
The Balts or Baltic people are an ethno-linguistic group of people who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
The Chalcolithic, a name derived from the Greek: χαλκός khalkós, "copper" and from λίθος líthos, "stone" or Copper Age, also known as the Eneolithic or Aeneolithic, is an archaeological period that researchers now regard as part of the broader Neolithic. Earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. In the context of Eastern Europe, archaeologists often prefer the term "Eneolithic" to "Chalcolithic" or other alternatives.

Canaan was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur, and Gezer.

The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It was officially named the North Central Region by the Census Bureau until 1984. It is between the Northeastern United States and the Western United States, with Canada to the north and the Southern United States to the south.

The Bell Beaker culture is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from around 2800 BC, it lasted in Britain until as late as 1800 BC but in continental Europe only until 2300 BC, when it was succeeded by the Unetice culture. The culture was widely dispersed throughout Western Europe, from various regions in Iberia and spots facing northern Africa to the Danubian plains, the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, and also the islands of Sicily and Sardinia. The Bell Beaker phenomenon shows substantial regional variation, and a study from 2018 found that it was associated with genetically diverse populations.

A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.

Neolithic Europe is the period when Neolithic technology was present in Europe, roughly between 7000 BCE and c. 2000-1700 BCE. The Neolithic overlaps the Mesolithic and Bronze Age periods in Europe as cultural changes moved from the southeast to northwest at about 1 km/year – this is called the Neolithic Expansion.

The North European Plain is a geomorphological region in Europe, mostly in Poland, Denmark, Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, along with small parts of northern France and the Czech Republic.

Neve Monosson, also known as Neve Efraim and Neve Efraim Monosson, commonly called Monosson by its residents, is a municipal borough within the joint municipality of Yehud-Monosson in central Israel. In 2003 it had a population of 2,600 but its population is growing considerably due to the ongoing implementation of the Tamar Project, within which 200 family apartments are being replaced by 800 family apartments within a residents-initiated Pinui-Binui Project; this project is expected to almost double the population of Monosson.

Staig is a municipality in the district of Alb-Donau in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. The community belongs to the Gemeindeverwaltungsverband-Kirchberg Weihungstal with headquarter in Illerkirchberg.

The South-Western Iberian Bronze is a loosely defined Bronze Age culture of Southern Portugal and nearby areas of SW Spain. It replaced the earlier urban and Megalithic existing in that same region in the Chalcolithic age.

Ghassulian refers to a culture and an archaeological stage dating to the Middle and Late Chalcolithic Period in the Southern Levant. Its type-site, Teleilat Ghassul, is located in the eastern Jordan Valley near the northern edge of the Dead Sea, in modern Jordan. It was excavated in 1929-1938 and in 1959–1960, by the Jesuits. Basil Hennessy dug at the site in 1967 and in 1975–1977, and Stephen Bourke in 1994–1999.

The prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula begins with the arrival of the first hominins 1.2 million years ago and ends with the Punic Wars, when the territory enters the domains of written history. In this long period, some of its most significant landmarks were to host the last stand of the Neanderthal people, to develop some of the most impressive Paleolithic art, alongside Southern France, to be the seat of the earliest civilizations of Western Europe and finally to become a most desired colonial objective due to its strategic position and its many mineral riches.

The Prehistory of Siberia is marked by several archaeologically distinct cultures. In the Chalcolithic, the cultures of western and southern Siberia were pastoralists, while the eastern taiga and the tundra were dominated by hunter-gatherers until the Late Middle Ages and even beyond. Substantial changes in society, economics and art indicate the development of nomadism in the Central Asian steppes in the first millennium BC.
Chalcolithic Europe, the Chalcolithic period of Prehistoric Europe, lasted roughly from 3500 to 1700 BC.
Dizə is a village and municipality in the Sharur District of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Azerbaijan. It is located on the left bank of the river Arpachay (Arpa), on the Sharur plain. On the other side of the river is the village of Oglanqala.
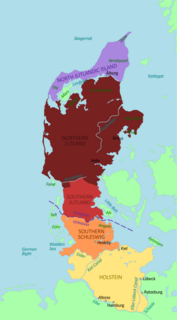
Jutland, known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula, is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany. The names are derived from the Jutes and the Cimbri, respectively.
Pandu Rajar Dhibi in the valley of the river Ajay is an Archaeological site in Ausgram II block in the Sadar North subdivision of Purba Bardhaman district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It was the first Chalcolithic site discovered in West Bengal. It was excavated by a team led by Dr. Paresh Chandra Dasgupta. The common man believes that the main mound at Pandu Rajar Dhibi is associated with King Pandu mentioned in the epic Mahabharata, hence the name came into being from the folklore.

Siswal is a village in Hisar district, Haryana, India. It located 28 km from Hisar city. It is a site of Chalcolithic age. It is a typesite for Siswal culture, dating from around 3800 BC, also known as Sothi–Siswal culture.

Cord-marked pottery or Cordmarked pottery is an early form of a simple earthenware pottery made in precontact villages. It allowed food to be stored and cooked over fire. Cord-marked pottery varied slightly around the world, depending upon the clay and raw materials that were available. It generally coincided with cultures moving to an agrarian and more settled lifestyle, like that of the Woodland period, as compared to a strictly hunter-gatherer lifestyle.















