A vowel is one of the two principal classes of speech sound, the other being a consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (length). They are usually voiced, and are closely involved in prosodic variation such as tone, intonation and stress. Vowel sounds are produced with an open vocal tract. The word vowel comes from the Latin word vocalis, meaning "vocal". In English, the word vowel is commonly used to refer both to vowel sounds and to the written symbols that represent them.
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning – that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast, and other such features in what is called intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that do have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with phoneme. Tonal languages are common in East and Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Africa, and the Americas; as many as seventy percent of world languages may be tonal.

Zulu or isiZulu is the language of the Zulu people, with about 10 million speakers, the vast majority of whom live in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa, and it is understood by over 50% of its population. It became one of South Africa's 11 official languages in 1994.
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word, or to a certain word in a phrase or sentence. This emphasis is typically caused by such properties as increased loudness and vowel length, full articulation of the vowel, and changes in pitch. The terms stress and accent are often used synonymously in this context, but they are sometimes distinguished. For example, when emphasis is produced through pitch alone, it is called pitch accent, and when produced through length alone, it is called quantitative accent. When caused by a combination of various intensified properties, it is called stress accent or dynamic accent; English uses what is called variable stress accent.
Whistled languages use whistling to emulate speech and facilitate communication. A whistled language is a system of whistled communication which allows fluent whistlers to transmit and comprehend a potentially unlimited number of messages over long distances. Whistled languages are different in this respect from the restricted codes sometimes used by herders or animal trainers to transmit simple messages or instructions. Generally, whistled languages emulate the tones or vowel formants of a natural spoken language, as well as aspects of its intonation and prosody, so that trained listeners who speak that language can understand the encoded message.
A pitch-accent language is a language that has word-accents—that is, where one syllable in a word or morpheme is more prominent than the others, but the accentuated syllable is indicated by a particular pitch contour rather than by stress. This contrasts with fully tonal languages like Standard Chinese, in which each syllable can have an independent tone.
Like many other languages, English has wide variation in pronunciation, both historically and from dialect to dialect. In general, however, the regional dialects of English share a largely similar phonological system. Among other things, most dialects have vowel reduction in unstressed syllables and a complex set of phonological features that distinguish fortis and lenis consonants. Most dialects of English preserve the consonant and many preserve, while most other Germanic languages have shifted them to and : compare English will and then with German will[vɪl](listen) ('want') and denn[dɛn](listen) ('because').
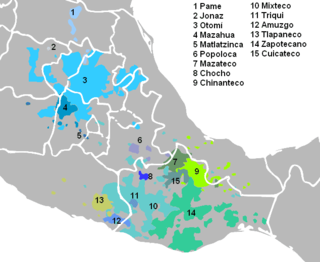
Oto-Manguean languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean branch of the family, which is now extinct, was spoken as far south as Nicaragua and Costa Rica. Oto-Manguean is widely viewed as a proven language family. However, this status has been recently challenged.
This article is a technical description of the sound system of the Vietnamese language, including phonetics and phonology. Two main varieties of Vietnamese, Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon), are described below.

The Mazatecan languages are a group of closely related indigenous languages spoken by some 200,000 people in the area known as the Sierra Mazateca, which is in the northern part of the state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico, as well as in adjacent areas of the states of Puebla and Veracruz.
Dinka is a Nilotic dialect cluster spoken by the Dinka people, the major ethnic group of South Sudan. There are several main varieties, Padang, Rek, Agaar, Awiel, Twic Mayardit, Hol, Nyarweng, Twi and Bor, which are distinct enough to require separate literary standards. Jaang, Jieng or Monyjieng is used as a general term to cover all Dinka languages. Rek is the standard and prestige dialect.
The phonology of second languages is different from the phonology of first languages in various ways. The differences are considered to come from general characteristics of second languages, such as slower speech rate, lower proficiency than native speakers, and from the interaction between non-native speakers' first and second languages.
Puinave, AKA Waipunavi (Guaipunabi) or Wanse (Wãnsöhöt), is a poorly attested and generally unclassified language of South America.
Jalapa Mazatec is a Mazatecan language, as of 1990 spoken by ca. 15,000 people, one-third of whom are monolingual, in 13 villages in the vicinity of the town of San Felipe Jalapa de Díaz in the Tuxtepec District of the Mexican state of Oaxaca. Egland (1978) found 73% intelligibility with Huautla, the prestige variety of Mazatec. Literacy in Jalapa is taught alongside Spanish in local schools.
This article summarizes the phonology of Standard Chinese.
Meixian dialect, also known as Meizhou (梅州話), Moiyen, Jiaying dialect and Yue-Tai, is the prestige dialect of Hakka Chinese and the basis for the Hakka dialects in Taiwan. It is named after Meixian District, Guangdong previously known as Jiaying county.
Palantla Chinantec, also known as Chinanteco de San Pedro Tlatepuzco, is a major Chinantecan language of Mexico, spoken in San Juan Palantla and a couple dozen neighboring towns in northern Oaxaca. The variety of San Mateo Yetla, known as Valle Nacional Chinantec, has marginal mutual intelligibility.
Pitch accent is a term used in autosegmental-metrical theory for local intonational features that are associated with particular syllables. Within this framework, pitch accents are distinguished from both the abstract metrical stress and the acoustic stress of a syllable. Different languages specify different relationships between pitch accent and stress placement.



