured in 1935 by Japanese forces and executed in 1936. She is considered a national hero in China, and an eponymous biopic was made for her in 1950. The 2005 film My Mother Zhao Yiman was based on her son's memory of her.
Aboriginal Australian kinship are the systems of law governing social interaction, particularly marriage, in traditional Australian Aboriginal cultures. It is an integral part of the culture of every Aboriginal group across Australia.
The Sichuanese, Sze Chuan or Si Ch'uan (previous romanize spelling) people (Sichuanese: 巴蜀人 Ba1su2ren2; IPA: ; alternatively 川人, 川渝人, 四川人 or 巴蜀民系) are a subgroup of Han Chinese living in mostly Sichuan province and Chongqing municipality of China (100,000,000 Million).

Maran or Maric is an extinct branch of the Pama–Nyungan family of Australian languages formerly spoken throughout much of Queensland by many of the Murri peoples. The well attested Maric languages are clearly related; however, many languages of the area became extinct before much could be documented of them, and their classification is uncertain. The clear Maric languages are:
The Yiman language is an Australian Aboriginal language of Queensland. Ethnically the speakers were Bidjara; that and geography suggests that it may have been a Maric language, assuming it was a distinct language at all. It is attested in a word list collected by Meston and held in the State Library of Queensland, but as of 2014 the data had not been verified by the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies.
The Yiman, also known as Yeeman, Eoman or Jiman, and by themselves in modern times as Iman, are an Aboriginal Australian people living in the Upper Dawson River region around Taroom of eastern Central Queensland.
The Wulili were an indigenous Australian people of the state of Queensland.
Zhang Yiman is a Chinese badminton player.