Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell.

Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.

The halogens are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would exclude tennessine as its chemistry is unknown and is theoretically expected to be more like that of gallium. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17.

A polyatomic ion is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zero. The term molecule may or may not be used to refer to a polyatomic ion, depending on the definition used. The prefix poly- carries the meaning "many" in Greek, but even ions of two atoms are commonly described as polyatomic.
In chemistry, a structural isomer of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept.
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula HCl and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl.
In chemistry, a halide is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, astatide, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX. Many salts are halides; the hal- syllable in halide and halite reflects this correlation. All Group 1 metals form halides that are white solids at room temperature.

The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rule is especially applicable to carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens; although more generally the rule is applicable for the s-block and p-block of the periodic table. Other rules exist for other elements, such as the duplet rule for hydrogen and helium, or the 18-electron rule for transition metals.
In chemistry, an interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.

Fluoromethane, also known as methyl fluoride, Freon 41, Halocarbon-41 and HFC-41, is a non-toxic, liquefiable, and flammable gas at standard temperature and pressure. It is made of carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine. The name stems from the fact that it is methane (CH4) with a fluorine atom substituted for one of the hydrogen atoms. It is used in semiconductor manufacturing processes as an etching gas in plasma etch reactors.
In chemistry, the valence or valency of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
The ozone depletion potential (ODP) of a chemical compound is the relative amount of degradation to the ozone layer it can cause, with trichlorofluoromethane being fixed at an ODP of 1.0. Chlorodifluoromethane (R-22), for example, has an ODP of 0.05. CFC 11, or R-11 has the maximum potential amongst chlorocarbons because of the presence of three chlorine atoms in the molecule.
In quantum chemistry, the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM), sometimes referred to as atoms in molecules (AIM), is a model of molecular and condensed matter electronic systems in which the principal objects of molecular structure - atoms and bonds - are natural expressions of a system's observable electron density distribution function. An electron density distribution of a molecule is a probability distribution that describes the average manner in which the electronic charge is distributed throughout real space in the attractive field exerted by the nuclei. According to QTAIM, molecular structure is revealed by the stationary points of the electron density together with the gradient paths of the electron density that originate and terminate at these points.
An oxyacid, oxoacid, or ternary acid is an acid that contains oxygen. Specifically, it is a compound that contains hydrogen, oxygen, and at least one other element, with at least one hydrogen atom bonded to oxygen that can dissociate to produce the H+ cation and the anion of the acid.

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.

Xenon dichloride (XeCl2) is a xenon compound and the only known stable chloride of xenon. The compound can be prepared by using microwave discharges towards the mixture of xenon and chlorine, and it can be isolated from a condensate trap. One experiment tried to use xenon, chlorine and boron trichloride to produce XeCl2·BCl3, but only generated xenon dichloride.

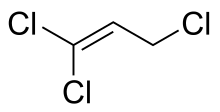
1,1,2,2,3,3-Hexachloropropane is a compound of chlorine, hydrogen, and carbon, with structural formula Cl2HC−CCl2−CCl2H. Its molecule can be described as that of propane with chlorine atoms substituted for six hydrogen atoms, two on each carbon. It is a liquid at ambient temperature.
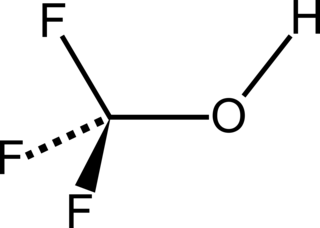
Trifluoromethanol is the organic compound with the formula CHF
3O. It is also referred to as perfluoromethanol or trifluoromethyl alcohol. The compound is the simplest perfluoroalcohol. The substance is a colorless gas, which is unstable at room temperature.
Eulim or ilm is a chemistry library written in Ruby under the MIT license. It supports the calculation of molecular mass of compound, balancing chemical equations, efficient handling of states of chemical species and many more things.