
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbine involves advanced metalwork to form high-grade steel alloys into precision parts using technologies that first became available in the 20th century; continued advances in durability and efficiency of steam turbines remains central to the energy economics of the 21st century.

A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
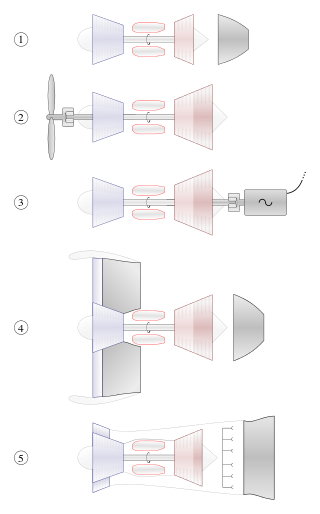
A gas turbine, gas turbine engine, or also known by its old name internal combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part and are, in the direction of flow:

The Airbus A400M Atlas is a European four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft. It was designed by Airbus Military, now Airbus Defence and Space, as a tactical airlifter with strategic capabilities to replace older transport aircraft, such as the Transall C-160 and the Lockheed C-130 Hercules. The A400M is sized between the C-130 and the Boeing C-17 Globemaster III. It can carry heavier loads than the C-130 and can use rough landing strips. In addition to its transport capabilities, the A400M can perform aerial refueling and medical evacuation when fitted with appropriate equipment.

The Rolls-Royce Turbomeca RTM322 is a turboshaft engine produced by Safran Helicopter Engines. It was originally conceived and manufactured by Rolls-Royce Turbomeca Limited, a joint venture between Rolls-Royce plc and Turbomeca. The engine was designed to suit a wide range of military and commercial helicopter designs. The RTM322 can also be employed in maritime and industrial applications.

MTU Aero Engines AG is a German aircraft engine manufacturer. MTU develops, manufactures and provides service support for military and civil aircraft engines. MTU Aero Engines was formerly known as MTU München.

The Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6 is a turboprop aircraft engine produced by Pratt & Whitney Canada. Its design was started in 1958, it first ran in February 1960, first flew on 30 May 1961, entered service in 1964, and has been continuously updated since. The PT6 consists of two basic sections: a gas generator with accessory gearbox, and a free-power turbine with reduction gearbox. In aircraft, the engine is often mounted "backwards," with the intake at the rear and the exhaust at the front, so that the turbine is directly connected to the propeller. Many variants of the PT6 have been produced, not only as turboprops but also as turboshaft engines for helicopters, land vehicles, hovercraft, and boats; as auxiliary power units; and for industrial uses. By November 2015, 51,000 had been produced, which had logged 400 million flight hours from 1963 to 2016. It is known for its reliability, with an in-flight shutdown rate of 1 per 651,126 hours in 2016. The PT6A turboprop engine covers the power range between 580 and 1,940 shp, while the PT6B/C are turboshaft variants for helicopters.

The Europrop International TP400-D6 is an 11,000 shp (8,200 kW) powerplant, developed and produced by Europrop International for the Airbus A400M Atlas military transport aircraft. The TP400 is the most powerful turboprop in service using a single propeller; only the Kuznetsov NK-12 from Russia and Progress D-27 from Ukraine, using contra-rotating propellers, is larger.

A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant, which is a kind of gas-fired power plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a combined gas and steam (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs.

Rolls-Royce Deutschland is a subsidiary of British aircraft engine maker Rolls-Royce plc. Its primarily facilities are located at Dahlewitz outside Berlin and Motorenfabrik Oberursel at Oberursel near Frankfurt am Main.
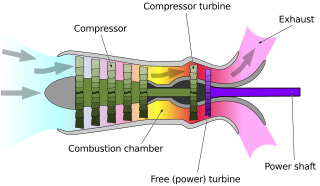
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaft horsepower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the exhaust and convert it into output shaft power. They are even more similar to turboprops, with only minor differences, and a single engine is often sold in both forms.

Safran Aircraft Engines, previously Snecma or Snecma Moteurs, is a French aerospace engine manufacturer headquartered in Courcouronnes and a subsidiary of Safran. It designs, manufactures and maintains engines for commercial and military aircraft as well as rocket engines for launch vehicles and satellites.

A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine enters a steam condenser where it is cooled to produce hot condensate which is recycled to the heating process to generate more high pressure steam. This is known as a Rankine cycle.

A constant speed drive (CSD) also known as a constant speed generator, is a type of transmission that takes an input shaft rotating at a wide range of speeds, delivering this power to an output shaft that rotates at a constant speed, despite the varying input. They are used to drive mechanisms, typically electrical generators, that require a constant input speed.

A turbo generator is an electric generator connected to the shaft of a water turbine or steam turbine or gas turbine for the generation of electric power. Large steam-powered turbo generators provide the majority of the world's electricity and are also used by steam-powered turbo-electric ships.

ITP Aero is a Spanish aero engine and gas turbine manufacturer.
Sener Aeronáutica is the aerospace arm of the Spanish company Grupo SENER. Since its formation in 1956, the group has developed expertise a number of fields including Marine, Power Systems, and Space. The group has links with a number of Spanish universities.
Europrop International (EPI) GmbH is a consortium set up in 2002 in the form of a company governed by German law, by the four main European aircraft engine manufacturers, MTU Aero Engines, Safran Aircraft Engines, Rolls-Royce and ITP Aero.
The Rolls-Royce RB3011 is a prototype propfan engine in development by Rolls-Royce plc. The design is also known as an "open rotor" engine.

A free-turbine turboshaft is a form of turboshaft or turboprop gas turbine engine where the power is extracted from the exhaust stream of a gas turbine by an independent turbine, downstream of the gas turbine. The power turbine is not mechanically connected to the turbines that drive the compressors, hence the term "free", referring to the independence of the power output shaft. This is opposed to the power being extracted from the turbine/compressor shaft via a gearbox.















