Related Research Articles
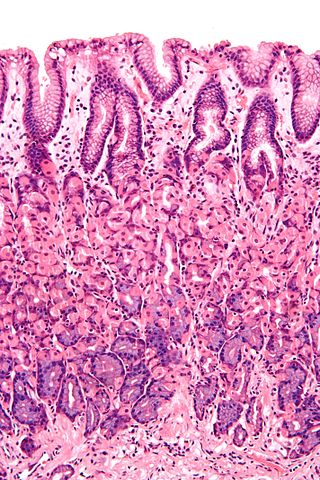
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated.
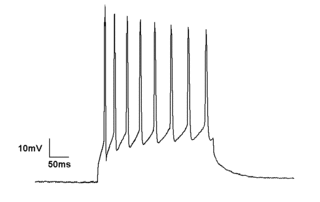
Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring.

Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm and mesoderm. Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastrula, which develops into the endoderm.

Thyroid follicular cells (also called thyroid epithelial cells or thyrocytes) are the major cell type in the thyroid gland, and are responsible for the production and secretion of the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). They form the single layer of cuboidal epithelium that makes up the outer structure of the almost spherical thyroid follicle.

The endodermis is the innermost layer of cortex in land plants. It is a cylinder of compact living cells, the radial walls of which are impregnated with hydrophobic substances to restrict apoplastic flow of water to the inside. The endodermis is the boundary between the cortex and the stele.

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology used to study ionic currents in individual isolated living cells, tissue sections, or patches of cell membrane. The technique is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells, and can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.

The Casparian strip is a band-like thickening in the center of the root endodermis of vascular plants. The composition of the region is mainly suberin, lignin and some structural proteins, which are capable of reducing the diffusive apoplastic flow of water and solutes into the stele and its width varies between species. The Casparian strip is impervious to water so can control the transportation of water and inorganic salts between the cortex and the vascular bundle, preventing water and inorganic salts from being transported to the stele through the apoplast, so that it must enter the cell membrane and move to the stele through the symplastic pathway, blocking the internal and external objects of the cell. The function of mass transportation are similar to that of animal tissues.. The development of the Casparian strip is regulated by transcription factors such as SHORT-ROOT (SHR), SCARECROW (SCR) and MYB36, as well as polypeptide hormone synthesised by midcolumn cells.

The symplast of a plant is the region enclosed by the cell membranes, within which water and solutes can diffuse freely. By contrast the apoplast is any fluid-filled space within the cell wall and extracellular space. Neighbouring cells are interconnected by microscopic channels known as plasmodesmata that traverse the cell walls. These channels, allow the flow of small molecules such as sugars, amino acids, and ions between cells. Larger molecules, including transcription factors and plant viruses, can also be transported through with the help of actin structures. The symplast allows direct cytoplasm-to-cytoplasm flow of water and other nutrients along concentration gradients. In particular, symplastic flow is used in the root systems to bring in nutrients from soil. Nutrient solutes move in this way through three skin layers of the roots: from cells of the epidermis, the outermost layer, through the cortex into the endodermis.
The primitive node is the organizer for gastrulation in most amniote embryos. In birds, it is known as Hensen's node, and in amphibians, it is known as the Spemann-Mangold organizer. It is induced by the Nieuwkoop center in amphibians, or by the posterior marginal zone in amniotes including birds.

In the embryonic development of vertebrates, pharyngeal pouches form on the endodermal side between the pharyngeal arches. The pharyngeal grooves form the lateral ectodermal surface of the neck region to separate the arches.

The lung bud sometimes referred to as the respiratory bud forms from the respiratory diverticulum, an embryological endodermal structure that develops into the respiratory tract organs such as the larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. It arises from part of the laryngotracheal tube.

The development of fishes is unique in some specific aspects compared to the development of other animals.

In amniote embryology, the hypoblast is one of two distinct layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastodisc in reptiles and birds. The hypoblast gives rise to the yolk sac, which in turn gives rise to the chorion.

Transcription factor GATA-6, also known as GATA-binding factor 6 (GATA6), is protein that in humans is encoded by the GATA6 gene. The gene product preferentially binds (A/T/C)GAT(A/T)(A) of the consensus binding sequence.

Schiller–Duval body is a cellular structure seen by microscope in endodermal sinus tumors which are the most common testicular cancer in children. Schiller-Duval bodies are present in approximately 50% of these tumors, and if found are pathognomonic. They are named for Mathias-Marie Duval and Walter Schiller who described them in the late nineteenth century.
Karyolysus is a genus of coccidia. With the exception of K. sonomae whose vertebrate host is the yellow-legged frog, species in this genus only infect lizards of the genus Lacerta.

Endodermal sinus tumor (EST) is a member of the germ cell tumor group of cancers. It is the most common testicular tumor in children under three, and is also known as infantile embryonal carcinoma. This age group has a very good prognosis. In contrast to the pure form typical of infants, adult endodermal sinus tumors are often found in combination with other kinds of germ cell tumor, particularly teratoma and embryonal carcinoma. While pure teratoma is usually benign, endodermal sinus tumor is malignant.

The anal pore or cytoproct is a structure in various single-celled eukaryotes where waste is ejected after the nutrients from food have been absorbed into the cytoplasm.

SRY-box 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX17 gene.

Anatomical terminology is used to describe microanatomical structures. This helps describe precisely the structure, layout and position of an object, and minimises ambiguity. An internationally accepted lexicon is Terminologia Histologica.
References
- Frank J. Dye (21 February 2012). Dictionary of Developmental Biology and Embryology. John Wiley & Sons. p. 228. ISBN 978-0-470-90595-1.