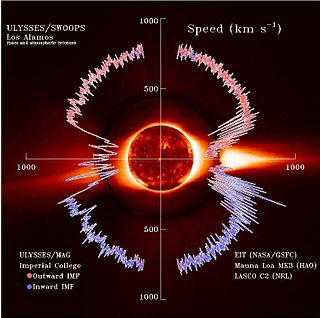
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface.

A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention.

An aurora , also commonly known as polar lights, northern lights, or southern lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions. Auroras display dynamic patterns of brilliant lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals, or dynamic flickers covering the entire sky.
Cyclotron radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by non-relativistic accelerating charged particles deflected by a magnetic field. The Lorentz force on the particles acts perpendicular to both the magnetic field lines and the particles' motion through them, creating an acceleration of charged particles that causes them to emit radiation as a result of the acceleration they undergo as they spiral around the lines of the magnetic field.

Synchrotron radiation is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity. It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization, and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.

A synchrotron is a particular type of cyclic particle accelerator, descended from the cyclotron, in which the accelerating particle beam travels around a fixed closed-loop path. The magnetic field which bends the particle beam into its closed path increases with time during the accelerating process, being synchronized to the increasing kinetic energy of the particles. The synchrotron is one of the first accelerator concepts to enable the construction of large-scale facilities, since bending, beam focusing and acceleration can be separated into different components. The most powerful modern particle accelerators use versions of the synchrotron design. The largest synchrotron-type accelerator, also the largest particle accelerator in the world, is the 27-kilometre-circumference (17 mi) Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, built in 2008 by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). It can accelerate beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 tera electronvolts (TeV or 1012 eV).

X-ray pulsars or accretion-powered pulsars are a class of astronomical objects that are X-ray sources displaying strict periodic variations in X-ray intensity. The X-ray periods range from as little as a fraction of a second to as much as several minutes.

A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes that generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of electrons in a strong magnetic field. Output frequencies range from about 20 to 527 GHz, covering wavelengths from microwave to the edge of the terahertz gap. Typical output powers range from tens of kilowatts to 1–2 megawatts. Gyrotrons can be designed for pulsed or continuous operation. The gyrotron was invented by Soviet scientists at NIRFI, based in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia.

The magnetosphere of Saturn is the cavity created in the flow of the solar wind by the planet's internally generated magnetic field. Discovered in 1979 by the Pioneer 11 spacecraft, Saturn's magnetosphere is the second largest of any planet in the Solar System after Jupiter. The magnetopause, the boundary between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind, is located at a distance of about 20 Saturn radii from the planet's center, while its magnetotail stretches hundreds of Saturn radii behind it.

A Birkeland current is a set of electrical currents that flow along geomagnetic field lines connecting the Earth's magnetosphere to the Earth's high latitude ionosphere. In the Earth's magnetosphere, the currents are driven by the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field and by bulk motions of plasma through the magnetosphere. The strength of the Birkeland currents changes with activity in the magnetosphere. Small scale variations in the upward current sheets accelerate magnetospheric electrons which, when they reach the upper atmosphere, create the Auroras Borealis and Australis. In the high latitude ionosphere, the Birkeland currents close through the region of the auroral electrojet, which flows perpendicular to the local magnetic field in the ionosphere. The Birkeland currents occur in two pairs of field-aligned current sheets. One pair extends from noon through the dusk sector to the midnight sector. The other pair extends from noon through the dawn sector to the midnight sector. The sheet on the high latitude side of the auroral zone is referred to as the Region 1 current sheet and the sheet on the low latitude side is referred to as the Region 2 current sheet.
The following is a chronology of discoveries concerning the magnetosphere.
The electrodeless plasma thruster is a spacecraft propulsion engine commercialized under the acronym "E-IMPAcT" for "Electrodeless-Ionization Magnetized Ponderomotive Acceleration Thruster". It was created by Mr. Gregory Emsellem based on technology developed by French Atomic Energy Commission scientist Dr Richard Geller and Dr. Terenzio Consoli, for high speed plasma beam production.

The magnetosphere of Jupiter is the cavity created in the solar wind by Jupiter's magnetic field. Extending up to seven million kilometers in the Sun's direction and almost to the orbit of Saturn in the opposite direction, Jupiter's magnetosphere is the largest and most powerful of any planetary magnetosphere in the Solar System, and by volume the largest known continuous structure in the Solar System after the heliosphere. Wider and flatter than the Earth's magnetosphere, Jupiter's is stronger by an order of magnitude, while its magnetic moment is roughly 18,000 times larger. The existence of Jupiter's magnetic field was first inferred from observations of radio emissions at the end of the 1950s and was directly observed by the Pioneer 10 spacecraft in 1973.

The L-shell, L-value, or McIlwain L-parameter is a parameter describing a particular set of planetary magnetic field lines. Colloquially, L-value often describes the set of magnetic field lines which cross the Earth's magnetic equator at a number of Earth-radii equal to the L-value. For example, describes the set of the Earth's magnetic field lines which cross the Earth's magnetic equator two earth radii from the center of the Earth. L-shell parameters can also describe the magnetic fields of other planets. In such cases, the parameter is renormalized for that planet's radius and magnetic field model.

A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.
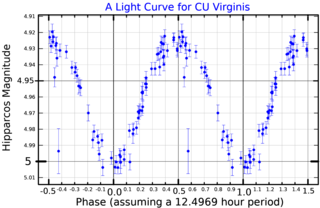
CU Virginis is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.99, which is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The distance to this star can be estimated from its annual parallax shift of 13.9 mas, yielding a separation of 234 light years.

JEDI (Jupiter Energetic-particle Detector Instrument) is an instrument on the Juno spacecraft orbiting planet Jupiter. JEDI coordinates with the several other space physics instruments on the Juno spacecraft to characterize and understand the space environment of Jupiter's polar regions, and specifically to understand the generation of Jupiter's powerful aurora. It is part of a suite of instruments to study the magnetosphere of Jupiter. JEDI consists of three identical detectors that use microchannel plates and foil layers to detect the energy, angle, and types of ion within a certain range. It can detect electrons between 40 and 500 keV (Kilo electron-volts), and hydrogen and oxygen from a few tens of keV to less than 1000 keV (1 MeV). JEDI uses radiation hardened Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC)s. JEDI was turned on in January 2016 while still en route to Jupiter to also study interplanetary space. JEDI uses solid state detectors (SSD's) to measure the total energy (E) of both the ions and the electrons. The MCP anodes and the SSD arrays are configured to determine the directions of arrivals of the incoming charged particles. The instruments also use fast triple coincidence and optimum shielding to suppress penetrating background radiation and incoming UV foreground.

Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the atmosphere of the Sun. These phenomena take many forms, including solar wind, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, coronal heating and sunspots.















