
Noscapine is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae. It lacks significant hypnotic, euphoric, or analgesic effects affording it with very low addictive potential. This agent is primarily used for its antitussive (cough-suppressing) effects.

Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids
In enzymology, a (RS)-norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
(S)-Tetrahydroberberine oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the final transformation in the biosynthesis of berberine, a quaternary benzylisoquinoline alkaloid of the protoberberine structural subgroup. This reaction pathway catalyzes the four-electron oxidation of (S)-tetrahydroberberine in the presence of oxygen to produce berberine and hydrogen peroxide as products.
In enzymology, a reticuline oxidase (EC 1.21.3.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a berbamunine synthase (EC 1.14.19.66, Formerly EC 1.1.3.34 and EC 1.14.21.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-canadine synthase (EC 1.14.21.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-cheilanthifoline synthase (EC 1.14.21.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase is a zinc-dependent enzyme and a member of the YgbB N terminal protein domain, which participates in the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It catalyzes the following reaction:
The enzyme deacetylipecoside synthase (EC 4.3.3.4) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme deacetylisoipecoside synthase (EC 4.3.3.3) catalyzes the chemical reaction
Strictosidine synthase (EC 4.3.3.2) is an enzyme in alkaloid biosynthesis that catalyses the condensation of tryptamine with secologanin to form strictosidine in a formal Pictet–Spengler reaction:
The enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.80) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme germacrene-A synthase (EC 4.2.3.23) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme pseudouridylate synthase (EC 4.2.1.70) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Higenamine (norcoclaurine) is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants including Nandina domestica (fruit), Aconitum carmichaelii (root), Asarum heterotropioides, Galium divaricatum, Annona squamosa, and Nelumbo nucifera.
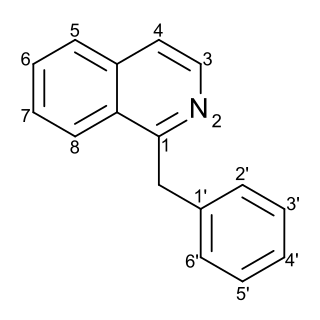
Substitution of the heterocycle isoquinoline at the C1 position by a benzyl group provides 1‑benzylisoquinoline, the most widely examined of the numerous benzylisoquinoline structural isomers. The 1-benzylisoquinoline moiety can be identified within numerous compounds of pharmaceutical interest, such as moxaverine; but most notably it is found within the structures of a wide variety of plant natural products, collectively referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. This class is exemplified in part by the following compounds: papaverine, noscapine, codeine, morphine, apomorphine, berberine, tubocurarine.

(S)-Canadine, also known as (S)-tetrahydroberberine and xanthopuccine, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA), of the protoberberine structural subgroup, and is present in many plants from the family Papaveraceae, such as Corydalis yanhusuo and C. turtschaninovii.

4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, also known as p-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, is a natural product with the formula HOC6H4CH2CHO. It is a derivative of phenylacetaldehyde and occurs as a white solid at room temperature.







