Zootope is the total habitat available for colonisation within any certain ecotope or biotope by animal life. The community of animals so established constitutes the zoocoenosis of that ecotope.

In ecology, a habitat is the type of natural environment in which a particular species of organism lives. It is characterized by both physical and biological features. A species' habitat is those places where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction.
Ecotopes are the smallest ecologically distinct landscape features in a landscape mapping and classification system. As such, they represent relatively homogeneous, spatially explicit landscape functional units that are useful for stratifying landscapes into ecologically distinct features for the measurement and mapping of landscape structure, function and change.

A biotope is an area of uniform environmental conditions providing a living place for a specific assemblage of plants and animals. Biotope is almost synonymous with the term habitat, which is more commonly used in English-speaking countries. However, in some countries these two terms are distinguished: the subject of a habitat is a population, the subject of a biotope is a biocoenosis or biological community.
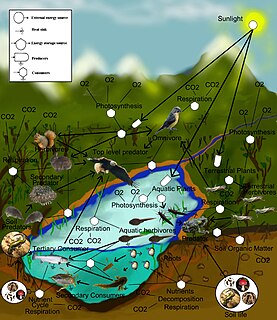
All these words (ecotope, biotope, zootope and others) describe environmental niches at very small scales of consideration. The rabbits and squirrels and mosquitoes of any suburban garden or village park, or the deer and wolves and birds of a wilderness ravine would each be deserving of the label.

A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the display, cultivation, or enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The garden can incorporate both natural and man-made materials. The most common form today is known as a residential garden, but the term garden has traditionally been a more general one. Zoos, which display wild animals in simulated natural habitats, were formerly called zoological gardens. Western gardens are almost universally based on plants, with garden often signifying a shortened form of botanical garden. Some traditional types of eastern gardens, such as Zen gardens, use plants sparsely or not at all.

A park is an area of natural, semi-natural or planted space set aside for human enjoyment and recreation or for the protection of wildlife or natural habitats. Urban parks are green spaces set aside for recreation inside towns and cities. National parks and Country parks are green spaces used for recreation in the countryside. State parks and Provincial parks are administered by sub-national government states and agencies. Parks may consist of grassy areas, rocks, soil and trees, but may also contain buildings and other artifacts such as monuments, fountains or playground structures. Many parks have fields for playing sports such as soccer, baseball and football, and paved areas for games such as basketball. Many parks have trails for walking, biking and other activities. Some parks are built adjacent to bodies of water or watercourses and may comprise a beach or boat dock area. Urban parks often have benches for sitting and may contain picnic tables and barbecue grills.

Wilderness or wildland is a natural environment on Earth that has not been significantly modified by human activity. It may also be defined as: "The most intact, undisturbed wild natural areas left on our planet—those last truly wild places that humans do not control and have not developed with roads, pipelines or other industrial infrastructure." The term has traditionally referred to terrestrial environments, though growing attention is being placed on marine wilderness. Recent maps of wilderness suggest it covers roughly one quarter of Earth's terrestrial surface, but is being rapidly degraded by human activity. Even less wilderness remains in the ocean, with only 13.2% free from intense human activity.