
The Battle of Fredericksburg was fought December 11–15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. The combat, between the Union Army of the Potomac commanded by Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside and the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia under Gen. Robert E. Lee, included futile frontal attacks by the Union army on December 13 against entrenched Confederate defenders along the Sunken Wall on the heights behind the city. It is remembered as one of the most one-sided battles of the war, with Union casualties more than twice as heavy as those suffered by the Confederates. A visitor to the battlefield described the battle as a "butchery" to U.S. President Abraham Lincoln.

The Second Battle of Bull Run or Battle of Second Manassas was fought August 28–30, 1862, in Prince William County, Virginia, as part of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of the Northern Virginia Campaign waged by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia against Union Maj. Gen. John Pope's Army of Virginia, and a battle of much larger scale and numbers than the First Battle of Bull Run fought on July 21, 1861, on the same ground.

The Army of the Potomac was the primary field army of the Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in April.

The Battle of Yorktown or siege of Yorktown was fought from April 5 to May 4, 1862, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. Marching from Fort Monroe, Union Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan's Army of the Potomac encountered Maj. Gen. John B. Magruder's small Confederate force at Yorktown behind the Warwick Line. McClellan suspended his march up the Peninsula toward Richmond and settled in for siege operations.

The Peninsula campaign of the American Civil War was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March to July 1862, the first large-scale offensive in the Eastern Theater. The operation, commanded by Major General George B. McClellan, was an amphibious turning movement against the Confederate States Army in Northern Virginia, intended to capture the Confederate capital of Richmond. McClellan was initially successful against the equally cautious General Joseph E. Johnston, but the emergence of the more aggressive General Robert E. Lee turned the subsequent Seven Days Battles into a humiliating Union defeat.

The Seven Days Battles were a series of seven battles over seven days from June 25 to July 1, 1862, near Richmond, Virginia, during the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee drove the invading Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, away from Richmond and into a retreat down the Virginia Peninsula. The series of battles is sometimes known erroneously as the Seven Days Campaign, but it was actually the culmination of the Peninsula Campaign, not a separate campaign in its own right.

The Battle of Brandy Station, also called the Battle of Fleetwood Hill, was the largest predominantly cavalry engagement of the American Civil War, as well as the largest ever to take place on American soil. It was fought on June 9, 1863, around Brandy Station, Virginia, at the beginning of the Gettysburg Campaign by the Union cavalry under Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton against Maj. Gen. J. E. B. Stuart's Confederate cavalry.

The Battle of Williamsburg, also known as the Battle of Fort Magruder, took place on May 5, 1862, in York County, James City County, and Williamsburg, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the first pitched battle of the Peninsula Campaign, in which nearly 41,000 Federals and 32,000 Confederates were engaged, fighting an inconclusive battle that ended with the Confederates continuing their withdrawal.

The Battle of Hanover Court House, also known as the Battle of Slash Church, took place on May 27, 1862, in Hanover County, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War.

The Battle of Seven Pines, also known as the Battle of Fair Oaks or Fair Oaks Station, took place on May 31 and June 1, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, nearby Sandston, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of an offensive up the Virginia Peninsula by Union Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, in which the Army of the Potomac reached the outskirts of Richmond.
The Battle of Oak Grove, also known as the Battle of French's Field or King's School House, took place on June 25, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, the first of the Seven Days Battles of the American Civil War. Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan advanced his lines with the objective of bringing Richmond within range of his siege guns. Two Union divisions of the III Corps attacked across the headwaters of White Oak Swamp, but were repulsed by Maj. Gen. Benjamin Huger's Confederate division. McClellan, who was 3 miles (4.8 km) in the rear, initially telegraphed to call off the attack, but ordered another attack over the same ground when he arrived at the front. Darkness halted the fighting. Union troops gained only 600 yards (550 m), at a cost of over a thousand casualties on both sides.

The Battle of Beaver Dam Creek, also known as the Battle of Mechanicsville or Ellerson's Mill, took place on June 26, 1862, in Hanover County, Virginia. It was the first major engagement of the Seven Days Battles during the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the start of Confederate General Robert E. Lee's counter-offensive against the Union Army of the Potomac, under Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, which threatened the Confederate capital of Richmond. Lee attempted to turn the Union right flank, north of the Chickahominy River, with troops under Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, but Jackson failed to arrive on time. Instead, Maj. Gen. A.P. Hill threw his division, reinforced by one of Maj. Gen. D.H. Hill's brigades, into a series of futile assaults against Brig. Gen. Fitz John Porter's V Corps, which occupied defensive works behind Beaver Dam Creek. Confederate attacks were driven back with heavy casualties. Porter withdrew his corps safely to Gaines Mill, with the exception of Company F of the 8th Pennsylvania Reserve Regiment who did not receive the orders to retreat.

The Battle of Gaines' Mill, sometimes known as the Battle of Chickahominy River, took place on June 27, 1862, in Hanover County, Virginia, as the third of the Seven Days Battles which together decided the outcome of the Union's Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. Following the inconclusive Battle of Beaver Dam Creek (Mechanicsville) the previous day, Confederate General Robert E. Lee renewed his attacks against the right flank of the Union Army, relatively isolated on the northern side of the Chickahominy River. There, Brig. Gen. Fitz John Porter's V Corps had established a strong defensive line behind Boatswain's Swamp. Lee's force was destined to launch the largest Confederate attack of the war, about 57,000 men in six divisions. Porter's reinforced V Corps held fast for the afternoon as the Confederates attacked in a disjointed manner, first with the division of Maj. Gen. A.P. Hill, then Maj. Gen. Richard S. Ewell, suffering heavy casualties. The arrival of Maj. Gen. Stonewall Jackson's command was delayed, preventing the full concentration of Confederate force before Porter received some reinforcements from the VI Corps.

The Battle of White Oak Swamp took place on June 30, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, as part of the Seven Days Battles of the American Civil War. As the Union Army of the Potomac retreated southeast toward the James River, its rearguard under Maj. Gen. William B. Franklin stopped Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's divisions at the White Oak Bridge crossing, resulting in an artillery duel, while the main Battle of Glendale raged two miles (3 km) farther south around Frayser's Farm. White Oak Swamp is generally considered to be part of the larger Glendale engagement. Because of this resistance from Brig. Gen. William B. Franklin's VI Corps, Jackson was prevented from joining the consolidated assault on the Union Army at Glendale that had been ordered by General Robert E. Lee, producing an inconclusive result, but one in which the Union Army avoided destruction and was able to assume a strong defensive position at Malvern Hill.

The Battle of Glendale, also known as the Battle of Frayser's Farm, Frazier's Farm, Nelson's Farm, Charles City Crossroads, New Market Road, or Riddell's Shop, took place on June 30, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, on the sixth day of the Seven Days Battles of the American Civil War.

John Bankhead Magruder was an American and Confederate military officer. A graduate of West Point, Magruder served with distinction during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) and was a prominent Confederate Army general during the American Civil War (1861–1865). As a major general, he received recognition for delaying the advance of Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan's large force, the Army of the Potomac, during the 1862 Peninsula Campaign, as well as recapturing Galveston, Texas the following year.

The Northern Virginia Campaign, also known as the Second Bull Run Campaign or Second Manassas Campaign, was a series of battles fought in Virginia during August and September 1862 in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee followed up his successes of the Seven Days Battles in the Peninsula campaign by moving north toward Washington, D.C., and defeating Maj. Gen. John Pope and his Army of Virginia.

The Maryland campaign occurred September 4–20, 1862, during the American Civil War. The campaign was Confederate General Robert E. Lee's first invasion of the North. It was repulsed by the Army of the Potomac under Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, who moved to intercept Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia and eventually attacked it near Sharpsburg, Maryland. The resulting Battle of Antietam was the bloodiest day of battle in American history.

The Battle of Malvern Hill, also known as the Battle of Poindexter's Farm, was fought on July 1, 1862, between the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, led by Gen. Robert E. Lee, and the Union Army of the Potomac under Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan. It was the final battle of the Seven Days Battles during the American Civil War, taking place on a 130-foot (40 m) elevation of land known as Malvern Hill, near the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia and just one mile (1.6 km) from the James River. Including inactive reserves, more than fifty thousand soldiers from each side took part, using more than two hundred pieces of artillery and three warships.
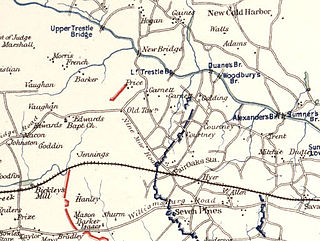
The Battle of Garnett's and Golding's Farms took place June 27–28, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, as part of the Seven Days Battles of the American Civil War's Peninsula Campaign. While the battle at Gaines's Mill raged north of the Chickahominy River, the forces of Confederate general John B. Magruder conducted a reconnaissance in force that developed into a minor attack against the Union line south of the river at Garnett's Farm. The Confederates attacked again near Golding's Farm on the morning of June 28 but in both cases were easily repulsed. The action at the Garnett and Golding farms accomplished little beyond convincing McClellan that he was being attacked from both sides of the Chickahominy.




















