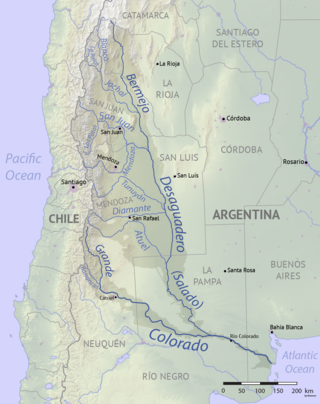
The Colorado River is a river in the center of Argentina.

The Uruguay River is a major river in South America. It flows from north to south and forms parts of the boundaries of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, separating some of the Argentine provinces of La Mesopotamia from the other two countries. It passes between the states of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil; forms the eastern border of the provinces of Misiones, Corrientes, and Entre Ríos in Argentina; and makes up the western borders of the departments of Artigas, Salto, Paysandú, Río Negro, Soriano, and Colonia in Uruguay.

The Nizhnyaya Tunguska is a river in Siberia, Russia, that flows through the Irkutsk Oblast and the Krasnoyarsk Krai. The river is a right tributary of the Yenisey joining it at Turukhansk. The ice-free period on the Nizhnyaya Tunguska starts in mid-June and ends in the first half of October. The river forms the western limit of the Lena Plateau.

The Ogoki River is a river in the Thunder Bay and Cochrane Districts of Ontario. It springs from the wilderness just east of Savant Lake, flowing north of Lake Nipigon to Ogoki, where it joins the Albany River which empties into James Bay. The river is 480 kilometres (300 mi) long.

The Salado River is a river that crosses several provinces of Argentina, flowing 1,150 kilometres (710 mi) from its source in the Salta Province to end in the Paraná River, in the Santa Fe Province. Because its origin, its flow varies widely within the year, and it can dry out in some parts of its path during the winter. The only important tributary to the river is the Horcones River, which is born in Salta as Cajón River, and joins the Salado in the Santiago del Estero Province.

The lake known as O'Higgins in Chile and San Martín in Argentina is located around coordinates 48°50′S72°36′W in Patagonia, between the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region and the Santa Cruz Province.

The Desaguadero River is a river in Argentina. Originating near the Tipas volcano in La Rioja at about 5,500 m (18,000 ft) elevation, the river is known in its upper reaches as the Bermejo or Vinchina. In its lower reaches it is also known as the Salado. It joins the Colorado River in La Pampa Province near Pichi Mahuida. The Desaguadero River has a total length of 1,498 km (931 mi) and its drainage basin is about 260,000 km2 (100,000 sq mi).

The Los Molinos Dam is a dam over the course of the Los Molinos River in the center-west of the province of Córdoba, Argentina, about 769 metres (2,523 ft) above mean sea level.

San Rafael is a city in the southern region of the Mendoza Province, Argentina. With more than 118,000 inhabitants, it is the largest city in and the seat of San Rafael Department.

The Jáchal River is a river in the province of San Juan, Argentina. It is part of the Desaguadero River basin, and one of the most important permanent watercourses in the province, with an average flow of 9 cubic metres per second (320 cu ft/s). It is born from the confluence of the Río de la Palca and the Blanco River, in the northwest of San Juan.

The San Juan River is, together with the Jáchal, the most important river of the Argentine province of San Juan. Both join the Desaguadero/Colorado system that ends at the Atlantic Ocean.

The Mendoza River is a river in the province of Mendoza, Argentina. It is formed in the Andes range between the Aconcagua and the Tupungato, by the confluence of the Vacas, the Cuevas and the Tupungato rivers, the last being its major tributary.

The Diamante River is a river in the Argentine province of Mendoza. It is born from glaciers on the Maipo, a volcano in the Andes range in the Argentine–Chilean border, and flows east until emptying in the Desaguadero River. Its drainage basin covers an area of 2,750 square kilometres (1,060 sq mi) in the central region of Mendoza.

The El Carrizal Dam is a dam on the upper-middle course of the Tunuyán River, in the center-north of the province of Mendoza, Argentina upstream from the city of Rivadavia. Its reservoir measures about 15 by 5 kilometres, and its maximum water level stands at 785.5 metres (2,577 ft) above the sea, covering an area of 34.8 square kilometres (13.4 sq mi). It has a maximum volume of 462 million cubic metres.

The Piedra del Águila Dam is the second of five dams on the Limay River in northwestern Argentine Patagonia and 590 metres (1,940 ft) above mean sea level, downstream from the confluence of the Limay and the Collón Curá River. It was inaugurated in 1993.

The El Chocón Dam is the fourth of the five dams on the Limay River in the northwestern Argentine Patagonia, at 381 metres (1,250 ft) above mean sea level. El Chocón is on the Limay River at about 80 km (50 mi) upstream of its confluence with the Neuquén River.

Mendoza Province is Argentina's most important wine region, accounting for nearly two-thirds of the country's entire wine production. Located in the eastern foothills of the Andes, in the shadow of Aconcagua, vineyards are planted at some of the highest altitudes in the world, with the average site located 600–1,100 metres (2,000–3,600 ft) above sea level. The principal wine producing areas fall into two main departments-Maipú and Luján, which includes Argentina's first delineated appellation established in 1993 in Luján de Cuyo. The pink-skinned grapes of Criolla Grande and Cereza account for more than a quarter of all plantings but Malbec is the region's most important planting, followed closely by Cabernet Sauvignon, Tempranillo and Chardonnay. Mendoza is considered the heart of the winemaking industry in Argentina with the vast majority of large wineries located in the provincial capital of Mendoza.
The Redstone River is a large river in the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is about 289 kilometres (180 mi) long. It is a tributary of the Mackenzie River, joining it on the left bank some 100 kilometres (62 mi) north of Wrigley. Draining a rugged and high area of the Mackenzie Mountains, the Redstone watershed is sparsely populated by people but remains an ecological haven for wildlife including moose, caribou, wolves Dall's Sheep and Bears. It is a pristine mountain wilderness.

The Atuel Canyon is a narrow canyon and popular tourist attraction within Valle Grande, Argentina. The canyon is popular location for adventure sports, including river rafting, hiking, climbing, horse riding and mountain biking.

The Argentine Monte (NT0802), or Low Monte, is an ecoregion of dry thorn scrub and grasslands in Argentina. It is one of the driest regions in the country. Human settlements are mainly near water supplies such as rivers or oases. Deforestation and over-grazing around these settlements have caused desertification.




















