Bran is the hard outer layer of cereal grains.
Contents
Bran may also refer to:
Bran is the hard outer layer of cereal grains.
Bran may also refer to:

Irish mythology is the body of myths native to the island of Ireland. It was originally passed down orally in the prehistoric era, being part of ancient Celtic religion. Many myths were later written down in the early medieval era by Christian scribes, who modified and Christianized them to some extent. This body of myths is the largest and best preserved of all the branches of Celtic mythology. The tales and themes continued to be developed over time, and the oral tradition continued in Irish folklore alongside the written tradition, but the main themes and characters remained largely consistent.

Manannán or Manann, also known as Manannán mac Lir, is a warrior and king of the Otherworld in Irish and Manx mythology who is associated with the sea and often interpreted as a sea god, usually as a member of the Tuatha Dé Danann.
Manawydan fab Llŷr is a figure of Welsh mythology, the son of Llŷr and the brother of Brân the Blessed and Brânwen. The first element in his name is cognate with the stem of the name of the Irish sea god Manannán mac Lir, and likely originated from the same Celtic deity as Manannán. Unlike Manannán, however, no surviving material connects him with the sea in any way except for his patronymic. Manawydan's most important appearances occur in the Second and Third Branches of the Mabinogi, but he is also referenced frequently in medieval poetry and the Welsh Triads.
Matholwch, King of Ireland, is a character in the Second Branch of the Mabinogi, the tale of Branwen ferch Llŷr.

Brân the Blessed is a giant and king of Britain in Welsh mythology. He appears in several of the Welsh Triads, but his most significant role is in the Second Branch of the Mabinogi, Branwen ferch Llŷr. He is a son of Llŷr and Penarddun, and the brother of Brânwen, Manawydan, Nisien and Efnysien. The name "Brân" in Welsh is usually translated as crow or raven.
Simon may refer to:

Brașov County is a county (județ) of Romania, in Transylvania. Its capital city is Brașov. The county incorporates within its boundaries most of the Medieval "lands" (țări) Burzenland and Făgăraș.
Var or VAR may refer to:

Bran Castle is a castle in Bran, 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of Brașov. It is a national monument and landmark in Transylvania. The fortress is on the Transylvanian side of the historical border with Wallachia, on road DN73.
Ban is the King of Benwick or Benoic in Arthurian legend. First appearing by this name in the Lancelot propre part of the Vulgate Cycle, he is the father of Sir Lancelot and Sir Hector de Maris, and is the brother of King Bors. Ban largely corresponds to the other versions of the father of Lancelot, including Pant of Gen[n]ewis in Lanzelet, Haud of Schuwake in the English ballad Sir Lancelot du Lake, and Domolot of Lokva in Povest' o Tryshchane.

Welsh mythology consists of both folk traditions developed in Wales, and traditions developed by the Celtic Britons elsewhere before the end of the first millennium. As in most of the predominantly oral societies Celtic mythology and history were recorded orally by specialists such as druids. This oral record has been lost or altered as a result of outside contact and invasion over the years. Much of this altered mythology and history is preserved in medieval Welsh manuscripts, which include the Red Book of Hergest, the White Book of Rhydderch, the Book of Aneirin and the Book of Taliesin. Other works connected to Welsh mythology include the ninth-century Latin historical compilation Historia Brittonum and Geoffrey of Monmouth's twelfth-century Latin chronicle Historia Regum Britanniae, as well as later folklore, such as the materials collected in The Welsh Fairy Book by William Jenkyn Thomas (1908).

Bran is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of the city of Brașov and consists of five villages: Bran, Poarta, Predeluț (Kispredeál), Șimon (Simon), and Sohodol (Szohodol).

Crimthann Mór, son of Fidach, also written Crimthand Mór, was a semi-mythological king of Munster and High King of Ireland of the 4th century. He gained territory in Britain and Gaul, but died poisoned by his sister Mongfind. It is possible that he was also recognized as king of Scotland. This Crimthann is to be distinguished from two previous High Kings of Ireland of the same name, two Kings of Leinster, and another King of Munster, among others. Importantly, he is included in the Baile Chuinn Chétchathaig (summary), and is thus the last High King of Ireland from Munster until Brian Bóruma, over six hundred years later.
Garat may refer to

The Rucăr-Bran Pass, also called in English the Bran Pass, is a mountain pass in Romania, linking the counties of Brașov and Argeș. It has some of the most spectacular natural views in Romania, looking over the Bucegi Mountains of the Southern Carpathians.

Celtic mythology is the body of myths belonging to the Celtic peoples. Like other Iron Age Europeans, Celtic peoples followed a polytheistic religion, having many gods and goddesses. The mythologies of continental Celtic peoples, such as the Gauls and Celtiberians, did not survive their conquest by the Roman Empire, the loss of their Celtic languages and their subsequent conversion to Christianity. Only remnants are found in Greco-Roman sources and archaeology. Most surviving Celtic mythology belongs to the Insular Celtic peoples. They preserved some of their myths in oral lore, which were eventually written down by Christian scribes in the Middle Ages. Irish mythology has the largest written body of myths, followed by Welsh mythology.
Sohodol may refer to several places in Romania:

Dominic von Habsburg is a member of the Grand Ducal Family of Tuscany and the House of Habsburg-Lorraine. He is also the Carlist-Carloctavismo pretender to the throne of Spain under the name Domingo I.

The Land of Maidens is a motif in Irish mythology and medieval literature, especially in the chivalric romance genre. The latter often also features a castle instead of an island, sometimes known as the Castle of Maidens.
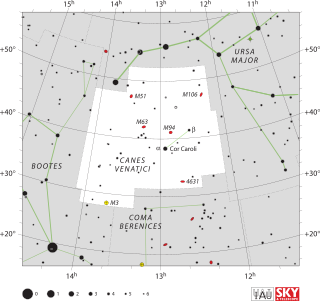
HAT-P-36, also referred to as Tuiren is a 12th magnitude G-type main-sequence star estimated to be approximately 958 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Canes Venatici. HAT-P-36 is too faint to be seen with the naked eye, but it is possible to view it with binoculars or a small telescope. In 2012 a hot Jupiter-type exoplanet was discovered orbiting HAT-P-36 with an orbital period of about 1.3 Earth days. In December 2019, HAT-P-36 was named Tuiren and its planetary companion, HAT-P-36b, was named Bran as a result of Ireland's contribution to the 2019 NameExoWorlds campaign. Bran has a mass approximately 1.8 times that of Jupiter and a radius 1.2 times larger.