This article needs to be updated.(June 2018) |
 |
|---|
|
The Assembly of the Autonomous Island of Grande Comore is the island's legislative body.
This article needs to be updated.(June 2018) |
 |
|---|
|
The Assembly of the Autonomous Island of Grande Comore is the island's legislative body.
The Assembly, formed following elections held on 14 and 21 March 2004, has a total of 20 members. Supporters of the Island President, Abdou Soulé Elbak, won 14 seats while supporters of Union President Azali Assoumani won 6.

The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an archipelagic country made up of three islands in Southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city is Moroni. The religion of the majority of the population, and the official state religion, is Sunni Islam. Comoros proclaimed its independence from France on 6 July 1975. A member of the Arab League, it is the only country in the Arab world which is entirely in the Southern Hemisphere. It is a member state of the African Union, the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, the Organisation of Islamic Co-operation, and the Indian Ocean Commission. The country has three official languages: Shikomori, French and Arabic.
The history of the Comoros extends to about 800–1000 AD when the archipelago was first inhabited. The Comoros have been inhabited by various groups and sultanates throughout this time. France colonised the islands in the 19th century, and they became independent in 1975.

The Union of the Comoros consists of the three islands Njazidja, Mwali (Moheli) and Nzwani (Anjouan) while the island of Mayotte remains under French administration. The Politics of the Union of the Comoros take place in a framework of a unitary presidential republic, whereby the President of the Comoros is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The precolonial legacies of the sultanates linger while the political situation in Comoros has been extremely fluid since the country's independence in 1975, subject to the volatility of coups and political insurrection.

Anjouan is an autonomous volcanic island in the Comoro Islands in the southwestern Indian Ocean, part of the Union of the Comoros. It is known in Shikomori as Ndzuani, Ndzuwani or Nzwani, and, until the early twentieth century when the name fell out of general use, in English as Johanna. Historically it was also called Hinzuan or Hanzoan.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Comoros on 18 April 2004, with a second round on 25 April. The result was a victory for the Camp of the Autonomous Islands, which won 12 of the 18 elected seats.
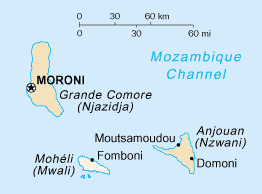
Mohéli, also known as Mwali, is an autonomously-governed island that forms part of the Union of the Comoros. It is the smallest of the three major islands in the country. It is located in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Africa and it is the smallest of the four major Comoro Islands. Its capital and largest city is Fomboni.
Colonel Mohamed Bacar is a Comorian former politician who was President of Anjouan, one of the three autonomous islands that make up the Union of the Comoros, from 2001 to 2008. He is a former chief of police on Anjouan and has studied extensively in France and the United States. He was part of a military coup on Anjouan in August 2001 and soon became President. It is alleged he rigged the elections to become the first president of Anjouan in March 2002, in part due to his leading role in the separatist movement. He was ousted by the combined forces of the Government of the Union of Comoros and the African Union in the March 2008 invasion of Anjouan.

Elections in the Comoros take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. The President and the majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Union are directly elected.

The unicameral Assembly of the Union of the Comoros is the country's legislative body. It was established in 2004.

The Assembly of the Autonomous Island of Anjouan is the island's legislative body.

The Assembly of the Autonomous Island of Mohéli is the island's legislative body.

In March and April 2002, the three islands of the Comoros held and approved new constitutions in referendums. The main points of the constitutions were to establish each island as an autonomous part of the Union of Comoros, along with provisions that created elected local assemblies and presidents.

Presidential elections were held in the Comoros on 16 April and 14 May 2006. As it was the turn of the island of Anjouan to hold the union presidency, a primary election was held in Anjouan on 16 April, prior to a national election on 14 May. The result was a victory for Ahmed Abdallah Mohamed Sambi, who received 58% of the vote in the national election.

The President of Anjouan is the head of Anjouan, one of the three islands of the Union of Comoros. The position was firstly established in 1997 after the Declaration of independence of Anjouan. Secondly the position became President of the autonomous island of Anjouan following the adoption of the Union of Comoros Constitution of 2001.

The President of Mohéli is the head of the autonomous government of Mohéli, the smallest island of the Comoros. The position was established in 2002 following the adoption of the Comorian Constitution of 2001.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Comoros on 6 December 2009, with a second round on 20 December. The elections were originally scheduled for July 2009, but were postponed until after a constitutional referendum was held in May 2009. They were then scheduled to take place on 29 November, but were delayed again. The result was a victory for the Baobab Movement, a coalition supporting President Ahmed Abdallah Mohamed Sambi.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Comoros on 25 January 2015, alongside local elections. A second round of voting was held on 22 February in the 21 constituencies where no candidate won in the first round. The Union for the Development of the Comoros emerged as the largest party, winning eight of the 24 seats in the Assembly of the Union.

The Movement for Democracy and Progress, also known as the People's Democratic Movement was a political party in the Comoros.

The National Rally for Development was a political party in the Comoros.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Comoros on 19 January 2020; in constituencies where no candidate received a majority, a second round was held alongside local elections on 23 February. The elections were boycotted by the main opposition parties, including the two largest parties in the outgoing Assembly, the Union for the Development of the Comoros and Juwa Party, in protest at constitutional reform and political repression, The result was a landslide victory for President Azali Assoumani's Convention for the Renewal of the Comoros, which won 20 of the 24 elected seats.