
A cooperative is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-controlled enterprise". Cooperatives are democratically controlled by their members, with each member having one vote in electing the board of directors. Cooperatives may include:

Financial institutions, sometimes called banking institutions, are business entities that provide services as intermediaries for different types of financial monetary transactions. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial institutions:
- Depository institutions – deposit-taking institutions that accept and manage deposits and make loans, including banks, building societies, credit unions, trust companies, and mortgage loan companies;
- Contractual institutions – insurance companies and pension funds
- Investment institutions – investment banks, underwriters, and other different types of financial entities managing investments.

Crédit Agricole Group, sometimes called La banque verte due to its historical ties to farming, is a French international banking group and the world's largest cooperative financial institution. It is France's second largest bank, after BNP Paribas, as well as the third largest in Europe and tenth largest in the world. It consists of a network of Crédit Agricole local banks, the 39 Crédit Agricole regional banks, and a central institute, the Crédit Agricole S.A.. It is listed through Crédit Agricole S.A., an intermediate holding company, on Euronext Paris' first market and is part of the CAC 40 stock market index. Local banks of the group owned the regional banks, in turn the regional banks majority owned the S.A. via a holding company, in turn the S.A. owned part of the subsidiaries of the group, such as LCL, the Italian network and the CIB unit. It is considered a systemically important bank by the Financial Stability Board.

Rabobank is a Dutch multinational banking and financial services company headquartered in Utrecht, Netherlands. The group comprises 89 local Dutch Rabobanks (2019), a central organisation, and many specialised international offices and subsidiaries. Food and agribusiness constitute the primary international focus of the Rabobank Group. Rabobank is the second-largest bank in the Netherlands in terms of total assets.

Raiffeisen Zentralbank Österreich A.G. was the central institution of the Raiffeisen Banking Group Austria (RBG). The central bank was merged with its subsidiary Raiffeisen Bank International in 2017.

Cooperative banking is retail and commercial banking organized on a cooperative basis. Cooperative banking institutions take deposits and lend money in most parts of the world.
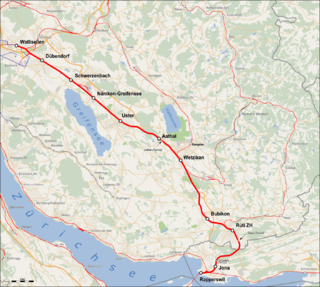
The Wallisellen–Uster–Rapperswil railway line is a railway line in the Swiss canton of Zurich. It is also known as the Glatthalbahn, Glatttalbahn or Glattalbahn (Gl-TB), although the latter name is now more commonly used to refer to the Stadtbahn Glattal, a nearby light rail system.

Banque Populaire was a French group of cooperative banks that in 2009 formed part of Groupe BPCE. The central entity was controlled by 15 independent regional banks and also operated under the CASDEN and the Crédit Coopératif subsidiaries.
China's banking sector had ¥319.7 trillion RMB in assets at the end of 2020. The "big four/five" state-owned commercial banks are the Bank of China, the China Construction Bank, the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, and the Agricultural Bank of China, all of which are among the largest banks in the world As of 2018. The Bank of Communications is sometimes included. Other notable big and also the largest banks in the world are China Merchants Bank and Ping An Bank.

There are several banks that operate under the name "Volksbank".
Co-operative Bank or Cooperative Bank may refer to:

Banking in Germany is a highly leveraged industry, as its average leverage ratio as of 11 October 2008 is 52 to 1 ; its short-term liabilities are equal to 60% of the German GDP or 167% of its national debt.

The German Cooperative Financial Group is a major cooperative banking network in Germany that includes local banks named Volksbanken and Raiffeisenbanken, the latter in tribute to 19th-century cooperative movement pioneer Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen. The Cooperative Group represents one of the three "pillars" of Germany's banking sector, the other two being, respectively, the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe of public banks, and the commercial banking sector represented by the Association of German Banks.

Crédit Mutuel is a French cooperative banking group, one of the country's top five banks with over 30 million customers. It traces its origins back to the German cooperative movement inspired by Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen in Alsace–Lorraine under German rule, in the 1880s. Crédit Mutuel was a member of the International Raiffeisen Union (IRU).

Raiffeisen Switzerland is a cooperative of cooperatives – the union of all independent Swiss Raiffeisen banks. It bears responsibility for the business policy and strategy within the Raiffeisen Group. The 246 independent Raiffeisen banks of Switzerland are organised as cooperatives. With 896 branch offices in total, they make up the densest branch network of any Swiss bank. In the 21st century, the Raiffeisen Group has become the third-largest banking group in Switzerland with total assets currently at CHF 229 billion. Since June 2014, Raiffeisen has been classified as one of Switzerland's systemically important banks and must therefore meet special requirements in terms of capital. Raiffeisen Switzerland has 3.8 million clients in Switzerland, of whom 1.9 million are cooperative members and thus co-owners of their regional Raiffeisen banks.

The Banking Regulation Act, 1949 is a legislation in India that regulates all banking firms in India. Passed as the Banking Companies Act 1949, it came into force from 16 March 1949 and changed to Banking Regulation Act 1949 from 1 March 1966. It is applicable in Jammu and Kashmir from 1956. Initially, the law was applicable only to banking companies. But, in 1965 it was amended to make it applicable to cooperative banks and to introduce other changes. In 2020 it was amended to bring the cooperative banks under the supervision of the Reserve Bank of India.
The Tamil Nadu State Apex Co-operative Bank, also known as TNSC Bank, is an Indian cooperative banking company headquartered in Chennai. It was incorporated in 1905 as an urban cooperative bank. As of 2015, TNSC Bank had 46 branches in Chennai. TNSC Bank coordinates India's entire short-term cooperative credit structure.
Lienhardt & Partner Privatbank Zürich is a traditional Swiss universal bank founded in 1868 and based in Zurich. Its core activities include private banking, financing and real estate.

The PSD Bankengruppe is a German cooperative banking group consisting of 14 autonomous and independent financial institutions. The business model of the PSD banks is a combination of regional direct and affiliated bank. It provides retail banking services via internet, telephone, e-mail, mail and fax or at local branches, it only provides services to retail clients and does not offer banking to self-employed and businesses.

Raiffeisenlandesbank Oberösterreich AG is a credit institution and grouping of cooperative banks founded in the 1900s and headquartered in Linz, Austria. It is the central institution of the Raiffeisen Banking Group in Upper Austria and the largest of Austria's eight provincial central banks.
















