Other
- Mineros de Zacatecas, Mexican football team
- "Zacatecas March", Zacatecas patriotic song
- Zacatecas ankasokellus , a species of moth in the monotypic genus Zacatecas
Zacatecas is a state of Mexico.
Zacatecas may also refer to:

Zacatecas is the principal city within the municipality in Mexico of the same name, and the capital and the largest city of the state of Zacatecas. Located in north-central Mexico, the city had its start as a Spanish mining camp in the mid-16th century. Native Americans had already known about the area's rich deposits of silver and other minerals. Due to the wealth that the mines provided, Zacatecas quickly became one of the most important mining cities in New Spain. The area saw battles during the turbulent 19th century, but the next major event was the Battle of Zacatecas during the Mexican Revolution when Francisco Villa captured the town, an event still celebrated every anniversary. Today, the colonial part of the city is a World Heritage Site, due to the Baroque and other structures built during its mining days. Mining still remains an important industry. The name Zacatecas is derived from the Zacateco people and has its roots in Nahuatl. The name means "people of the grasslands".
Hidalgo may refer to:
Guadalupe or Guadeloupe may refer to:

Aguascalientes, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Aguascalientes, is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. At 22°N and with an average altitude of 1,950 m (6,400 ft) above sea level it is predominantly of semi-arid climate. The state is located in west-central Mexico and is located in the northern part of the Bajío region, which is in the north-central part of the country, bordered by Zacatecas to the north, east and west, and by Jalisco to the south.

Fresnillo is a city in north central Mexico, founded in 1554 by Francisco de Ibarra. It is the second largest city in Zacatecas state and the seat of Fresnillo municipality. As a rail and highway junction, Fresnillo is the center of a rich mining area known especially for silver, and the location of one of the world's richest silver mines, the Mina Proaño or Fresnillo Mine, which belongs to the Peñoles mining company. Other important economic activities include agriculture, cattle raising, and a mining school. Fresnillo is also the municipal seat of the municipality of the same name which surrounds it. The municipality had a population of 196,538 and an areal extent of 4,947 square kilometres (1,910 sq mi).
Zacatecas, Mexico, may refer to:
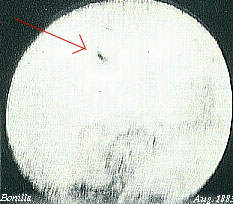
The Bonilla observation was an astronomical event in 1883 in which hundreds of unidentified flying objects were observed and photographed by Mexican astronomer José Bonilla.

Ignacio López Rayón was a general who led the insurgent forces of his country after Miguel Hidalgo's death, during the first years of the Mexican War of Independence. He subsequently established the first government, Zitacuaro Council, and first constitution of the proposed independent nation, called Constitutional Elements.

The Mixtón War (1540-1542) was a rebellion by the Caxcan people of northwestern Mexico against the Spanish conquerors. The war was named after Mixtón, a hill in Zacatecas which served as an Indigenous stronghold.

Ojuelos de Jalisco is a town and municipality in the state of Jalisco, Mexico. The town's 1990 population was 7,265, although by the year 2010 it had increased to 11,881.

The Bajío is a cultural and geographical region within the central Mexican plateau which roughly spans from northwest of Mexico City to the main silver mines in the northern-central part of the country. This includes the states of Querétaro, Guanajuato, parts of Jalisco, Aguascalientes and parts of Zacatecas, San Luis Potosí and Michoacán.
Florencia may refer to:

Guadalupe is a town in the state of Zacatecas, Mexico. It is located in the central region of the state and is the head of the Municipality of Guadalupe. With a population of 170,029 inhabitants, it is the most populated city in the state and with the city of Zacatecas and surrounding towns it forms a metropolitan area. On August 1, 2010, the Camino Real de Tierra Adentro was inscribed by UNESCO on the World Heritage List, being the former Apostolic College of Propaganda Fide of Our Lady of Guadalupe, one of the sites on the cultural itinerary that reached this title, for its architectural richness and contribution to the evangelization of the north of New Spain. On June 30, 2015, the Legislative Branch of the State of Zacatecas approved that the city of Guadalupe Zacatecas be declared a Historical City, a title that came into effect on Thursday, September 3 of that same year after its promulgation in decree number 400 published in the Official Newspaper of the State of Zacatecas. On October 11, 2018 at the Fifth National Fair of Pueblos Mágicos held in the city of Morelia, Michoacán, Guadalupe received incorporation into the Pueblos Mágicos program, being the sixth to have this registration in the state of Zacatecas.
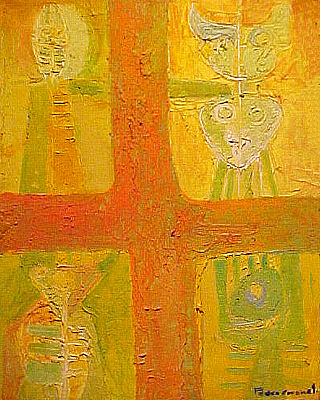
Pedro Coronel was a Mexican sculptor and painter, part of the Generación de la Ruptura, bringing innovation into Mexican art in the mid 20th century. Coronel’s training was with artists of the Mexican muralism tradition, with influence from artists like Diego Rivera. This influence remained with the use of pre Hispanic themes and colors in his work. However, his artistic trajectory took him towards more use of color and more abstract forms in his work, due to influences from artists such as Rufino Tamayo. His work was exhibited and gained recognition in Mexico, the United States and Europe. Shortly before his death, he donated his considerable personal art collection to the people of Mexico, which was used to open the Museo Pedro Coronel in the city of Zacatecas.

Zacatecas ( ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Zacatecas, is one of the 31 states of Mexico. It is divided into 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas.
The Battle of Zacatecas can refer to the following:

Club Deportivo Mineros de Zacatecas is a Mexican football club based in Zacatecas (city), Zacatecas, Mexico. The club compete in the Mexican Liga de Expansión MX. They are currently managed by Nacho Castro.

The Tuzos de la Universidad Autónoma de Zacatecas, commonly known as Tuzos UAZ, or just UAZ, is a Mexican football club based in Zacatecas City. The club was founded in 1990, and currently plays in the Serie A of Liga Premier.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Zacatecas since 30 December 2021. On 14 December 2021, the Congress of Zacatecas passed a same-sex marriage bill by 18 votes to 10. The legislation was published in the official state gazette on 29 December, and came into force the following day. Prior to statewide legalisation, five municipalities of Zacatecas issued marriage licenses to same-sex couples despite a state ban, comprising about a quarter of the state population. These five municipalities were Zacatecas City, Cuauhtémoc, Villanueva, Miguel Auza and Fresnillo.