Balochistan is a province of Pakistan. Located in the southwestern region of the country, Balochistan is the largest province of Pakistan by land area but is the least populated one. It is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the north-east, Punjab to the east and Sindh to the south-east; shares international borders with Iran to the west and Afghanistan to the north; and is bound by the Arabian Sea to the south. Balochistan is an extensive plateau of rough terrain divided into basins by ranges of sufficient heights and ruggedness. It has the world's largest deep sea port, the Port of Gwadar lying in the Arabian Sea.

West Pakistan was the western polity of Pakistan, it was one of the two provincial exclaves created under the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was created to ensure population-based equality with its eastern counter-part and it was dissolved to once again form former provinces for the General Elections in 1970 under the 1970 Legal Framework Order.
The Kakar is a Gharghashti Pashtun tribe, based in Afghanistan, parts of Iran, northern Balochistan in Pakistan.

Quetta is a district in the north-west of the Balochistan province of Pakistan, on the border with Kandahar province, Afghanistan. It is part of Quetta Division. The district is famous for its agriculture produce, most notably fruit orchards but also including apples and grapes. The Hanna Valley is an area where almonds are grown. The population counted in the 1998 census was 760,000, while in 2010 it was estimated at 1,235,000.

Sir Robert Groves Sandeman, KCSI (1835–1892) was a British Indian Army officer and colonial administrator. He was known for his activities in Balochistan, where he introduced a system of "tribal pacification" that endured until the partition of India in 1947.

The history of Balochistan refers to the history of the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Iran and Afghanistan. Vague allusions to the region were found in Greek historical records of around 650 BCE. Prehistoric Balochistan dates to the Paleolithic.

Zhob, formerly known as Appozai, is a city and district headquarters of the Zhob District in the Balochistan province of Pakistan. Zhob is located on the banks of the Zhob river. It is 337 kilometers away from Quetta, the capital of Balochistan.

The former administrative units of Pakistan are states, provinces and territories which mainly existed between 1947 and 1975 when the current provinces and territories were established. The former units have no administrative function today but some remain as historical and cultural legacies. In some cases, the current provinces and territories correspond to the former units – for example the province of Punjab includes almost all the territory of the former province of West Punjab.

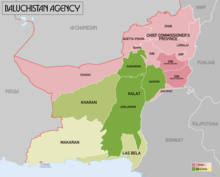
The Baluchistan States Union or Balochistan States Union (BSU) was an administrative division of Pakistan that existed between 3 October 1952 and 14 October 1955 in the southwestern part of West Pakistan. It was formed by the four princely states of Kalat, Kharan, Las Bela and Makran with the capital at the town of Kalat. The area of the Union was roughly the south-western half of the modern province of Balochistan. The Union was separate from the Chief Commissioners Province of Baluchistan which comprised areas to the northeast of the Union. The Union did not include the enclave of Gwadar which was part of the Muscat and Oman. The four state rulers continued in office and retained autonomy.

The Khanate of Kalat was a Brahui Khanate that originated from the Kalat region of Pakistan. Formed in 1666 due to the threat of Mughal expansion in the region, it controlled the wider Balochistan at its greatest extent in the mid-18th century, extending from Kerman in the west to Sindh in the east and from Helmand river in the north to the Arabian sea in the south. Khanate of Kalat lost considerable area to Qajar Iran and Emirate of Afghanistan in the early 19th century, and the city of Kalat was itself sacked by the British in 1839. Kalat became a self-governing state in a subsidiary alliance with British Raj after the signature of the Treaty of Kalat by the Khan of Kalat and the Baloch Sardars in 1875, and the supervision of Kalat became task of the Baluchistan Agency. Kalat was briefly independent from 12 August 1947 until 27 March 1948, when its ruler Ahmad Yar Khan acceded to Pakistan, making it one of the Princely states of Pakistan.

The four provinces, capital territory and two autonomous territories of Pakistan are subdivided into 39 administrative "divisions", which are further subdivided into districts, tehsils and finally union councils. These divisions were abolished in 2000, but restored in 2008.
Quetta is a natural fort, surrounded as it is by imposing hills on all sides. It is encircled by hills Chiltan, Takatoo, Mordar and Zarghun. It is believed that the earliest Muslim inhabitants and rulers/owners of the city were the Pashtun Kasi Tribe. Quetta was first mentioned in the 11th century when it was captured by Mahmood of Ghazni on one of his invasions of the subcontinent. In 1543 the Mughal emperor Humayun rested here on his retreat to Persia, leaving his one-year-old son Akbar until he returned two years later. The Ghilzai power in Kandahar at the beginning of the eighteenth century, simultaneously with that of the Baloch in Kalat, Quetta and Pishin became the battle-ground between the Afghans and Baloch in the region. Ahmed Shah Durrani finally handed Quetta over to the Khan of Kalat Mir Noori Naseer Khan Baloch for helping him with his army in 1751 against the Marathas in the Battle of Panipat (1761), and against the Sikhs in 1765. Today, it is an important city in Pakistan. Quetta has a majority Pashtun population, with more than 20% of its inhabitants being Pashtun.

The Insurgency in Balochistan is an insurgency or revolt by Baloch nationalists and Islamist militants against the governments of Pakistan and Iran in the Balochistan region, which covers the Balochistan Province in southwestern Pakistan, Sistan and Baluchestan Province in southeastern Iran, and the Balochistan region of southern Afghanistan. Rich in natural resources like natural gas, oil, coal, copper, sulphur, fluoride and gold, this is the largest, least populated and least developed province in Pakistan. Armed groups demand greater control of the province's natural resources and political autonomy. Baloch separatists have attacked civilians from other ethnicities throughout the province. In the 2010s, attacks against the Shia community by sectarian groups—though not always directly related to the political struggle—have risen, contributing to tensions in Balochistan. In Pakistan, the ethnic separatist insurgency is low-scale but ongoing mainly in southern Balochistan, as well as sectarian and religiously motivated militancy concentrated mainly in northern and central Balochistan.

The Baluchistan Agency was one of agencies of British India during the colonial era. It was located in the present-day Pakistani Balochistan province.

Balochistan is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. This arid region of desert and mountains is primarily populated by ethnic Baloch people.

The Governor of Balochistan is the head of the province of Balochistan, Pakistan. The post was established on 1 July 1970, after the dissolution of West Pakistan province and the end of One Unit. Under Pakistan's current parliamentary system, the governorship is a ceremonial position, as a symbol of the federation. The governor is appointed by the centre, whereas the principal head of the provincial government remains the elected Chief Minister of Balochistan.

Shahzada Rehmatullah Khan Durrani was a Pakistan Movement activist born on 10 October 1919 in the Sadozai dynasty of Durrani, the ethnic Pashtun Sadozai tribe, section of the Popalzai sub clan of Durrani Abdali Pashtun tribe in British India, Quetta.

Gul Khan Naseer, also known as Malek o-Sho'arā Balochistan was a Pakistani politician, poet, historian, and journalist from Balochistan. Most of his work is in Balochi language, but he also wrote in English, Urdu, Brahui and Persian.

Nawab Sardar Baz Mohammad Khan Jogezai was a Pashtun tribal elder and the only representative from Baluchistan Province to the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.