See also
- Aquastar (watch brand)
- Aquastax , a mobile game
Aquastat is a device used in hydronic heating systems.
Aquastat may refer to:
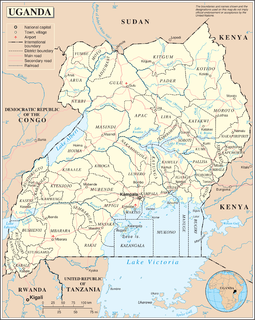
Uganda is located in eastern Africa, west of Kenya, south of South Sudan, east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and north of Rwanda and Tanzania. It is in the heart of the Great Lakes region, and is surrounded by three of them, Lake Edward, Lake Albert, and Lake Victoria. While much of its border is lakeshore, Uganda is landlocked with no access to the sea.

The Lielupe is a river in central Latvia. Its length is 119 km. The surface area of its drainage basin is 17,600 km². The average fall of the Lielupe is about and its average flow is 106 m³/s, although a maximum of 1380 m³/s has been reached during floods.

The Mahaweli River, is a 335 km (208 mi) long river, ranking as the longest river in Sri Lanka. It has a drainage basin of 10,448 km2 (4,034 sq mi), the largest in the country, which covers almost one-fifth of the total area of the island. The real beginning of Mahaweli Ganga starts at Polwathura(at Mahawila area), a remote village of Nuwara-Eliya District in bank Nawalapitiya of Kandy District by further joining of Hatton Oya and Kotmale Oya. The river reaches the Bay of Bengal on the southwestern side of Trincomalee Bay. The bay includes the first of a number submarine canyons, making Trincomalee one of the finest deep-sea harbors in the world.

A row crop is a crop that can be planted in rows wide enough to allow it to be tilled or otherwise cultivated by agricultural machinery, machinery tailored for the seasonal activities of row crops. Such crops are sown by drilling rather than broadcasting.
An aquastat is a device used in hydronic heating systems for controlling water temperature. To prevent the boiler from firing too often, aquastats have a high limit temperature and a low limit. If the thermostat is calling for heat, the boiler will fire until the high limit is reached, then shut off. The boiler will re-fire if the boiler water temperature drops below a range around the high limit. The high limit exists for the sake of efficiency and safety. The boiler will also fire when the boiler water temperature goes below a range around the low limit, ensuring that the boiler water temperature remains above a certain point. The low limit is intended for tankless domestic hot water---it ensures that boiler water is always warm enough to heat the domestic hot water. Many aquastats also have a differential ("diff") control which determines the size of the range around the "low" and/or "high" controls.
Syria is a semi-arid country with scarce water resources. The largest water-consuming sector in Syria is agriculture. Domestic water use is only about 9% of total water use. A big challenge for Syria is its high population growth, with a rapidly increasing demand for urban and industrial water. In 2006, the population of Syria was 19.4 million with a growth rate of 2.7%.

The Von Bach Dam is a rock-fill embankment dam on the Swakop River near Okahandja in the Otjozondjupa Region of Namibia. Built in 1968 and commissioned in 1970, the dam provides Namibia's capital of Windhoek with much of the city's water. It also supplies Okahandja. The dam has a capacity of 48.56 million cubic metres (63,510,000 cu yd). Water from the reservoir is sent directly to a water treatment plant downstream. The treatment plant was completed in 1971 and upgraded in 1997.
Water supply and sanitation in Iraq is characterized by poor water and service quality. Three decades of war, combined with limited environmental awareness, have destroyed Iraq's water resources management system. Thus, Iraq faces difficulties to realize the target of 91% of households using safe drinking water supply by 2015. Currently, 16% of households report daily problems with supply and 20% use an unsafe drinking water source. Furthermore, animal waste and septic tanks pollute the drinking water network.(11)
Health in the State of Palestine should be addressed by the healthcare system in the State of Palestine. There are problems arising from difficulty of access, water scarcity while burden of non-communicable diseases in Palestine is high; the problems are compounded in Gaza.

The Hatillo Dam is an earth and rock-filled embankment dam on the Yuna River about 6 km (3.7 mi) southwest of Cotuí in Sánchez Ramírez Province of the Dominican Republic. With a storage capacity of 710,000,000 m3 (580,000 acre⋅ft), the dam's reservoir is the largest in the country. The purpose of the dam is to produce hydroelectric power, provide water for irrigation and to control floods. The power station is located at the base of the dam and contains a single 8 MW Francis turbine-generator. Construction on the dam began in August 1977 and it was completed in 1984.

The Zaza Dam is an embankment dam on the Zaza River about 15 km (9.3 mi) southwest of Sancti Spíritus in Sancti Spíritus Province, Cuba. The dam was completed in 1972 with the primary purpose of irrigation but it also supports a small hydroelectric power station. The dam's reservoir, Zaza Reservoir, has a storage capacity of 1,020,000,000 m3 (830,000 acre⋅ft), making it the largest in the country. Beginning in the 1990s, the Chinese government helped plan and install the hydroelectric power station. It contains two 1.35 MW Kaplan turbine-generators. The first was commissioned in October 2008, the second in February 2009.

The Gudongkou Dam is a concrete-face rock-fill dam on the Xiangxi River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, in Xingshan County of Hubei Province, China. It is located about 64 km (40 mi) north of the Three Gorges Dam. The dam serves to provide for flood control and hydroelectric power generation. Preliminary construction started in 1990 but official construction on the dam and power station began on 1 March 1993. The dam began to impound its reservoir in 1996 and its three generators were commissioned between 1999 and 2000.

Goreangab Dam is a dam in the north-western suburbs of Windhoek, the capital of Namibia. It dams the ephemeral Arebbusch River and its tributary, the Gammams River, which both run across Windhoek. The reservoir behind the dam has a capacity of 3.6 million cubic metres (4,700,000 cu yd).

Barekese Dam is a dam on the Ofin River that supports the main water treatment plant for Kumasi in the Ashanti Region of Ghana, supplying about 80 percent of the potable water for the city and its surrounding environs. It is operated by the Ghana Water Company.